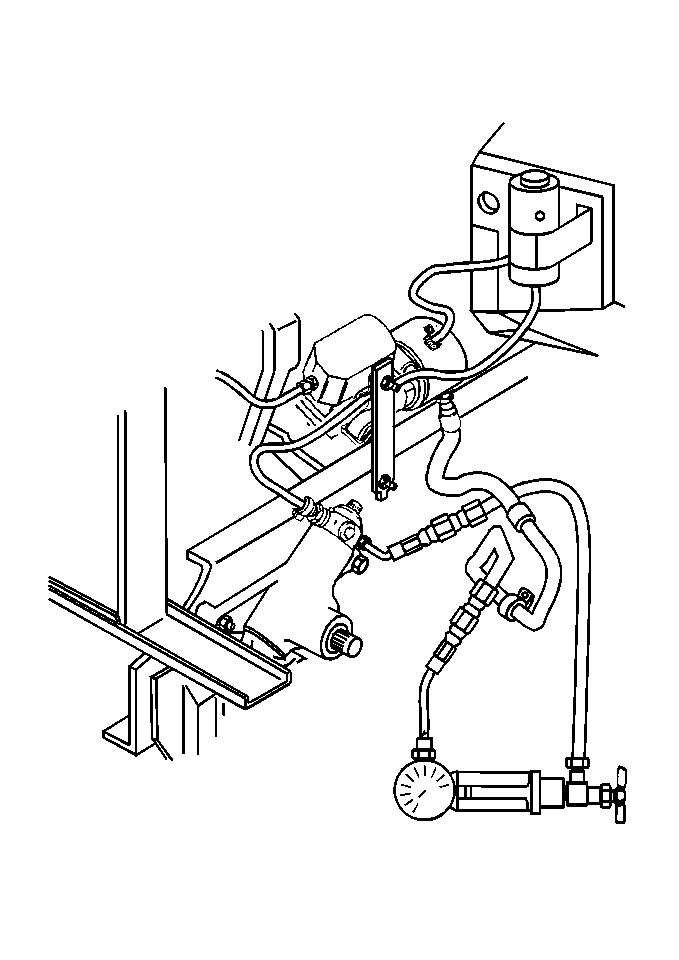
Important: The TRW Ross power steering gear includes poppet valves. The poppet
valves provide an increase in steering effort at a point within 1/3 turn of
the steering stop contact. This is normal operation.
- Place a container under the steering gear or pump in order to catch
the fluid when disconnecting or connecting the hoses.
- Clean the surface of the steering gear at the control valve.
- Remove the pressure hose fitting from the steering gear or the
power steering pump.
- Thread or connect the female adapter into the pressure hose.
Notice: Use the correct fastener in the correct location. Replacement fasteners
must be the correct part number for that application. Fasteners requiring
replacement or fasteners requiring the use of thread locking compound or sealant
are identified in the service procedure. Do not use paints, lubricants, or
corrosion inhibitors on fasteners or fastener joint surfaces unless specified.
These coatings affect fastener torque and joint clamping force and may damage
the fastener. Use the correct tightening sequence and specifications when
installing fasteners in order to avoid damage to parts and systems.
- Thread or connect
the male adapter into the pump or the gear.
Tighten
Tighten the threaded adapters to 40 N·m (30 lb ft).
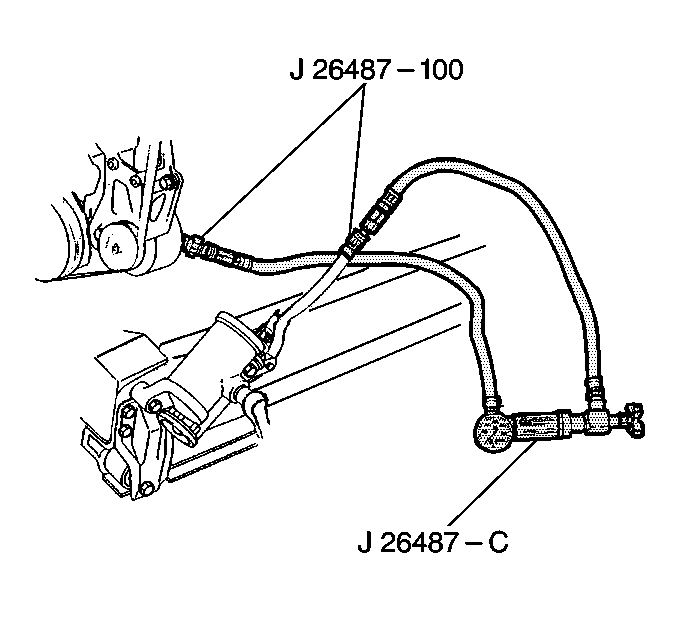
- Connect the analyzer hoses
to the adapters.
