Fuel Pressure Gauge Connection
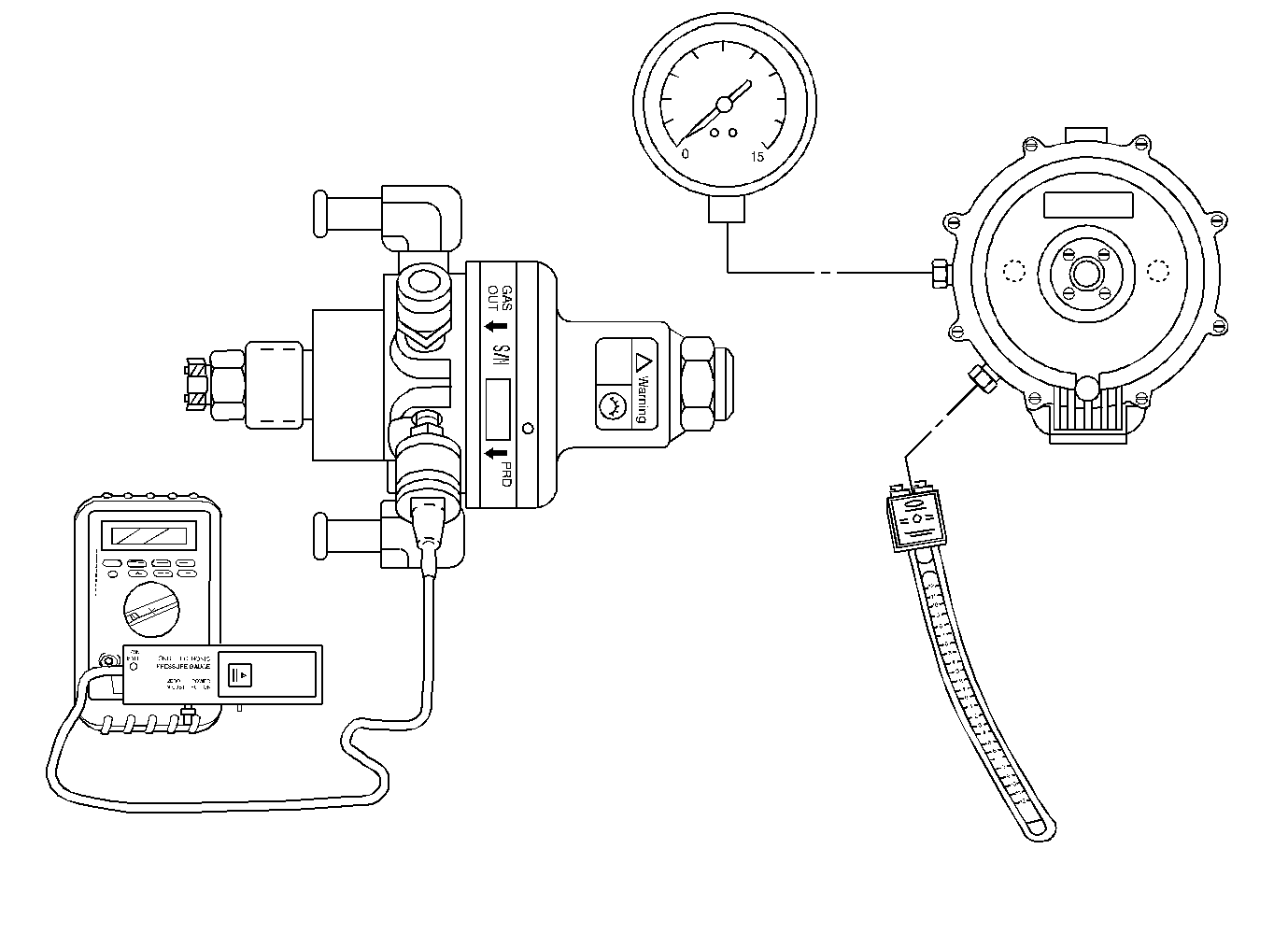
System Description
The alternative fuel engine control unit (AF ECU) controls the fuel system while the vehicle is operating on alternative fuel. The AF ECU receives signals from various engine sensors and determines the correct amount of fuel required by the engine. The fuel is stored in a cylindrical fuel tank. A full tank can contain fuel at 24,820 kPa (3600 psi ). A high pressure lock-off (HPL) solenoid in the tank and a Low Pressure Lock-off (LPL) solenoid in the fuel line prevent fuel flow. The AF ECU commands ONLY the HPL open for 1 second at every ignition ON for a CNG prime pulse. The CNG prime pulse is performed in order to charge the fuel line and also allows the fuel pressure sensor (FPS) to monitor the amount of fuel pressure in the tank. The AF ECU commands BOTH the HPL and the LPL open when engine RPM indicates the engine is cranking or running on CNG.
This fuel delivery system utilizes three different pressure stages in order to lower the fuel pressure from tank pressure down to a delivery pressure which is slightly above atmospheric pressure.
