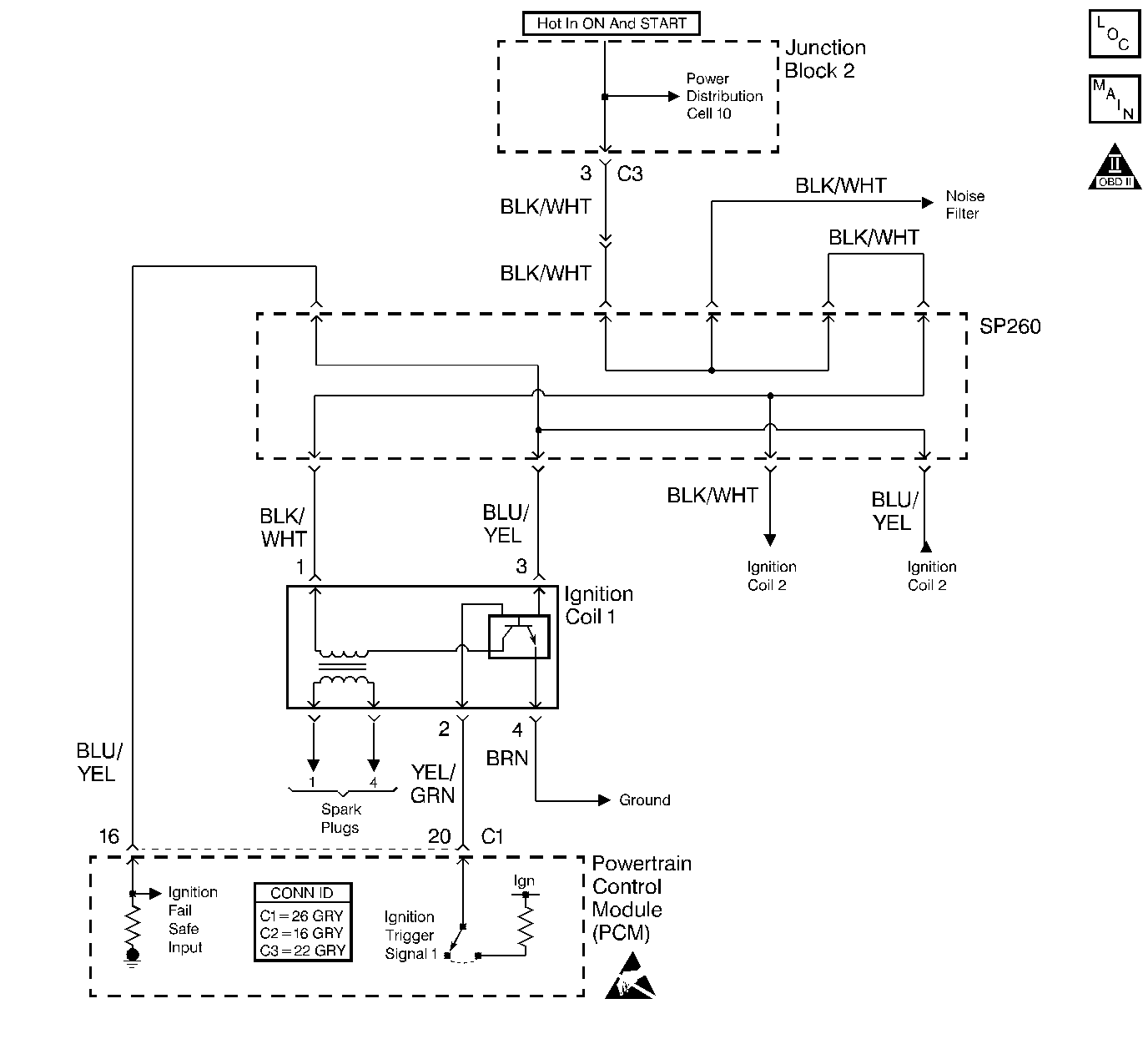
Circuit Description
The ignition trigger signal and ignition fail safe signal provide crucial information in the control of the ignition system timing, injector timing, and fail-safe activation. Based on an initial timing angle calculated from the crankshaft and the camshaft position signals, the PCM outputs an ignition trigger signal to the ignition coil control circuitry located in each ignition coil. Circuitry within the ignition coil controls the ignition dwell period by commanding the power transistor switch ON. When the PCM determines the proper time to provide spark, the PCM turns OFF the ignition signal. In response to the PCM the ignition coil control circuitry turns OFF the power transistor, producing a spark. After the spark has occurred, the ignition coil control circuitry sends an ignition fail safe signal back to the PCM, confirming that an ignition event has taken place. If the ignition fail safe signal is not received by the PCM, a fuel cut mode is activated and fuel injector operation is ceased. The suspension of fuel injection is a fail-safe function that protects the catalytic converter from overheating and damage.
