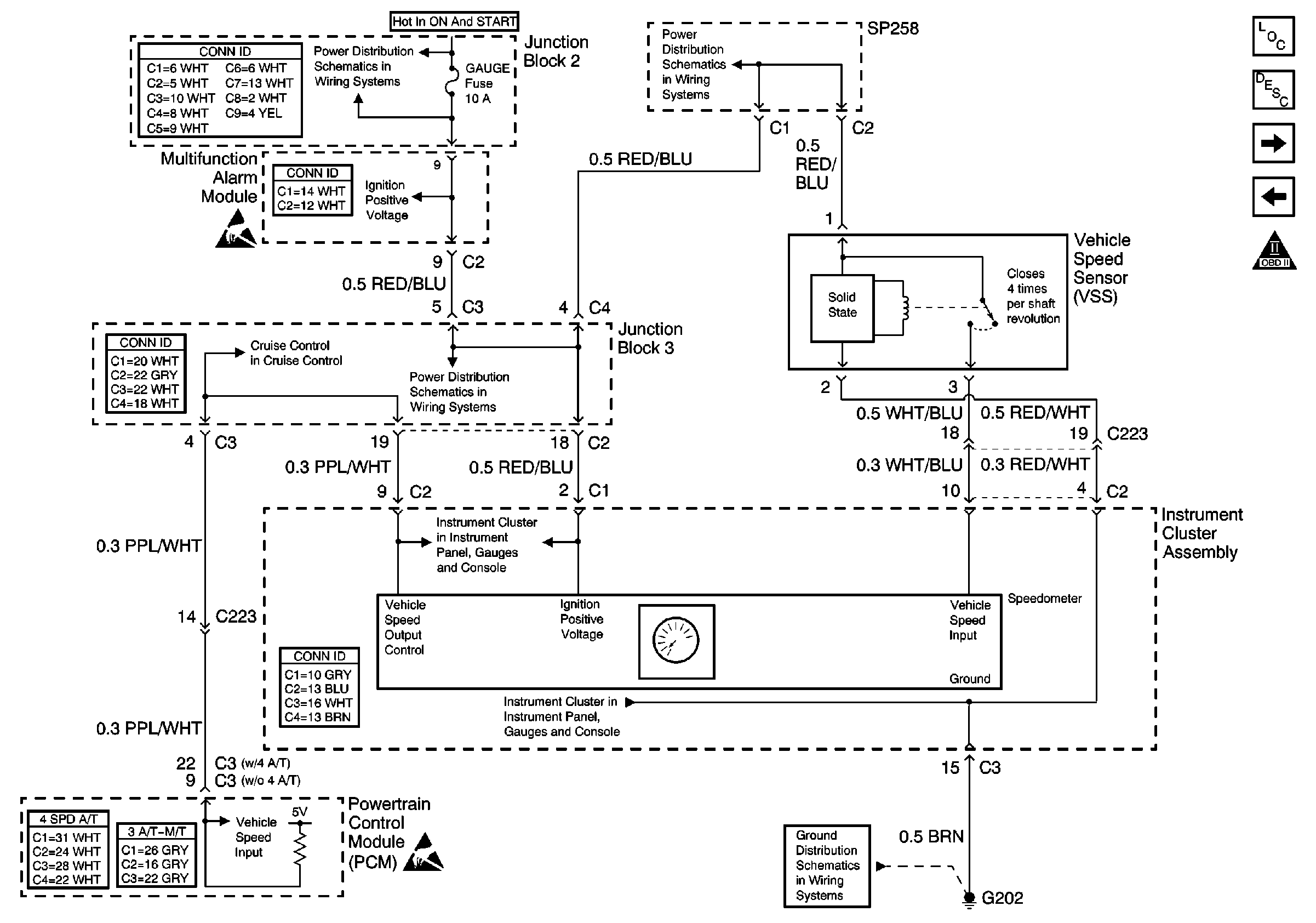
Circuit Description
The vehicle speed sensor (VSS) is mounted on the transaxle. As the transaxle turns the VSS, the VSS provides the speedometer with a vehicle speed input through voltage pulses. Each revolution of the axleshaft equals 4 pulses. This input is used to drive the speedometer.
The speedometer converts the vehicle speed input to a more precise output which is sent to the powertrain control module (PCM) and the cruise control module, if equipped. The PCM sends a 5 volt carrier signal to the speedometers vehicle speed output control circuit. On this same circuit, the speedometer produces a pulse width modulated signal that the PCM, and the cruise control module, use to determine the vehicle speed.
