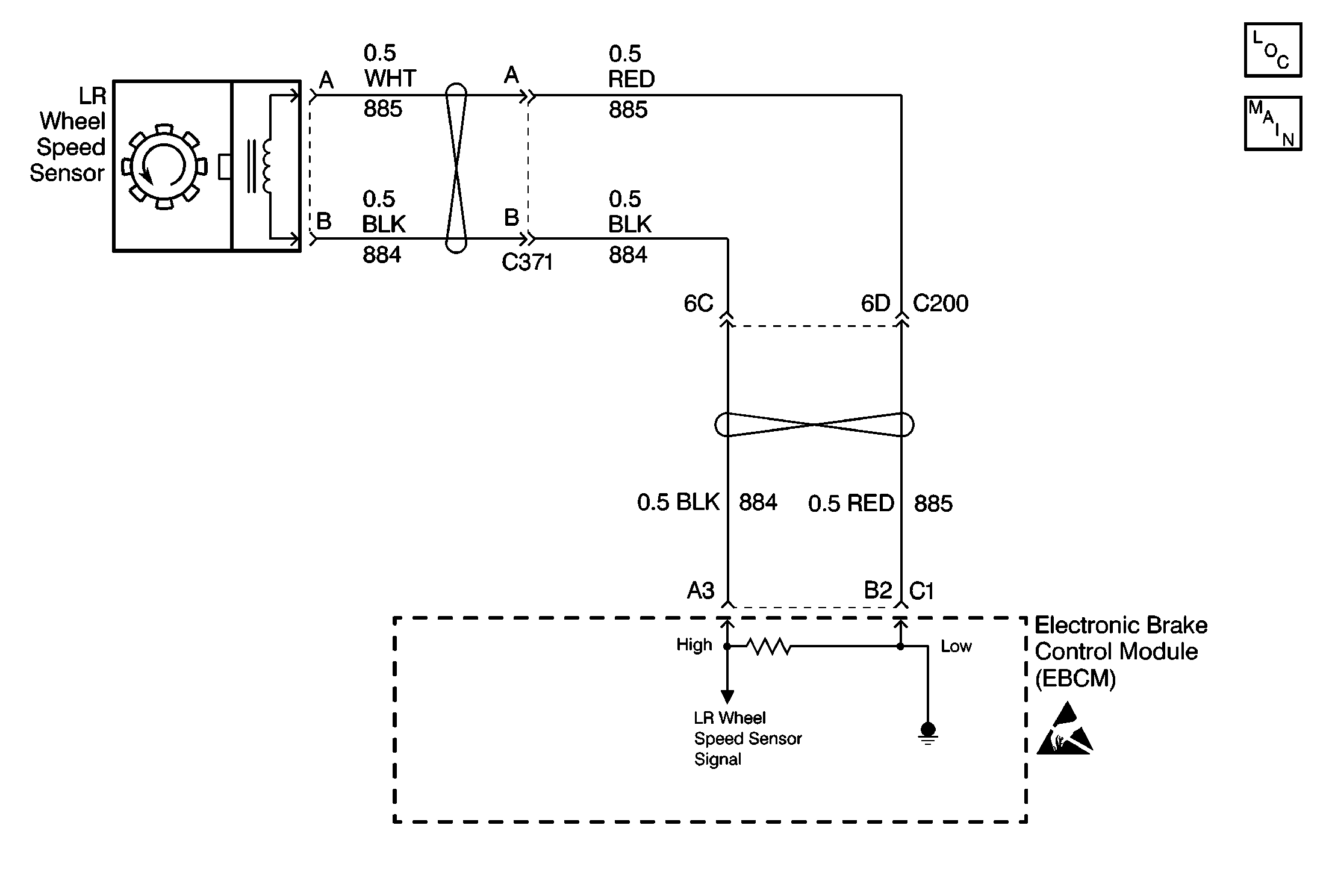
Circuit Description
As a toothed ring passes by the wheel speed sensor, changes in the electromagnetic field cause the wheel speed sensor to produce a AC voltage signal. The frequency of the sinusoidal (AC) voltage signal is proportional to the wheel speed. The amplitude of the AC voltage signal is directly related to wheel speed and the proximity of the wheel speed sensor to the toothed ring. The proximity of the wheel speed sensor to the toothed ring is also referred to as the air gap.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DTC C1234 can set anytime after initialization.
A malfunction exists if either of the left rear wheel speed sensor circuits are open or shorted to voltage or ground.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | A malfunction DTC stores. |
| • | The ABS disables. |
| • | The amber ABS warning indicators turn on. |
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
| • | The condition responsible for setting the DTC no longer exists and the Scan Tool Clear DTCs function is used. |
| • | 100 drive cycles pass with no DTCs detected. |
Diagnostic Aids
The following conditions may cause an intermittent malfunction:
| • | A poor connection |
| • | Rubbed-through wire insulation |
| • | A broken wire inside the insulation |
Use the enhanced diagnostic function of the Scan Tool in order to measure the frequency of the malfunction. Refer to the Scan Tool manual for the procedure.
If the customer's comments reflect that the amber ABS warning indicator is on only during moist environmental changes (rain, snow, vehicle wash), inspect all the wheel speed sensor circuitry for signs of water intrusion. If the DTC is not current, clear all DTCs and simulate the effects of water intrusion by using the following procedure:
- Spray the suspected area with a five percent saltwater solution.
