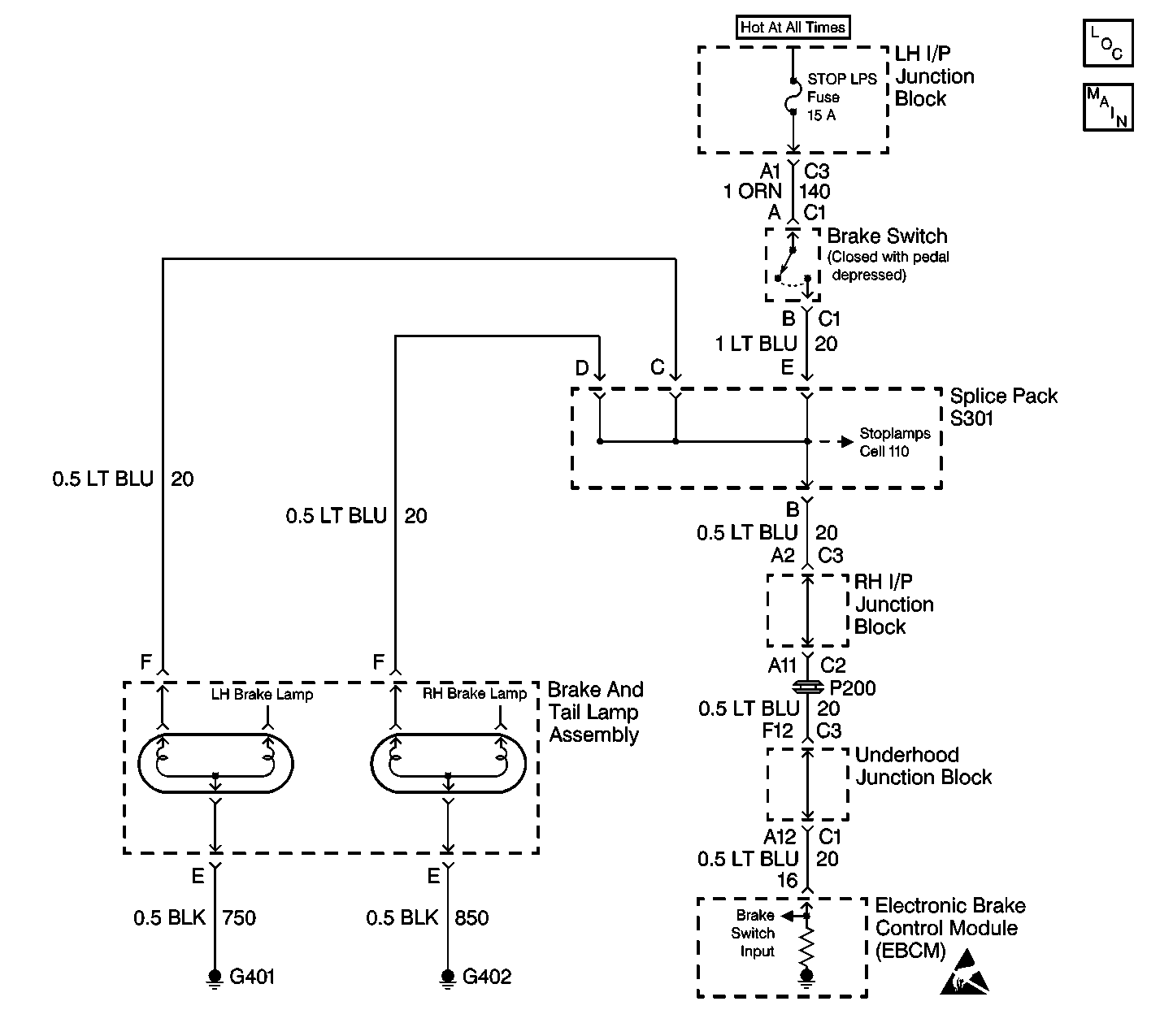
Circuit Description
DTC C1292 determines the proper operation of the brake switch. Proper operation of the brake switch is important because the brake switch activates the ABS when the brake switch is on. If the brake switch is off, the ABS will never activate. This malfunction is only detected when ABS is required because it is difficult to detect the malfunction under normal braking conditions.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DTC C1292 can set if the vehicle speed is greater than 8 km/h (5 mph).
