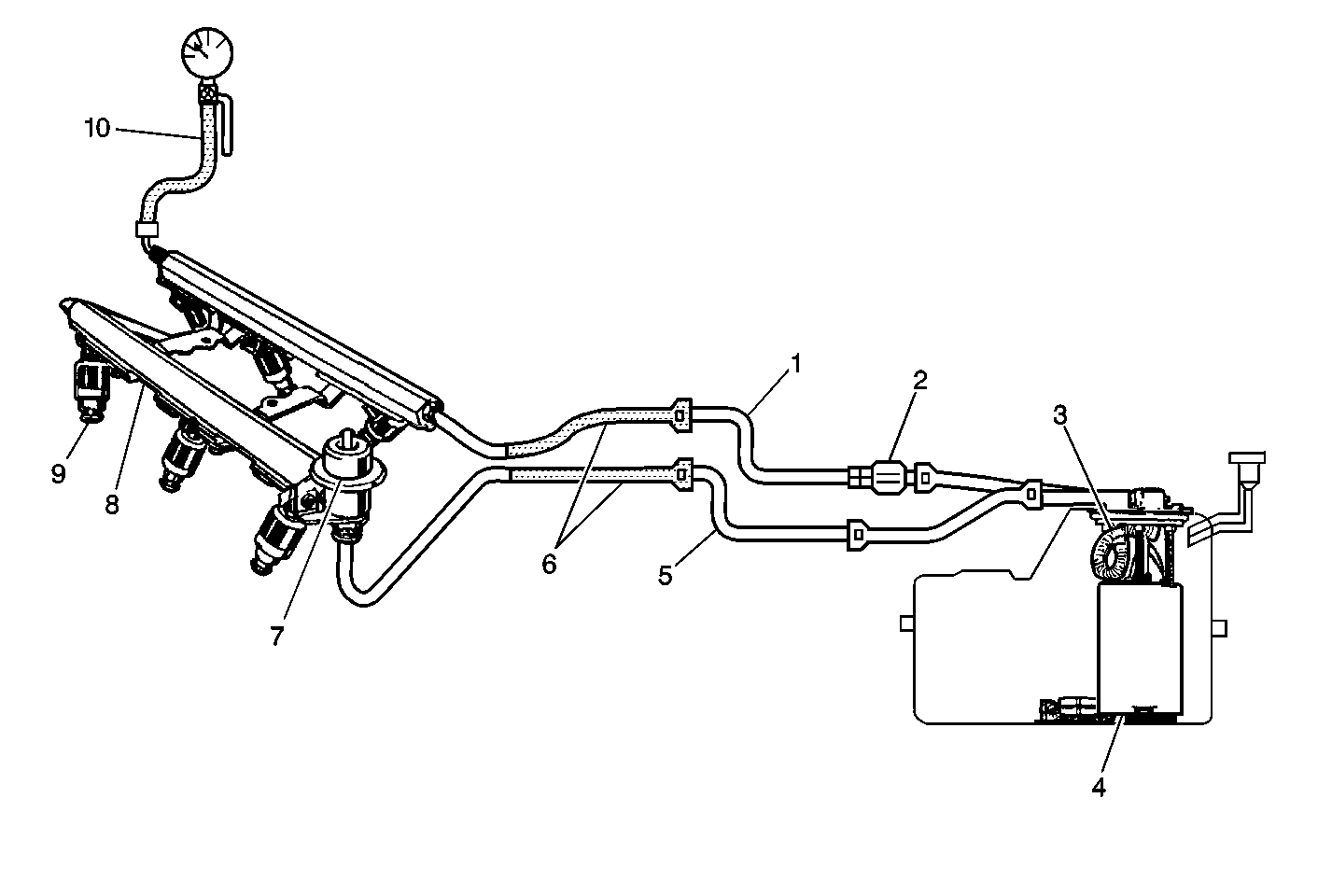
Circuit Description
When the ignition switch is turned ON, the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) will turn ON the in-tank fuel pump. The in-tank fuel pump will remain ON as long as the engine is cranking or running and the PCM is receiving reference pulses. If there are no reference pulses, the PCM will turn the in-tank fuel pump OFF 2 seconds after the ignition switch is turned ON or 2 seconds after the engine stops running. The in-tank fuel pump is an electric pump within an integral reservoir (4). The in-tank fuel pump supplies fuel through the fuel feed pipe (1), and in-line fuel filter (2) to the Fuel Rail Assembly (8). The fuel pump is designed to provide fuel at a pressure above the pressure needed by the fuel injectors (9). A fuel pressure regulator (7), attached to the Fuel Rail, keeps the fuel available to the fuel injectors at a regulated pressure. Unused fuel is returned to the fuel tank by a separate fuel return pipe (5). The fuel pump flex pipe (3) functions as a conduit for transporting pressurized fuel from the fuel pump to the above cover fuel feed pipe. The fuel pump flex pipe also eliminates fuel pump generated pressure pulse noise, and eliminates clamps formerly needed for rubber hoses or nylon pipes. The fuel pressure gauge J 34730-1A (10). The fuel pipe return and feed hose assemblys are the pinch points used during the fuel system pressure test (6).