- Test drive the vehicle over various road surfaces (bumps, turns, etc.) above 24 km/h (15 mph) for at least 30 seconds.
- If the DTC returns, replace the suspected harness.
Add two teaspoons of salt to twelve ounces of water to make a five percent saltwater solution.
Thoroughly inspect any circuitry that may be causing the intermittent complaint for the following conditions:
| • | Backed out terminals |
| • | Improper mating |
| • | Broken locks |
| • | Improperly formed or damaged terminals |
| • | Poor terminal-to-wiring connections |
| • | Physical damage to the wiring harness |
Resistance of the wheel speed sensor will increase with an increase in sensor temperature.
Use the following procedure in order to replace a wheel speed sensor:
- Inspect the wheel speed sensor terminals and harness connector for corrosion and/or water intrusion.
- Replace the wheel speed sensor if evidence of corrosion or water intrusion exists.
Refer to Wheel Speed Sensor Replacement .
Use the following procedure in order to replace the wheel speed sensor jumper harness:
- Inspect the wheel speed sensor jumper harness terminals for corrosion and/or water intrusion.
- Replace the wheel speed sensor jumper harness if evidence of corrosion or water intrusion exists.
Rear Wheel Speed Sensor Resistance
The following table contains resistance values for the rear wheel speed sensors at varying temperatures for use in diagnosis. The values are approximate and should be used as a guideline for diagnosis.
Temperature (°C) | Temperature (°F) | Resistance (Ohms) |
|---|---|---|
-34 to 4 | -30 to 40 | 800 to 1100 |
5 to 43 | 41 to 110 | 950 to 1300 |
44 to 93 | 111 to 200 | 1100 to 1600 |
Important: Zero the J 39200 test leads before making any resistance measurements.
Important: Difficulty may occur when trying to locate intermittent malfunctions in the wheel speed sensor.
Do not disturb any of the electrical connections. Change the electrical connections only when instructed to do so by a step in the diagnostic table. Changing the electrical connections at the correct time will ensure that an intermittent electrical connection will not be corrected until the source of the malfunction is found.Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Was the Diagnostic System Check performed? | -- | ||||||||||||||
2 |
Is the resistance within the specified range? | 1020-1137 ohms at 20°C (68°F) | ||||||||||||||
3 | Use the J 39200 in order to measure the resistance between the 24-way EBCM harness connector C1 terminal B2 and ground. Is the resistance within the specified range? | OL (Infinite) | ||||||||||||||
4 |
Do not start the engine. Is the voltage within the specified range? | 0-1 V | ||||||||||||||
5 |
Do not start the engine. Is the voltage within the specified range? | 0-1 V | ||||||||||||||
6 | Use the J 39200 in order to measure the voltage between the 24-way EBCM harness connector C1 terminal A3 and ground. Is the voltage within the specified range? | 0-1 V | ||||||||||||||
7 |
Are there signs of poor terminal contact, terminal corrosion, or damaged terminals? | -- | ||||||||||||||
8 | Inspect the wiring of CKT 884 and CKT 885 for signs of wire damage. Wire damage may cause the following conditions in CKT 884 and CKT 885:
Are there signs of damaged wiring? | -- | ||||||||||||||
9 | Inspect the harness connectors of CKT 884 and CKT 885 for signs of wire damage. Wire damage may cause the following conditions in CKT 884 and CKT 885:
Are there signs of damaged connectors? | -- | ||||||||||||||
10 |
Does DTC C1234 set as a current DTC? | -- | ||||||||||||||
11 |
Is the resistance within the specified range? | 0-2 ohms | ||||||||||||||
12 | Use the J 39200 in order to measure the resistance between the 24-way EBCM connector C1 terminal A3 and the rear wheel speed sensor harness connector terminal B. Is the resistance within the specified range? | 0-2 ohms | ||||||||||||||
13 | Use the J 39200 in order to measure the resistance between the left rear wheel speed sensor connector terminal A and the rear wheel speed sensor connector terminal B. Is the resistance within the specified range? | 1020-1137 ohms at 20°C (68°F) | ||||||||||||||
14 |
Is the resistance within the specified range? | OL (Infinite) | ||||||||||||||
15 | Use the J 39200 in order to measure the resistance between the 24-way EBCM connector C1 terminal A3 and ground. Is the resistance within the specified range? | OL (Infinite) | ||||||||||||||
16 |
Is the resistance within the specified range? | OL (Infinite) | ||||||||||||||
17 | Use the J 39200 in order to measure the resistance between the left rear wheel speed sensor jumper harness connector terminal B and ground. Is the resistance within the specified range? | OL (Infinite) | ||||||||||||||
18 | Use the J 39200 in order to measure the resistance between the left rear wheel speed sensor jumper connector terminal A and ground. Is the resistance within the specified range? | OL (Infinite) | ||||||||||||||
19 |
Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||||
20 |
Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||||
21 |
Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||||
22 |
Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||||
23 |
Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||||
24 | Replace all of the terminals and the connectors that exhibit signs of poor terminal contact, corrosion, or damaged terminals. Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||||
25 | Replace the left rear wheel speed sensor. Refer to Wheel Speed Sensor Replacement . Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||||
26 | Replace the rear wheel speed sensor jumper harness. Refer to Wheel Speed Sensor Jumper Harness Replacement . Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||||
27 | Replace the EBCM. Refer to Electronic Brake Control Module Replacement . Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||||
28 | Is the malfunction intermittent or not present at this time? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | -- |
