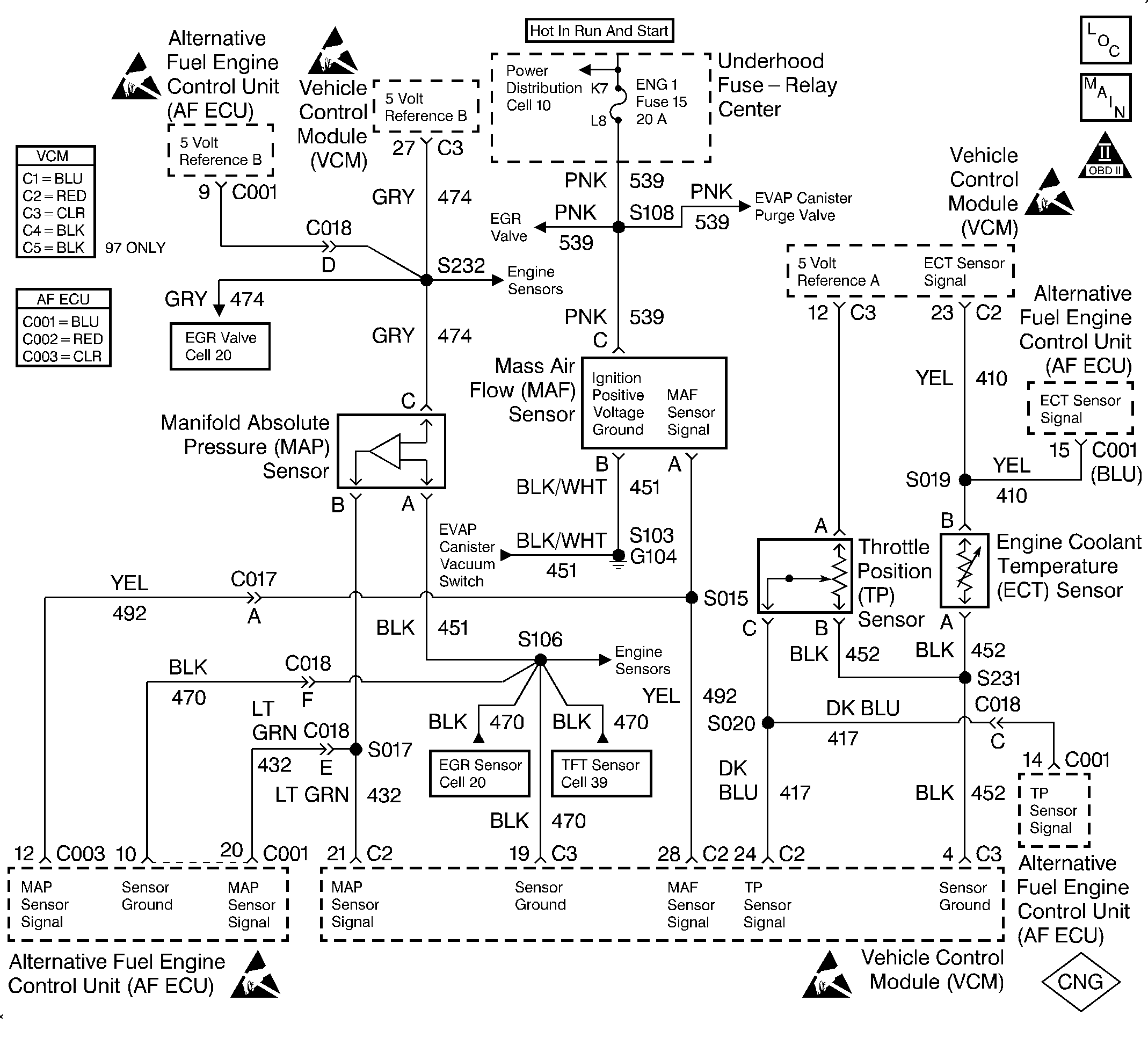
Circuit Description
The Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor measures the amount of air entering the engine during a given time. The ECU uses the MAF information for fuel delivery calculations. A large quantity of air entering the engine indicates an acceleration or high load situation. A small quantity of air indicates deceleration or idle.