A malfunction exists if the following conditions occur:
| • | The brake was not on. |
| • | A release was required on two channels for 0.5 second. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | A malfunction DTC stores. |
| • | The ABS disables. |
| • | The ABS warning indicator turns ON. |
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
| • | The condition responsible for setting the DTC no longer exists and the Scan Tool Clear DTCs function is used. |
| • | 100 drive cycles pass with no DTCs detected. A drive cycle consists of starting the vehicle, driving the vehicle over 16 km/h (10 mph), stopping and then turning the ignition off. |
Diagnostic Aids
The following conditions may cause an intermittent malfunction:
| • | A poor connection |
| • | Rubbed-through wire insulation |
| • | A broken wire inside the insulation |
Use the enhanced diagnostic function of the Scan Tool in order to measure the frequency of the malfunction.
Thoroughly inspect any circuitry that may cause the intermittent complaint for the following conditions:
| • | Backed out terminals |
| • | Improper mating |
| • | Broken locks |
| • | Improperly formed or damaged terminals |
| • | Poor terminal-to-wiring connections |
| • | Physical damage to the wiring harness |
| • | Sticking brake switch |
Test Description
-
This test determines if the brake switch signal is being received by the EBCM.
-
This test checks for an open in the brake switch circuit.
-
This test determines if the malfunction is caused by the EBCM.
-
This test checks for voltage entering the brake switch.
-
This test checks for voltage exiting the brake switch.
-
This test checks for an open in the brake switch input circuit.
-
This test checks for an open in the battery feed circuit.
-
This test checks for a short to ground in the battery feed circuit.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Important: Zero the J 39200 test leads before making any resistance measurements. Refer to the J 39200 user's manual. | ||||||||||
1 | Was the ABS Diagnostic System Check performed? | -- | ||||||||
2 |
Do not start the engine. Is DTC C1295 set as either a current and/or history DTC? | -- | ||||||||
Does the Scan Tool indicate that the brake switch is on within 25 mm (1.0 in) of brake pedal travel? | -- | |||||||||
4 |
Are the rear brake lamps on? | -- | ||||||||
Do not start the engine. Is the voltage equal to or greater than the specified voltage? | 10.0 V | |||||||||
6 | Inspect the EBCM connector and the EBCM harness connector for the following conditions:
Is there poor terminal contact, terminal corrosion, or damaged terminals? | -- | ||||||||
Does DTC C1291 or DTC C1292 set as a current DTC? | -- | |||||||||
Use the J 39200 in order to measure the voltage between the stoplamp switch harness connector terminal A and ground. Is the voltage equal to or greater than the specified voltage? | 10.0 V | |||||||||
Is the voltage equal to or greater than the specified voltage? | 10.0 V | |||||||||
10 | Inspect for proper adjustment of the stoplamp switch. Is the stoplamp switch adjusted correctly? | -- | ||||||||
11 |
Is the fuse open? | -- | ||||||||
Is the resistance within the specified range? | 0.0-2.0 ohms | |||||||||
13 |
Is the resistance within the specified range? | OL (Infinite) | ||||||||
Use the J 39200 in order to measure the voltage between the STOP-LPS Fuse terminal of the fuse block and ground. Is the voltage equal to or greater than the specified voltage? | 10 V | Go to Power Distribution Schematics in Wiring Systems | ||||||||
Is the resistance within the specified range? | OL (Infinite) | |||||||||
16 | Repair the open in CKT 20. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |||||||
17 | Replace all the terminal or the connectors that exhibit the following conditions:
Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |||||||
18 | Replace the stoplamp switch. Refer to Stop Lamp Switch Replacement . Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |||||||
19 | Adjust the stoplamp switch. Refer to Stop Lamp Switch Adjustment . Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |||||||
20 |
Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |||||||
21 | Repair the open in CKT 140. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |||||||
22 |
Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |||||||
23 | Replace the EBCM. Refer to Electronic Brake Control Module Replacement . Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |||||||
24 | Replace the STOP-LPS Fuse (15A) with a known good fuse (15A). Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |||||||
25 | The malfunction is intermittent or is not present at this time. Refer to Diagnostic Aids for more information. Is the action complete? | -- | System OK | -- | ||||||
