Refer to
Power and Ground
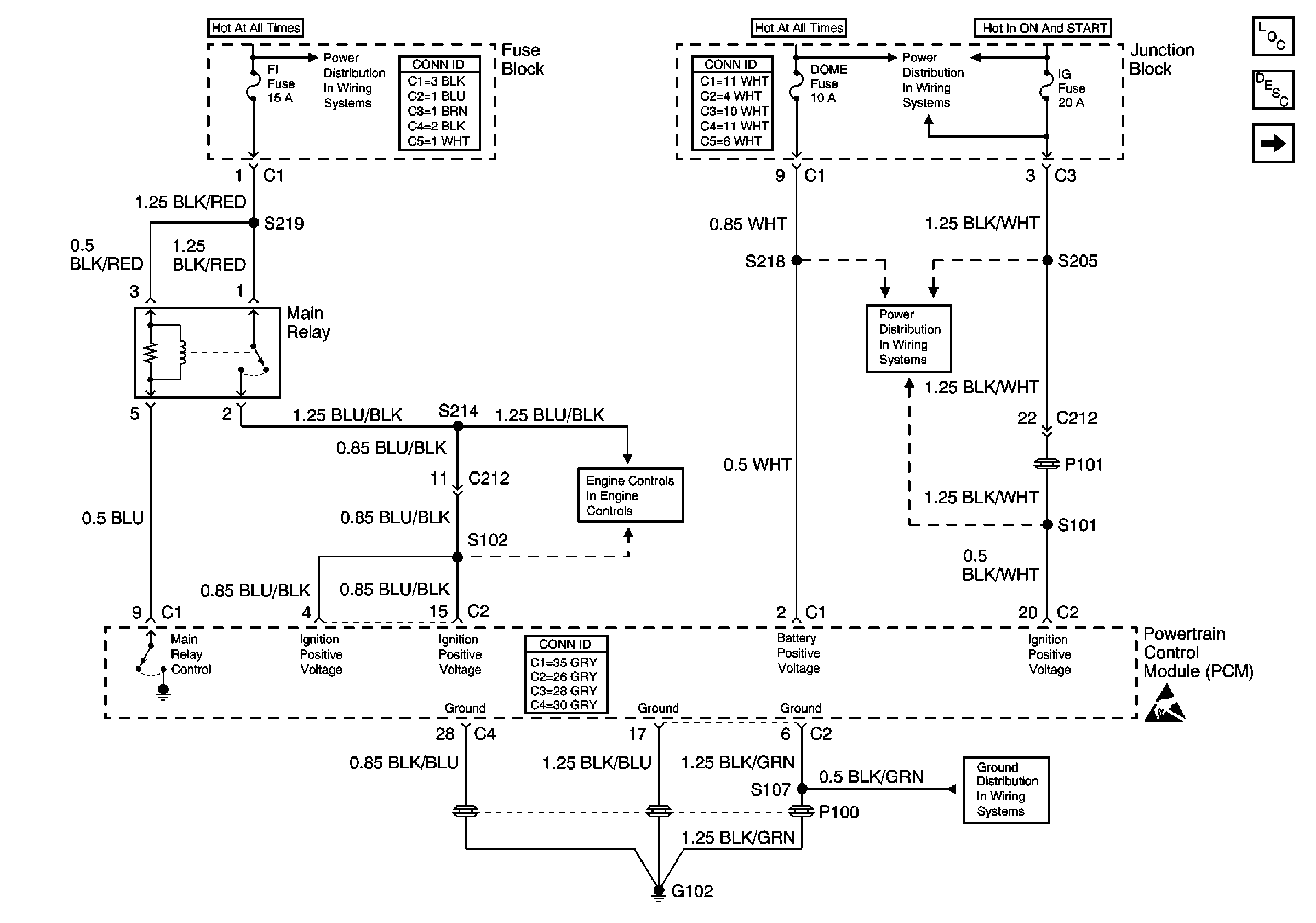
.
Circuit Description
The powertrain control module (PCM) controls each individual fuel injector sequentially. The PCM energizes the solenoid coil of the fuel injectors. When energized the fuel injector solenoid operates the solenoid plunger allowing pressurized fuel to be injected into the intake port of the cylinder. The fuel pump will pressurize the fuel rail and the fuel injectors as long as the engine is cranking, and the PCM is receiving ignition system reference pulses. The fuel pump will stop after 2 seconds if the PCM does not receive any ignition system reference pulses.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for any of the following conditions:
| • | Water, contaminated fuel, or an inferior quality fuel can cause a no start or hard start condition even though the fuel injectors and the circuitry are OK. |
| • | Check for a faulty spray pattern from the fuel injector nozzle if both the fuel injector solenoid and the fuel injector circuit are OK. |
| • | A leaking or stuck closed fuel injector can cause a fuel related engine misfire or performance concern. Refer to Fuel Injector Balance Test in order to check the operation of the fuel injectors. |
| • | The fuel injectors may spray fuel, but not enough fuel to operate the engine. Check the engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor reading with a scan tool. The indicated temperature should be close to the actual engine temperature in order for the PCM to deliver the correct amount of fuel. |
| • | The normal fuel injector resistance is 13-16 ohms at 20°C (68°F). Refer to Fuel Injector Solenoid Coil Test - Engine Coolant Temperature Between 10-35 Degrees C (50-95 Degrees F) . |
An intermittent malfunction may be caused by a fault in the fuel injector electrical circuit. Inspect the wiring harness and components for any of the following conditions:
| • | Any backed-out terminals |
| • | Any improper mating of terminals |
| • | Any broken electrical connector locks |
| • | Any improperly formed or damaged terminals |
| • | Any faulty terminal-to-wire connections |
| • | Any physical damage to the wiring harness |
| • | A broken conductor inside the wire insulation |
| • | Any corrosion of the electrical connections, the splices, or the terminals |
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers in the diagnostic table.
-
The Powertrain OBD System Check prompts the technician to complete some basic checks and store the Freeze Frame data on the scan tool if applicable. This creates an electronic copy of the data taken when the fault occurred. The information is then stored in the scan tool for later reference.
-
This step checks if the PCM is controlling the fuel injector signals.
-
This step checks for a short in the fuel injector control circuit.
-
This step checks for voltage at the fuel injector.
-
This step checks for an open in fuel injector control circuit or for a faulty PCM.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | |||
|
Important: This table assumes that the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) and the data link connector (DLC) function normally. Check that MIL operation and DLC communication is OK before using this table.
Did the injector test lamp flash for each injector while cranking the engine? | -- | |||
Was the injector test lamp illuminated all the time, for any injector circuit, while cranking the engine? | -- | |||
4 |
Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||
Did the test lamp illuminate? | -- | |||
Does the test lamp flash while cranking the engine? | -- | |||
7 | Repair the faulty electrical connections at the fuel injector harness connector. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
8 | Repair the open in the ignition feed circuit between the fuel injector and the main relay. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
9 |
Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||
10 |
Important: The replacement PCM must be programmed. Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement/Programming . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
11 | Operate the vehicle within the conditions under which the original symptom was noted. Does the system now operate properly? | -- | System OK | Go to Diagnostic Aids |