The MAF sensor produces a signal which can be monitored using a scan tool. The signal varies within a range of around 5 to 7 g/s at idle to near 125 g/s at maximum engine load. This DTC sets if the signal from the MAF sensor does not match a predicted value based on the MAP pressure, coolant temperature, throttle position and engine speed.
This is a type A DTC.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The following conditions will set the DTC:
| • | The vehicle is in the CNG operation mode. |
| • | None of the following DTCs are active: 14, 15, 16, 21, 22, 23, 25, 26, 32, 33, 34, 36, 37. |
| • | The engine run time is greater than 10 seconds. |
| • | The engine is running at greater than 500 RPMs. |
| • | The battery voltage is greater than 10 volts. |
| • | The MAP range/performance diagnostic (DTC 32) has run at least once since the engine has been running. |
| • | No extreme deceleration is in progress. |
This DTC will set when the actual MAF reading ±40% of a calculated speed density air flow requirement for any given engine operating point.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The ECU will set DTC 35 and illuminate the MIL lamp after 1 fault has occurred if an MAF range/performance fault is detected. The ECU will simultaneously initiate a fuel mode switch-over to gasoline. The vehicle will not attempt to operate on CNG again until the next key cycle.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
The ECU turns the MIL OFF after 3 consecutive driving trips without a fault conditions present. A DTC will clear if no fault conditions have been detected for 40 warm-up cycles (coolant temperature has risen 40°C (72°F) from the start-up coolant temperature and the engine coolant temperature exceeds 70°C (160°F) during that same ignition cycle) or the code clearing procedure has been used.
Diagnostic Aids
Always diagnose ANY VCM codes that are present before beginning this diagnostic procedure.
Inspect for the following conditions:
| • | A skewed or stuck TP sensor. A faulty TP sensor or TP sensor circuit can cause the ECU to incorrectly calculate the predicted mass air flow value. Observe the throttle angle with the throttle closed. If the throttle range reading is 0%, check for the following conditions: |
| - | The throttle plate is sticking. |
| - | There are excessive deposits on the throttle plate or the throttle bore. |
| - | There is a poor connection or high resistance in the TP sensor ground or signal circuit. |
| • | Repair any of the above conditions. If none of the above conditions are noted and the throttle angle reading at closed throttle is not 0%, replace the TP sensor. |
| • | A poor connection at the ECU. Inspect the harness connectors for the following conditions: |
| - | Backed-out terminals |
| - | Improper mating |
| - | Broken locks |
| - | Improperly formed or damaged terminals |
| - | Poor terminal to wire connection |
| • | A mis-routed harness. Inspect the MAF sensor harness in order to ensure it is not routed too close to high voltage wires, such as spark plug leads. |
| • | A damaged harness. Inspect the wiring harness for damage. If the harness appears to be OK, observe the scan tool while moving the connectors and the wiring harnesses related to the MAF sensor. A change in the display indicates the location of the fault. |
| • | A plugged intake air duct or dirty air filter element. A wide open throttle acceleration from a stop should cause the MAF displayed on a scan tool to increase from about 4 to 7 g/s at idle to 100 g/s or greater at the time of the 1-2 shift. If not, check for a restriction. |
| • | A skewed MAP sensor. A skewed MAP sensor can cause the anticipated air flow measurements to be incorrectly calculated. In order to check the MAP sensor, compare the BARO reading on the vehicle being diagnosed to the BARO reading on a known good vehicle. If a large difference is noted (over 8 kPa), replace the MAP sensor. |
| • | Inspect for a skewed ECT sensor. |
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the diagnostic table.
-
This step verifies that the MAF circuit to the ECU is in good condition.
