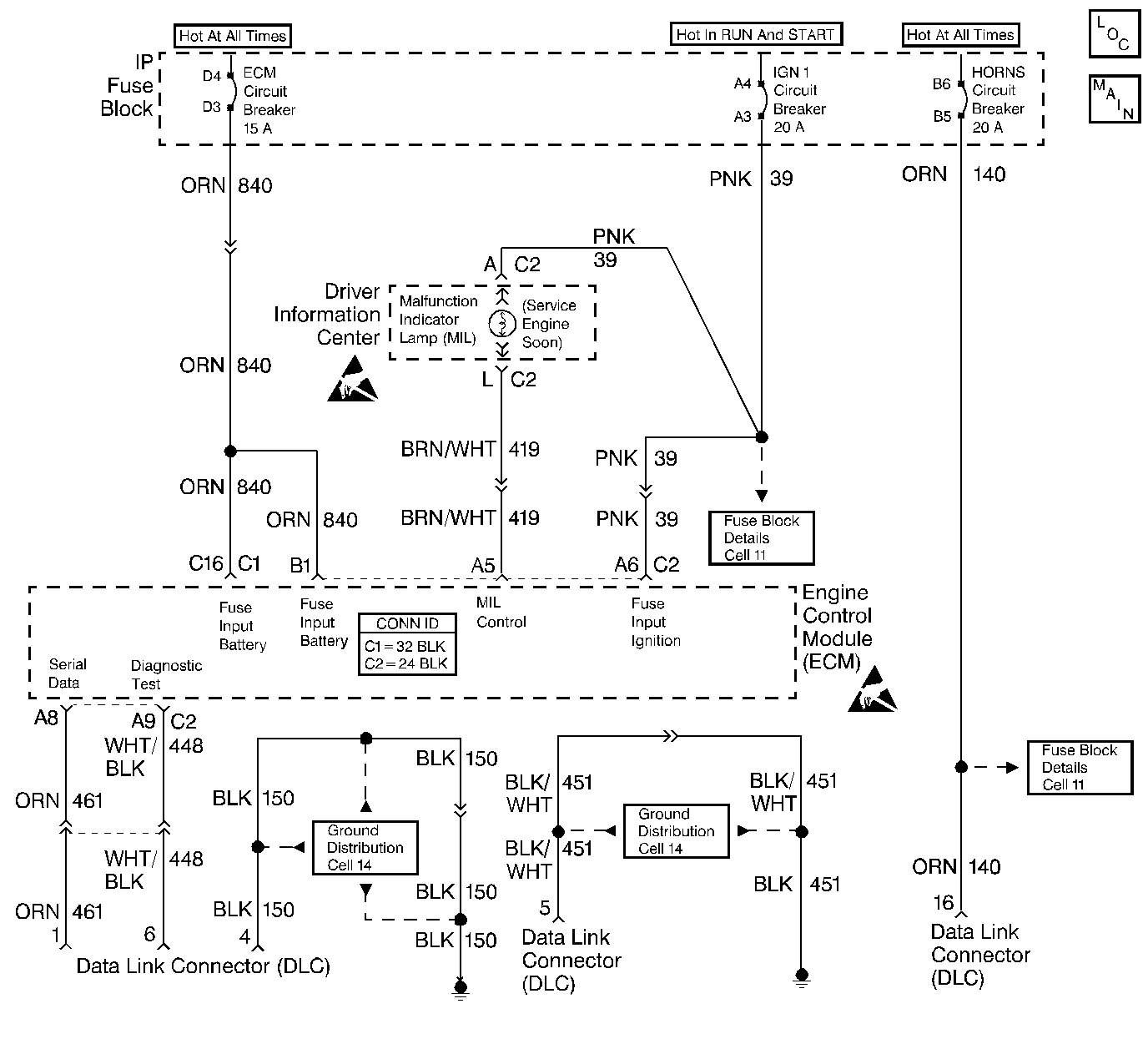
Circuit Description
The On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) system check is an organized approach to identifying a problem created by a control module system malfunction. The OBD System Check is the starting point for any driveability complaint diagnosis because it directs the service technician to the next logical step in diagnosing the complaint. Understanding the table and using it correctly will reduce diagnostic time and prevent the unnecessary replacement of good parts.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the Diagnostic Table.
-
This step is a check for the proper operation of the Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL). The MIL should be ON steady. No MIL at this point indicates that there is a problem with the MIL circuit or the ECM control of that circuit.
-
This test checks the ability of the ECM to control the MIL. With the diagnostic terminal grounded, the MIL should flash a DTC 12 three times, followed by any DTC stored in memory. PROM error may result in the inability to flash DTC 12.
-
Most of the diagnostic procedures use a scan tool to aid diagnosis, therefore, engine data must be available. If a PROM error is present, the ECM may have been able to flash DTC 12/51, but not enable engine data.
-
Although the ECM is powered up, a Engine Cranks but Does Not Run symptom could exist because of an ECM or system problem.
-
This step will isolate if the customer complaint is a MIL or a driveability problem with no MIL. Refer to Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) List in this section for a list of valid DTCs. An invalid DTC may be the result of a faulty scan tool, PROM or ECM.
-
Comparison of scan data with the typical scan data values is a quick check to determine if any data value is not within limits. Keep in mind that a base engine problem (i.e., advanced cam timing) may substantially alter sensor values. If the actual data is not within the typical values established, the diagnosis tables in this section will provide a functional check of the suspect component or system.
-
Installation of a scan tool will provide a good ground path for the ECM and may hide a ground path for the ECM and may hide a driveability complaint due to poor ECM grounds.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Is the MIL ON steady? | -- | |||
2 | Is the MIL flashing? | -- | ||
Does the MIL flash DTC 12? | -- | |||
4 |
Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
Does the scan tool display ECM data? | -- | |||
Start the engine. Did the engine start and continue to run? | -- | |||
Check for any stored DTCs. Are any DTCs stored? | -- | Go to Appropriate DTC Table | ||
Are the ECM scan data values within the typical ranges? | -- | Go to the Diagnostic Check for that component | ||
For the engine driveability symptoms, refer to a specific driveability symptom diagnostic table. Refer to Symptoms . Is the action complete? | -- | System OK | -- |