- Bleed the power steering system. If the analyzer has never before
been used, ensure that the analyzer valve gate remains open during the bleeding
procedure. Refer to
Power Steering System Bleeding
.
Important: Throughout the following testing procedure, the letters in parentheses
indicate specific pressures and flows.
Document the values of the pressures and the flows. Use the letters
in parentheses as references for comparing the values.
- Run the engine at idle speed with the gate valve open.
Record the flow (A) and the pressure (B).
| • | If the flow is less than 2 gpm, the pump may need repair.
Continue the test. |
| • | If the pressure is above 1 379 kPa (200 psi),
inspect the hoses for any restriction. |
- Partially close the gate valve in order for pressure to build
to 4 827 kPa (700 psi) of pressure. Record the flow (C).
- Compare the values of flow (A) and flow (C).
If flow (C) drops more than 1 gpm under flow (A) then:
Important: The Hobourn model S205 and Saginaw pumps can not be overhauled. Repairs
should not be attempted.
- Replace or rebuild the pump. Refer to
Power Steering Pump Replacement
.
- Replace the following components:
- Complete the following steps in order to obtain the pressure value
(D):
| 13.1. | Close the gate valve for not more than five seconds. |
Partially open the gate valve.
| 13.2. | Close and partially open the valve two more times. |
| 13.3. | Observe and record the pressure (D) each time that the gate is
closed. |
- Compare the pressures (D) to the specified pressures. Refer to
Power Steering Pump Specifications
.
| • | If the recorded pressures (D) are 690 kPa (100 psi)
lower than the specified pressures, than replace the pump flow control valve. |
| • | If the pressures (D) are greater than the low specifications and
vary from each other by more than 690 kPa (100 psi) then remove
and clean the pump flow control valve. |
| • | Inspect the pump flow control valve bore for dirt or foreign materials.
Clean the pump flow control valve bore. |
| • | Inspect the system fluid for contamination. If the fluid is contaminated,
disassemble and clean the steering gear and the pump before assembly. |
- Increase the engine speed from idle to approximately 1500 RPM.
- Compare the values of flow (A) and flow (E).
Record the flow (E).
Complete the following steps if flow (E) varies by more than 1 gpm
from flow (A).
| • | Remove and clean the pump flow control valve. |
| • | Inspect the pump flow control valve bore for dirt or foreign materials.
Clean the pump flow control valve bore. |
| • | Inspect the system fluid for contamination. If the fluid is contaminated,
disassemble and clean the steering gear and the pump before assembly. |
Caution: This test can be dangerous if not performed correctly. Keep your fingers
clear of steering stops and spacer block during this test. Make sure that
the spacer block contacts the steering stop squarely. Contact that is not
square could break the steering stop or dangerously throw or eject the spacer
block.
Notice: Do not hold the steering wheel in the full turn position longer than
five seconds. To do so may damage the power steering pump.
Important: It is necessary to use a non-hardened 1.3 cm (0.5 inch)
steel spacer on the TRW Ross power steering gear.
- Have an assistant lightly turn the steering wheel into the left steering
stop and then the right steering stop.
Use a long handle to hold the spacer in place in front of the steering
stops. This action will prevent pressure relief poppets from tripping.
- Record the pressure and the flow (F).
Verify that the following conditions exist:
| • | The pressures measured at the steering stops are close in value
to the maximum pump output (D) |
| • | The flow drops below 1 gpm. |
| • | If the above conditions do not exist, the steering gear is leaking internally.
Repair the steering gear. |
- Perform the following actions simultaneously:
| • | Have an assistant turn the steering wheel slightly in both directions
and then quickly release the wheel. |
| • | Observe the pressure gage. |
| • | Under normal conditions, the needle will move from the normal back pressure
reading and snap back when the wheel is released. A slow or sticking needle
indicates a sticking rotary valve in the steering gear. |
- Complete the following steps if the pressure gage needle moves
slowly or sticks:
| • | Remove the rotary valve. |
| • | Disassemble and clean the rotary valve. |
| • | Inspect the system oil for contamination. If the system oil is
contaminated, disassemble and clean the following components: |
Important: The Hobourn model S205 and Saginaw pumps can not be overhauled. Repairs
should not be attempted.
- Replace the power steering pump. Refer to
Power Steering Pump Replacement
.