Conditions for Running the DTC
The ignition is ON.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
No ignition coil 1 fail safe input signal to the PCM for 2 consecutive ignition trigger signal cycles, while the engine is cranking or running.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM illuminates the MIL. |
| • | The PCM stores the conditions that were present when the DTC set as Freeze Frame Data. |
| • | The PCM enters the Fail-Safe Function and begins fuel cut mode operation (terminates fuel delivery). |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The PCM turns OFF the MIL on the third consecutive trip cycle during which the diagnostic has been run and the fault condition is no longer present. |
| • | The DTC clears after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles have occurred without a fault. |
| • | A DTC can be cleared by using the scan tool Clear DTC Information function. |
Diagnostic Aids
Check for any of the following conditions:
| • | Check the ignition coil grounds at G105 for a clean and tight connection. |
| • | An interruption of the ground circuit or voltage supply to the ignition coil will prevent a proper ignition event from taking place. A DTC P1300 will set if there is a fault in any of the ignition coil circuits. |
| • | If both a DTC P1300 and P1310 are present, the fault is located in the shared electrical circuits or shared components of the two ignition coils. |
| • | An EFI relay that stays energized (ON) when the ignition is turned OFF can cause a false DTC P1300 and P1310 to set. With the EFI relay ON, the PCM remains alive and expects to continue to receive fail safe input from the ignition coils (even though the engine has stopped running). If the engine starts and runs fine, but has a constant MIL with DTCs P1300 and P1310 set, check for a faulty EFI relay. |
| • | Check the noise filter for an internal short or low resistance. The ignition coil may not receive adequate voltage during high load conditions if the noise filter is faulty. A good noise filter will indicate infinite resistance (OL) with a DMM after the capacitor within the filter is charged up. |
| • | Unless the ignition key is cycled or DTCs are cleared, the PCM waits to receive ignition fail safe signals before providing fuel injector operation. |
| • | Check the resistance of the ignition coil. The primary coil windings resistance is 4.8k to 5.2k ohms at 20°C (68°F). The secondary coil windings resistance is 12.7k to 13.7k ohms at 20°C (68°F). |
An intermittent malfunction may be caused by a fault in the ignition coil electrical circuit. Inspect the wiring harness and components for any of the following conditions:
| • | Backed out terminals. |
| • | Improper mating of terminals. |
| • | Broken electrical connectors locks. |
| • | Improperly formed or damaged terminals |
| • | Faulty terminal to wire connections. |
| • | Physical damage to the wiring harness. |
| • | A broken wire inside the insulation. |
| • | Corrosion of electrical connections, splices, or terminals. |
Repair any electrical circuit faults that were found. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems.
The information included in the Freeze Frame data can be useful in determining the vehicle operating conditions when the DTC first set.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers in the Diagnostic Table.
-
The OBD System Check prompts the technician to complete some basic checks and store the freeze frame data on the scan tool if applicable. This creates an electronic copy of the data taken when the fault occurred. The information is then stored in the scan tool for later reference.
-
If both DTCs P1300 and P1310 are present, the fault is located in the shared electrical circuits or shared components of the two ignition coils.
-
This step checks for a fault in the Ignition Fail Safe Input circuit. If the cause of the DTC P1300 is a fault in the Ignition Fail Safe Input circuit, the engine will start and run smoothly for 4-5 seconds until a DTC P1300 sets and fuel cut mode is initiated.
-
This step checks for an open or a short in the ignition trigger signal circuit. The voltage on the ignition trigger signal circuit will fluctuate very quickly when cranking the engine. The DMM voltage reading on the ignition trigger signal circuit should indicate 0.5 to 1.0 volts. Using the min/max feature on the DMM may indicate a maximum voltage as high as 3.5 volts.
-
This step checks for a fault in the Ignition Fail Safe Input circuit. If the cause of the DTCs P1300 and P1310 is a fault in the Ignition Fail Safe Input circuit, the engine will start and run smoothly for 4-5 seconds until the DTCs P1300 and P1310 set and fuel cutoff is initiated.
-
This step checks for a short in the ignition positive voltage supply to the ignition coils or for a faulty noise filter. A shorted noise filter may pull down the ignition coil primary voltage.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | |||||||||
Are both a DTC P1300 and P1310 set? | -- | |||||||||
Did the engine start and run smoothly (normal) for 4-5 seconds before stalling? | -- | |||||||||
4 |
Does the test lamp illuminate? | -- | ||||||||
Does the DMM read within the specified value? | 0.5-1.0 volts | |||||||||
6 | Probe terminal 4 of the ignition coil electrical connector (harness side), with a test lamp connected to battery positive voltage. Does the test lamp illuminate? | -- | ||||||||
7 | Repair the open or the short in the ignition power circuit between ignition coil #1 and splice SP260. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||
8 |
Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||||||||
9 |
Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||||||||
10 | Repair the open in the ignition ground circuit between ignition coil #1 and ground. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||
Did the engine start and run for 4-5 seconds before stalling? | -- | |||||||||
12 |
Does the test lamp illuminate? | -- | ||||||||
Is the action complete? | -- | -- | ||||||||
14 |
Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||||||||
15 | Repair the faulty ignition coil ground circuits at G105. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||
16 | Replace ignition coil #1. Refer to Ignition Coil Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||
17 | Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||
18 |
Are any DTCs displayed on scan tool? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | System OK |
