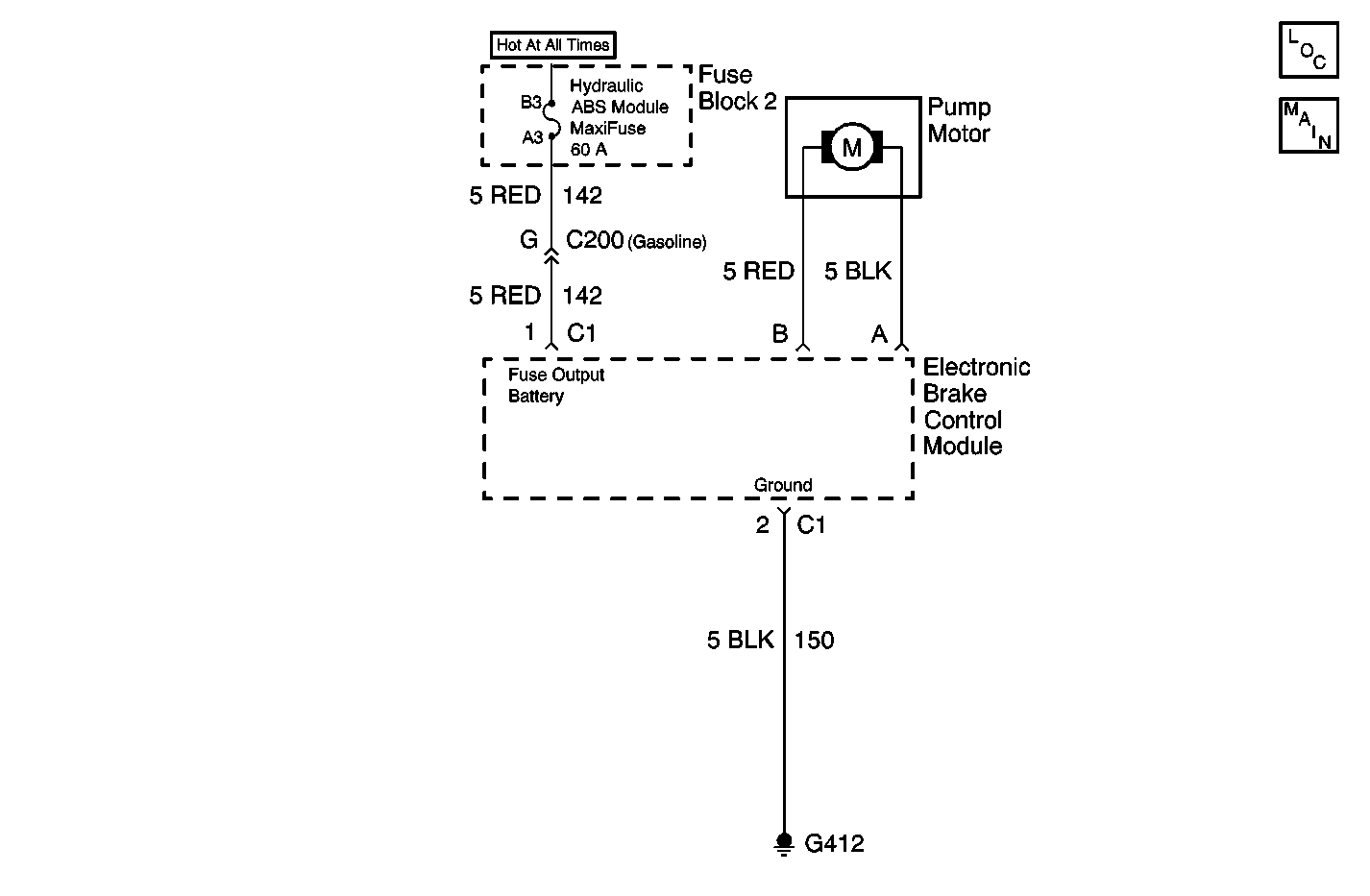
Circuit Description (DTC C0269)
The EBCM microprocessor grounds the dump valve coil(s) to energize and open the dump valve, allowing fluid to be dumped into the LPA. This is done with very short activation pulses opening and closing the dump valve passageway. Brake pressure is lowered at the wheel and allows the affected wheel to begin rolling again. Each dump valve is opened independently to control the deceleration of the wheel.
Circuit Description (DTC C0274)
The EBCM microprocessor grounds the isolation coil to energize and close the isolation valve. This will prevent any additional brake pressure applied by the driver from reaching the wheel. Further increases in brake pressure will be prohibited. Each isolation valve is closed independently to isolate each wheel. The EBCM microprocessor also uses a software subroutine to monitor for any ABS event which would initiate an isolation command. This subroutine is performed every 1.0 second.
Conditions for Setting the DTC (DTC C0269)
Dump time (pressure reduction ) exceeds 9 seconds, which can be caused from the following conditions:
| • | Locked rotors |
| • | Excessively low road surface friction |
Conditions for Setting the DTC (DTC C0274)
Isolation time (pressure hold) exceeding 120 consecutive 1.0 second checks
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The ABS indicator lamp turns on. |
| • | The ABS disables. |
DTCs C0269-C0274 are Ignition Latched DTCs, which indicates that the above actions remain true until the ignition is turned to OFF (even if the cause of the DTC is intermittent).
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
Repair the conditions responsible for setting the DTC.
Diagnostic Aids (DTC C0269/C0274)
If any other DTCs are set, repair those DTCs first. If there are no DTCs set, ensure the ABS is operating properly by performing using the Scan Tool Function Test.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the steps in the diagnostic table:
-
This step determines the resistance of the ground circuit.
-
This step determines the ignition voltage available to the EBCM.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Was the Diagnostic System Check performed? | -- | Go to Step 2 | Go to Diagnostic System Check |
2 |
Is the connector in good condition? | -- | Go to Step 3 | Go to Step 7 |
Using a J 39200 , measure the resistance between terminal 2 of the 2-way EBCM harness connector and ground. Is the resistance measurement within the specified range? | 0-2 ohms | Go to Step 4 | Go to Step 8 | |
Is the voltage equal to or greater than the specified value? | 10.0 V | Go to Step 6 | Go to Step 5 | |
5 | Inspect the 60-amp ABS maxi-fuse. Is the fuse open? | -- | Go to Step 10 | Go to Step 11 |
6 |
Does the DTC set as a current DTC? | -- | Go to Step 9 | Go to Diagnostic Aids |
7 | Repair the 2-way EBCM harness connector if necessary. Refer to Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check | -- |
8 | Repair the open or the high resistance in the CKT 150. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check | -- |
9 | Replace the EBCM. Refer to . Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check | -- |
10 | Repair the short to ground in the CKT 142. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check | -- |
11 | Repair the open or the high resistance in the CKT 142. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the repair complete? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check | -- |