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the Diagnostic Table.
-
To relieve the fuel pressure, refer to Fuel Pressure Relief . With the ignition switch ON and the fuel pump running, the fuel pressure indicated by the fuel pressure gage should be 284-325 kPa (41-47 psi). This pressure is controlled by the amount of pressure the spring inside the fuel pressure regulator can provide.
-
A fuel system that can not maintain a constant fuel pressure has a leak in one or more of the following areas:
-
Fuel pressure that drops-off during acceleration, cruise or hard cornering may cause a lean condition. A lean condition can cause a loss of power, surging, or misfire. A lean condition can be diagnosed using a scan tool. If an extremely lean condition occurs, the oxygen sensors will stop toggling. The oxygen sensor output voltage(s) will drop below 500 mV. Also, the fuel injector width will increase.
| • | The fuel pump check valve. |
| • | The fuel pump flex pipe. |
| • | The valve or valve seat within the fuel pressure regulator. |
| • | The fuel injector(s). |
Important: Make sure the fuel system is not operating in the Fuel Cut-Off Mode. This can cause false indications by the scan tool.
-
When the engine is at idle, the manifold pressure is low (high vacuum). This low pressure (high vacuum) is applied to the fuel pressure regulator diaphragm. The low pressure (high vacuum) will offset the pressure being applied to the fuel pressure regulator diaphragm by the spring inside fuel pressure regulator. When this happens, the result is lower fuel pressure. The fuel pressure at idle will vary slightly as the barometric pressure changes, but the fuel pressure at idle should always be less than the fuel pressure noted in Step 2 with the Engine OFF.
-
A rich condition may result from the fuel pressure being above 325 kPa (41 psi). A rich condition may cause a DTC P0132 or a DTC P0172 to set. Driveability conditions associated with rich conditions can include hard starting (followed by black smoke) and a strong sulfur smell in the exhaust.
-
This test determines if the high fuel pressure is due to a restricted fuel return pipe or if the high fuel pressure is due to a faulty fuel pressure regulator.
-
A lean condition may result from the fuel pressure being below 284 kPa (41 psi). A lean condition may cause a DTC P0131 or a DTC P0171 to set. Driveability conditions associated with lean conditions can include hard starting (when the engine is cold), hesitation, poor driveability, lack of power, surging, and misfiring.
-
Restricting the fuel return pipe by pinching the fuel return pipe hose causes the fuel pressure to rise above the regulated fuel pressure. Using a scan tool to pressurize the system, the fuel pressure should rise above 325 kPa (47 psi) as the gage outlet hose is pinched.
-
Notice: Do not allow the fuel pressure to exceed 450 kPa (65 psi). Fuel pressure in excess of 450 kPa (65 psi) may damage the Fuel Pressure Regulator.
