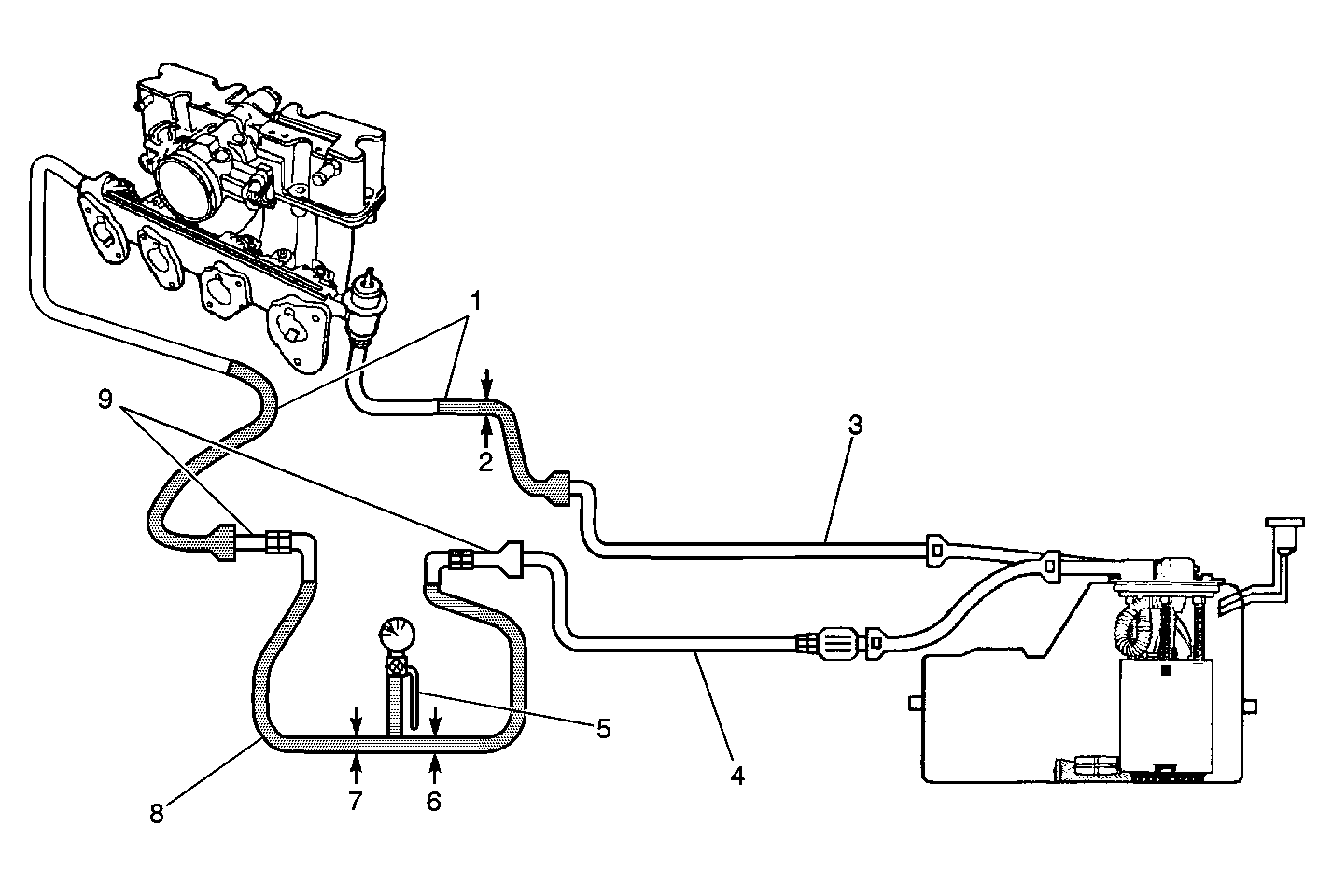
When the ignition switch is turned on, the Powertrain Control Module
(PCM) will turn on the in-tank fuel pump. The in-tank fuel pump remains on
as long as the engine cranks or runs and the PCM receives reference pulses.