Conditions for Running the DTC
The engine is running.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | No vehicle speed sensor signal is sent to the PCM. |
| • | The engine speed is between 2,000 and 5,000 RPM. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) after 2 consecutive ignition cycles in which the diagnostic runs with the fault active. |
| • | The PCM records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. This information is stored in the Freeze Frame buffer. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The MIL turns OFF after 3 consecutively passing trips without a fault present. |
| • | A History DTC clears after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles without a fault. |
| • | Use the scan tool Clear DTC Information function. |
Diagnostic Aids
A scan tool should indicate a vehicle speed whenever the drive wheels are turning at a speed of more than 5 km/h (3 mph). DTC P0500 can be falsely set if the engine is brake-torqued in gear. Disregard DTC P0500 if the DTC sets when the drive wheels are not turning.
An intermittent malfunction may be caused by a fault in the VSS sensor electrical circuit. Inspect the wiring harness and the components for any of the following conditions:
| • | Any backed-out terminals |
| • | Any improper mating of terminals |
| • | Any broken electrical connector locks |
| • | Any improperly formed or damaged terminals |
| • | Any faulty terminal-to-wire connections |
| • | Any physical damage to the wiring harness |
| • | A broken wire inside the insulation |
| • | Any corrosion of the electrical connections, the splices, or the terminals |
Repair any electrical circuit faults that were found. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems.
The information included in the Freeze Frame data can be useful in determining the vehicle operating conditions when the DTC first set.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers in the diagnostic table.
-
This step checks the VSS sensor for a battery positive supply.
-
This step checks the VSS sensor for a ground supply.
-
This step checks for a shorted to ground speedometer vehicle speed input circuit.
-
This step checks the VSS for an output signal.
-
This step checks the PCM vehicle speed input circuit for continuity to the speedometer.
-
This step checks the speedometer for an output signal. Each 1 Hz of frequency is approximately equal to one mile per hour.
Step | Action | Values | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Schematic Reference:
| ||||
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | Go to Step 2 | Go to Powertrain On Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check - Automatic Transmission |
2 |
Does the scan tool parameter indicate a vehicle speed? | -- | Go to Step 3 | Go to Step 4 |
3 |
Does DTC P0500 set? | -- | Go to Step 4 | Go to Diagnostic Aids |
4 |
Does the speedometer indicate a vehicle speed? | -- | Go to Step 10 | Go to Step 5 |
5 | Do all other instrument cluster assembly functions operate normally? | -- | Go to Step 6 | Go to Diagnostic Starting Point - Instrument Panel, Gages and Console |
Does the test lamp illuminate? | -- | Go to Step 7 | Go to Step 12 | |
Probe the VSS connector terminal 2 on the harness side with a test lamp connected to B+. Does the test lamp illuminate? | -- | Go to Step 8 | Go to Step 13 | |
Probe the VSS connector terminal 3 on the harness side with a test lamp connected to B+. Does the test lamp illuminate? | -- | Go to Step 14 | Go to Step 9 | |
Does the DMM indicate a frequency? | -- | Go to Step 18 | Go to Step 15 | |
Is the voltage within the specified value? | 9-12 V | Go to Step 11 | Go to Step 16 | |
Does the DMM indicate a frequency? | -- | Go to Step 20 | Go to Step 17 | |
12 | Repair the cause of no power to the VSS connector. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | Go to Step 21 | -- |
13 | Repair the cause of no ground to the VSS connector. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | Go to Step 21 | -- |
14 |
Was a repair necessary? | -- | Go to Step 21 | Go to Step 18 |
15 |
Was a repair necessary? | -- | Go to Step 21 | Go to Step 19 |
16 |
If equipped, ensure that the cruise control module is not shorted internally. Was a repair necessary? | -- | Go to Step 21 | Go to Step 18 |
17 |
Was a repair necessary? | -- | Go to Step 21 | Go to Step 18 |
18 | Replace the speedometer. Refer to Speedometer Replacement in Instrument Panel, Gauges, and Console. Is the replacement complete? | -- | Go to Step 21 | -- |
19 | Replace the VSS. Refer to Speedometer Replacement in Instrument Panel, Gauges, and Console. Is the replacement complete? | -- | Go to Step 21 | -- |
20 | Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement in Engine Controls - 1.8 L. Is the replacement complete? | -- | Go to Step 21 | -- |
21 |
Are any DTCs displayed on the scan tool? | -- | System OK | |