Rough, Unstable, or Incorrect Idle, Stalling
Checks
| Action
|
DEFINITION: The
engine runs unevenly at idle. If severe enough, the engine or vehicle may
shake. The engine idle speed may vary in RPM. Either condition
may be severe enough to stall the engine. The engine idles at
an incorrect speed.
|
Preliminary Check
|
|
Sensor Checks
|
| • | Inspect the heated oxygen sensors HO2S 1 and HO2S 2
for a condition that can affect sensor activity and response. Refer to Diagnostic
Aids for the following DTCs: |
| • | Inspect the throttle position (TP) sensor. A sticking throttle
shaft or a binding throttle linkage will causes a high TP sensor voltage.
Under these conditions the PCM may not control the idle. Monitor
the TP sensor angle with the scan tool. The indicated angle should
be approximately 11 percent with the throttle closed. |
| • | Inspect the engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor. A fixed or
inaccurate ECT sensor reading can cause the engine idle to surge or race.
Using the scan tool, compare the engine coolant temperature with the
ambient air temperature on a cold engine. If the engine coolant
temperature is 5°C (9°F) more than or 5°C (9°F) less
than the ambient air temperature, inspect the resistance of the coolant
sensor. Refer to
Temperature Versus Resistance
. If the engine coolant temperature is significantly less
than the ambient air temperature, inspect the coolant sensor electrical
circuit for high resistance. |
| • | Inspect the mass air flow (MAF) sensor operation. Run the engine
to normal operating temperature. Turn OFF all accessories and observe the
MAF sensor at idle with a scan tool. If the MAF sensor reading is
more than 3.5 g/s refer to
DTC P0101
. |
|
Fuel System Checks
|
| • | Inspect the operation of the fuel system for rich or lean condition.
Operate the vehicle under the conditions that caused the concern. Monitor
the Fuel Trim parameter on a scan tool in order to identify the problem. |
| - | Lean -- The Long Term Fuel Trim will be more than 20 percent.
Refer to Diagnostic Aids in
DTC P0171
. |
| - | Rich -- The Long Term Fuel Trim will be less than -20 percent.
Refer to Diagnostic Aids in
DTC P0172
. |
|
Ignition System Checks
|
| • | Test for the proper secondary voltage output with a J 26792
. |
| • | Inspect the spark plugs for correct operation and good ignition
system performance. Refer to
Spark Plug Inspection
. |
| • | Inspect the ignition coil boots for damage. |
| • | Observe the IAC Motor Command parameter on the scan tool at idle,
while operating the rear defogger, the A/C system, or the headlights.
The IAC Motor Command parameter should increase 2-7 percent
when operating the engine loads. If the IAC Motor Command parameter
remains fixed, check for a short to ground in the Diagnostic
Request circuit from the PCM to the TE1 terminal of the underhood
diagnostic link connector. |
|
Engine Mechanical Check
|
| • | Inspect for any of the following engine mechanical problems: |
| - | Any faulty hydraulic lifter assemblies |
| - | Any broken or weak valve springs |
| - | An incorrect valve timing |
| - | Any sticking or leaking valves |
| - | An incorrect or worn camshaft |
|
Additional Checks
|
| • | Inspect for vacuum leaks. Vacuum leaks can cause a higher than
normal idle speed. |
| • | Verify the PCM grounds are clean, tight, and in the proper locations.
Refer to
Power and Ground
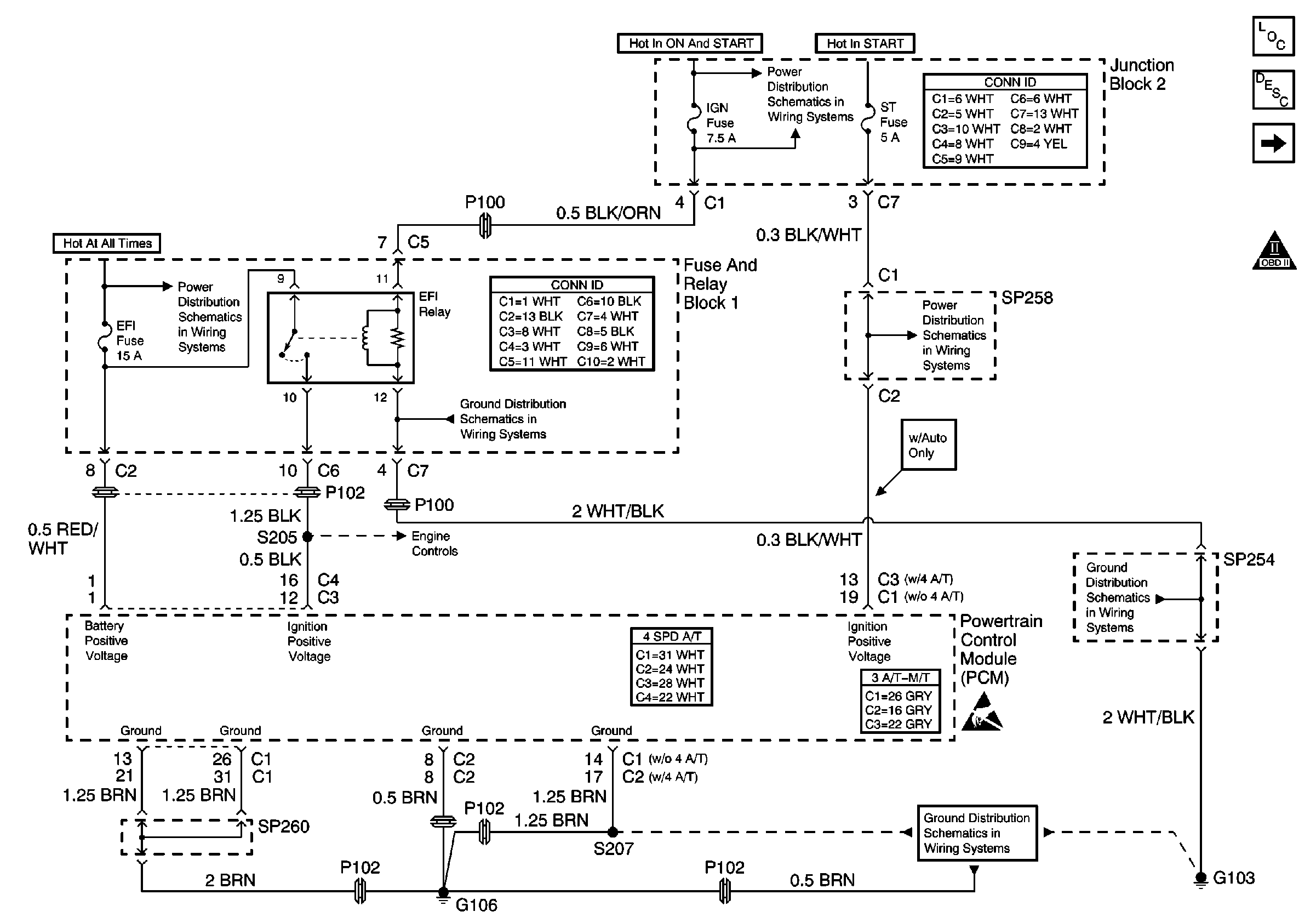
. |
| • | Inspect the battery cables and the ground straps. They should
be clean and secure. |
| • | The engine will run rough and the engine can stall if the CMP
actuator solenoid is advancing camshaft timing at idle. Inspect for a fully
energized or stuck CMP actuator solenoid. If the operation of the CMP
actuator solenoid is suspect, refer to
DTC P1349
. |
| • | Inspect for broken or worn motor and transmission mounts. |
|