If no reference pulses exist, the PCM will turn the in-tank fuel pump off
2 seconds after the ignition switch is turned on or 2 seconds after the engine
stops running.
The in-tank fuel pump is an electric pump within an integral reservoir.
The in-tank fuel pump supplies fuel through an in-line fuel filter to the
fuel passage within the lower manifold assembly. The fuel pump is designed
in order to provide fuel at a pressure above the pressure needed by the fuel
injectors. A fuel pressure regulator, attached to the lower manifold assembly,
keeps the fuel available to the fuel injectors at a regulated pressure. Unused
fuel returns to the fuel tank by a separate fuel return pipe.
The numbers below refer to the step numbers in the diagnostic table.
Step
| Action
| Value(s)
| Yes
| No
|
1
| Was the On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check performed?
| --
|
Go to Step 2
| Go to
Powertrain On Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check
|
2
|
- Turn OFF the ignition.
- Turn OFF the air conditioning system.
- Relieve the fuel pressure. Refer to the
Fuel Pressure Relief
.
- Install the fuel pressure gauge. Refer to figure on the facing
page.
- Turn ON the ignition.
- Bleed the air out of the fuel pressure gauge into an approved
gasoline container.
- For 10 seconds, turn OFF the ignition.
- Turn ON the ignition.
Important: The fuel pump will run for approximately 2 seconds. Cycle the ignition
as necessary in order to achieve the highest possible fuel pressure.
- Observe the fuel pressure indicated by the fuel pressure gauge with
the fuel pump running.
Is the fuel pressure within the specified limits?
| 284-325 kPa (41-47 psi)
|
Go to Step 3
|
Go to Step 11
|
3
|
Important: The fuel pressure may vary slightly when the fuel pump stops running.
After the fuel pump stops running, the fuel pressure should stabilize and
remain constant.
After the fuel pump stops running, does the fuel pressure remain constant?
| --
|
Go to Step 4
|
Go to Step 9
|
4
| Is the fuel pressure suspected
of dropping-off during acceleration, cruise, or hard cornering?
| --
|
Go to Step 5
|
Go to Step 7
|
5
| Visually and physically inspect
the following items for a restriction:
| • | The in-line fuel filter |
Was a restriction found?
| --
|
Go to Step 25
|
Go to Step 6
|
6
|
- Remove the fuel pump. Refer to Fuel Sender Assembly Replacement (Fuel Pump)
.
- Visually and physically inspect the following items:
| • | The fuel pump strainer for a restriction |
| • | The fuel pump coupling hose for leaks. |
Was a problem found in any of these areas?
| --
|
Go to Step 25
|
Go to Step 21
|
7
|
- Turn ON the ignition and the engine.
- Allow the engine to idle at the normal operating temperature.
Does the fuel pressure drop by the amount specified?
| 21-69 kPa (3-10 psi)
| Go to Driveability
Symptoms
|
Go to Step 8
|
8
|
- Disconnect the vacuum hose from the fuel pressure regulator.
- With the engine idling, apply 12-14 inches of vacuum
to the fuel pressure regulator.
Does the fuel pressure indicated by the fuel pressure gauge drop by
the amount specified?
| 21-69 kPa (3-10 psi)
|
Go to Step 19
|
Go to Step 20
|
9
|
- Turn OFF the ignition.
- Place the bleed hose of the fuel pressure gauge into an approved
gasoline container.
- Turn ON the ignition.
- Bleed the air out of the fuel pressure gauge.
- Using a scan tool pressurize the fuel system.
Important: The fuel pump will run for approximately 2 seconds. Repeat Step 5 as
necessary in order to achieve the highest possible fuel pressure.
- Wait for the fuel pressure to build.
- Pinch the gauge inlet hose (refer to A on the illustration.
Does the fuel pressure remain constant?
| --
|
Go to Step 21
|
Go to Step 10
|
10
|
- Using the scan tool pressurize the fuel system.
- Wait for the fuel pressure to build.
- Pinch the fuel return hose (refer to C on the illustration).