Check the spark plug associated with a particular fuel injector for fouling or saturation in order to determine if that particular fuel injector is leaking. If checking the spark plug associated with a particular fuel injector for fouling or saturation does not determine that a particular fuel injector is leaking, use the following procedure.
| 1. | Remove the fuel rail, but leave the fuel pipes connected to the fuel rail. Refer to Fuel Injection Fuel Rail Assembly Replacement . |
| 2. | Lift the fuel rail just enough to leave the fuel injector nozzles in the fuel injector ports. |
Caution: In order to reduce the risk of fire and personal injury that may result from fuel spraying on the engine, verify that the fuel rail is positioned over the fuel injector ports. Also verify that the fuel injector retaining clips are intact.
| 3. | Pressurize the fuel system by using a scan tool. |
| 4. | Visually and physically inspect the fuel injector nozzles for leaks. |
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Was the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check performed? | -- | ||||||||||||
|
Important: Before proceeding with this chart perform Fuel System Electrical Test. Refer to Fuel Pump Electrical Circuit Diagnosis .
Caution: Wrap a shop towel around the fuel pressure connection in order to reduce the risk of fire and personal injury. The towel will absorb any fuel leakage that occurs during the connection of the fuel pressure gage. Place the towel in an approved container when the connection of the fuel pressure gage is complete. Important:: The fuel pump will run for approximately 2 seconds. Cycle the ignition as necessary in order to achieve the highest possible fuel level Is the fuel pressure within the specified limits? | 284-325 kPa (41-47 psi) | |||||||||||||
|
Important: The fuel pressure may vary slightly when the fuel pump stops running, the fuel pressure should stabilize and remain constant. After the fuel pump stops running, does the fuel pressure remain constant? | -- | |||||||||||||
Is the fuel pressure suspected of dropping-off during acceleration, cruise, or hard cornering. | -- | |||||||||||||
5 | Visually and physically inspect the following items for a restriction:
Was a restriction found? | -- | ||||||||||||
6 |
Was a problem found in any of these areas? | -- | ||||||||||||
Does the fuel pressure drop by the amount specified? | 21-69 kPa (3-10 psi) | Go to Symptoms | ||||||||||||
8 |
Does the fuel pressure drop by the amount specified? | 21-69 kPa (3-10 psi) | ||||||||||||
9 |
Important: The fuel pump will run for approximately 2 seconds. Repeat Step 4 as necessary in order to achieve the highest possible fuel pressure. Notice: Do not allow the fuel pressure to exceed 450 kPa (65 psi). Fuel pressure in excess of 450 kPa (65 psi) may damage the Fuel Pressure Regulator. Does the fuel pressure indicated remain constant? | -- | ||||||||||||
10 |
Does the fuel pressure remain constant? | -- | ||||||||||||
Is the fuel pressure above the specified limit? | 325 kPa (47 psi) | |||||||||||||
Is the fuel pressure within the specified limits? | 284-325 kPa (41-47 psi) | |||||||||||||
13 | Visually and physically inspect the fuel rail outlet passages for a restriction. Was a restriction found? | -- | ||||||||||||
Remove the fuel pressure regulator. Refer to Fuel Pressure Regulator Replacement . Visually and physical inspect the fuel pressure regulator filter screen for a restriction. Was a restriction found? | -- | |||||||||||||
Is the fuel pressure above the specified value? | 0 kPa (0 psi) | |||||||||||||
Notice: Do not allow the fuel pressure to exceed 450 kPa (65 psi). Fuel pressure in excess of 450 kPa (65 psi) may damage the Fuel Pressure Regulator. Does the fuel pressure rise above the specified value? | 325 kPa (47 psi) | |||||||||||||
17 | Perform Fuel System Electrical Test. Refer to Fuel Pump Electrical Circuit Diagnosis . Was a problem found with the fuel pump electrical circuit? | -- | ||||||||||||
18 | Visually and physically inspect the following items:
Was a problem found in any of these areas? | -- | ||||||||||||
19 | Replace the modular fuel sender assembly. Is the action complete? | -- | System OK | -- | ||||||||||
20 | Locate and repair the loss of vacuum to the fuel pressure regulator. Is the action complete? | -- | System OK | -- | ||||||||||
21 | Replace the fuel pressure regulator. Is the action complete? | -- | System OK | -- | ||||||||||
Locate and replace any leaking fuel injector(s). Is the action complete? | -- | System OK | -- | |||||||||||
23 | Locate and correct the restriction in the fuel return pipe. Is the action complete? | -- | System OK | -- | ||||||||||
Is the action complete? | -- | System OK | -- | |||||||||||
25 | Repair the problem as necessary. Is the action complete? | -- | System OK | -- |