-
A voltage reading of less than 4.0 volts or over 6 volts at the MAF signal circuit indicates a fault in the wiring or a poor connection.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Was the Alternative Fuels (AF) Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check performed? | -- | Go to Step 2 | Go to Alternative Fuels (AF) Powertrain On Board (OBD) System Check | ||||||||||||
2 |
Was a problem found? | -- | Go to Step 23 | Go to Step 3 | ||||||||||||
3 |
Does the scan tool display a throttle angle less than the specified value? | 2% | Go to Step 4 | |||||||||||||
4 | Observe the MAP sensor voltage on the scan tool. Is the MAP sensor voltage within the typical scan tool data, plus or minus the specified value? Refer to Engine Scan Tool Data List . | 0.4 V | Go to Step 5 | |||||||||||||
5 | Compare the ECT display on the scan tool to the actual coolant temperature. The values should be close. Are the values close? | -- | Go to Step 6 | |||||||||||||
6 |
Is the resistance less than the specified value? | 0.4 ohms | Go to Step 7 | Go to Step 20 | ||||||||||||
7 |
Is the resistance less than the specified value? | 0.4 ohms | Go to Step 8 | Go to Step 20 | ||||||||||||
8 |
Is the resistance less than the specified value? | 0.4 ohms | Go to Step 9 | Go to Step 20 | ||||||||||||
Is the resistance less than the specified value? | 0.4 ohms | Go to Step 10 | Go to Step 20 | |||||||||||||
Is the voltage near the specified value? | 5.0 V | Go to Step 11 | Go to Step 12 | |||||||||||||
11 | Connect a test lamp between the MAF sensor ignition feed and the ground circuits at the MAF sensor harness connector. Is the test lamp ON? | -- | Go to Step 15 | Go to Step 14 | ||||||||||||
12 | Is the voltage less than the specified value? | 4.5 V | Go to Step 16 | Go to Step 13 | ||||||||||||
13 |
Is the voltage near the specified value? | 0.0 V | Go to Step 22 | Go to Step 19 | ||||||||||||
14 | Connect a test lamp between the MAF sensor ignition feed circuit and the chassis ground. Is the test lamp ON? | -- | Go to Step 17 | Go to Step 18 | ||||||||||||
15 |
Did you find a poor connection? | -- | Go to Step 23 | Go to Step 21 | ||||||||||||
16 |
Is the MAF signal circuit open or shorted? | -- | Go to Step 23 | Go to Step 22 | ||||||||||||
17 | Repair the open in the ground circuit to the MAF sensor. Refer to Repair Procedures in Electrical Diagnosis in the C/K Truck Service Manual. Is the action complete? | -- | Go to Step 23 | -- | ||||||||||||
18 | Repair the open in the ignition feed circuit to the MAF sensor. Refer to Repair Procedures in Electrical Diagnosis in the C/K Truck Service Manual. Is the action complete? | -- | Go to Step 23 | -- | ||||||||||||
19 | Repair the short to voltage in the MAF sensor signal circuit. Refer to Repair Procedures in Electrical Diagnosis in the C/K Truck Service Manual. Is the action complete? | -- | Go to Step 23 | -- | ||||||||||||
20 | The circuit is open or has high resistance. Repair as necessary. Refer to Repair Procedures in Electrical Diagnosis in the C/K Truck Service Manual. Is the action complete? | -- | Go to Step 23 | -- | ||||||||||||
21 | Replace the MAF sensor. Refer to MAF Sensor Replacement in Engine Controls - 5.0, 5.7L in the C/K Truck Service Manual. Is the action complete? | -- | Go to Step 23 | -- | ||||||||||||
22 | Replace the VCM. Important:: Reprogram the VCM if it is faulty. Refer to VCM Replacement/Programming in Engine Controls - 5.0, 5.7L in the C/K Truck Service Manual. Is the action complete? | -- | Go to Step 23 | -- | ||||||||||||
23 |
Does the diagnostic run and pass? | -- | Go to Step 24 | Go to Step 2 | ||||||||||||
24 | Are any ECU VCM DTCs displayed that have not been diagnosed? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | System OK |