Does the fuel pressure indicated by the fuel pressure gauge remain constant?
| --
|
Go to Step 20
|
Go to Step 22
|
11
| Is the fuel pressure above
the specified limit?
| 325 kPa (47 psi)
|
Go to Step 12
|
Go to Step 15
|
12
|
- Relieve the fuel pressure by placing the bleed hose of the fuel
pressure gauge into an approved gasoline container and opening the relief
valve.
- Disconnect the fuel return hose fitting. Refer to the figure.
- Place the open end of the flexible hose into an approved gasoline
container.
- For approximately 10 seconds, turn OFF the ignition.
- Turn ON the ignition.
- Observe the fuel pressure indicated by the fuel pressure gauge
with the fuel pump running.
Is the fuel pressure within the specified limits?
| 284-325 kPa (41-47 psi)
|
Go to Step 23
|
Go to Step 13
|
13
| Visually and physically inspect the fuel return outlet passages for a restriction.
Was a restriction found?
| --
|
Go to Step 25
|
Go to Step 14
|
14
|
- Remove the fuel pressure regulator. Refer to
Fuel Pressure Regulator Replacement
.
- Visually and physically inspect the fuel pressure regulator filter
screen and restriction?
Was a restriction found?
| --
|
Go to Step 24
|
Go to Step 20
|
15
| Is the fuel pressure above
the specified value?
| 0 kPa (0 psi)
|
Go to Step 16
|
Go to Step 17
|
16
|
Notice: Do not allow the fuel pressure to exceed the specified value because
damage to the fuel pressure regulator or the fuel pressure gage
may result.
- Relieve the fuel pressure by placing the bleed hose of the fuel pressure
gauge into an approved gasoline container and opening the relieve valve.
- Using a scan tool, pressurize the fuel system.
- Bleed the air out of the fuel pressure gauge.
Important: The fuel pump will run for approximately 2 seconds. Repeat Step 2 as
necessary in order to achieve the highest possible fuel pressure.
- Wait for the fuel pressure to build.
- Slowly pinch the gauge outlet hose (refer to B on the figure).
Does the fuel pressure gauge rise above the specified value?
| 414 kPa (60 psi)
325 kPa (47 psi)
|
Go to Step 20
|
Go to Step 6
|
17
| In order to diagnose the fuel
pump electrical circuit, refer to
Engine Cranks but Does Not Run
.
Was a problem found with the fuel pump electrical circuit?
| --
|
Go to Step 25
|
Go to Step 18
|
18
| Visually and physically inspect
the following items:
- The in-line fuel filter for obstructions
- The fuel feed pipe for a restriction
- The fuel pump strainer for obstructions
- The fuel pump coupling hose for leaks.
Was a problem found in any of these areas?
| --
|
Go to Step 25
|
Go to Step 21
|
19
|
- Locate the loss of the vacuum to the fuel pressure regulator.
- Repair the loss of the vacuum to the fuel pressure regulator.
Is the action complete?
| --
|
Go to Step 26
| --
|
20
| Replace the fuel pressure regulator. Refer
to
Fuel Pressure Regulator Replacement
.
Is the action complete?
| --
|
Go to Step 26
| --
|
21
| Replace the Fuel Pump. Refer to Fuel Sender Assembly Replacement (Fuel Pump)
.
Is the action complete?
| --
|
Go to Step 26
| --
|
22
|
- Locate any leaking fuel injectors.
- Replace any leaking fuel injectors.
Is the action complete?
| --
|
Go to Step 26
| --
|
23
|
- Locate the restriction in the fuel return pipe.
- Correct it.
Is the action complete?
| --
|
Go to Step 26
| --
|
24
|
- Remove the fuel pressure regulator filter screen.
- Discard the fuel pressure regulator filter screen.
Is the action complete?
| --
|
Go to Step 26
| --
|
25
| Repair the problem as necessary.
Is the action complete?
| --
|
Go to Step 26
| --
|
26
|
- Using the scan tool, clear DTCs.
- Attempt to start the engine.
Does the engine start and continue to run?
| --
|
Go to Step 27
|
Go to Step 2
|
27
|
- Allow the engine to idle until the vehicle reaches the normal
operating temperature.
- Check if any DTCs are set.
Are any DTCs displayed?
| --
| Go
to The Applicable DTC Table
| System OK
|