High Pressure (tank) Stage
When the AF ECU commands the HPL open fuel begins to flow (at up to 3600 psi) through the high pressure regulator (HPR). The HPR reduces fuel pressure to between 130 and 220 psi. The outlet of the HPR is the intermediate pressure stage.
Intermediate Pressure Stage
With a pressure between 130 and 220 psi the fuel exiting the HPR flows through the intermediate fuel line to the low pressure lock-off (LPL) solenoid. The LPL is controlled by the AF ECU. Fuel flows out of the LPL through another portion of intermediate fuel line and into the low pressure regulator (LPR). The inlet of the LPR is the Low Pressure Stage.
Low Pressure Stage
The low pressure regulator is a 2 stage regulator. The fuel enters the LPR at the intermediate stage pressure of 130 to 220 psi. The primary stage of LPR operation reduces the fuel pressure down to between 4 and 6 psi. The fuel pressure is then again reduced in the secondary stage of the LPR down to between 4.5 and 7 inches of water column. The fuel exits the LPR and flows through the low pressure hose and into the gas mass sensor/mixture control valve (GMS/MCV).
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
This step checks the fuel pressure output of the High Pressure Regulator (HPR).
-
This step checks the fuel pressure output of the primary stage of the Low Pressure Regulator (LPR).
-
CNG fuel may contain small amounts of fill station compressor oil. As the CNG fuel pressure drops in the LPR secondary chamber this oil separates from the CNG fuel and collects in the secondary chamber. Allow the oil to drain as this condition is normal and no repair is required.
This step checks the fuel pressure output of the secondary stage of the low pressure regulator.
-
This step performs a road-load test of the high pressure regulators ability to supply fuel at higher flow rates.
-
This step checks for a restricted High Pressure Regulator (HPR) filter. If a restricted HPR filter is found also inspect the fill valve filter for contamination, damage, or restriction.
-
This step checks the ability of the AF ECU to energize the High Pressure Lock-off (HPL) solenoid.
-
This step checks for a closed manual lock-down screw.
-
This step checks for the sound of a functioning HPL.
-
This step checks for damage to the fuel line between the HPL and the HPR.
-
This step checks the ability of the AF ECU to energize the Low Pressure Lock-off (LPL) solenoid.
-
This step checks for the sound of a functioning LPL.
-
This step checks for damage to the fuel line between the HPR and the LPR.
-
This step checks for proper operation of the system after repairs are complete.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Perform the Alternative Fuels (AF) Powertrain On Board (OBD) System Check . Are any AF ECU DTCs except P1202 set? | -- | Go to applicable DTC table. | |||||||||||
2 |
Does the vehicle have adequate CNG fuel pressure? | 8274 kPa (1200 psi) | -- | |||||||||||
Important: Rhythmic pressure fluctuation of 10-20 psi is normal. A defective HPR is not indicated unless the fluctuations become excessive. If a DTC sets that forces a switch-over (such as DTC P1202) the fuel pressure may only be observed up until the DTC sets. In the instances when the engine will not idle on CNG use the pressure values observed during cranking and proceed directly to the Step question.
Were all pressure values within the specified range? | 130-220 psi | |||||||||||||
4 | Is the pressure more than the specified value? | 220 psi | ||||||||||||
Leave the J 39970 Electronic Pressure Gauge connected to the HPR. If a DTC sets that forces a switch-over (such as DTC P1202) the fuel pressure may only be observed up until the DTC sets. In the instances when the engine will not idle on CNG use the pressure values observed during cranking and proceed directly to the Step question.
Were all pressure values within the specified range? | 4-6 psi | |||||||||||||
6 | Is the pressure more than the specified value? | 6 psi | ||||||||||||
A small amount of oil may drain from this port. Refer to Test Description. Important: Keep the vent port of the manometer CLOSED until AFTER the engine is started.
Are both values within the specified range? | 4.5-7 inches of water column | |||||||||||||
8 |
Was a repair or replacement performed? | -- | ||||||||||||
Ensure all testing equipment and wiring is correctly routed for on-road operation of the vehicle. Caution: Test drive the vehicle in a remote area away from traffic with a passenger watching the gauge in order to prevent personal injury.
Do not exceed posted speed limits. Is the pressure within the specified range? | 130-220 psi | |||||||||||||
If a DTC sets that forces a switch-over (such as DTC P1202) the fuel pressure may only be observed up until the DTC sets. In the instances when the engine will not idle on CNG use the pressure values observed during cranking and proceed directly to the Step question. Important: Rhythmic pressure fluctuation of 10-20 psi is normal. A defective HPR is not indicated unless the fluctuations become excessive.
Were all pressure values within the specified range? | 130-220 psi | |||||||||||||
Does the test lamp illuminate? | -- | Go to Lock-Off Relay Diagnosis | ||||||||||||
Is the manual lock-down screw fully open? | -- | |||||||||||||
Listen and/or feel for HPL operation as the ignition is turned ON. Is HPL operation heard or felt as the ignition is turned ON? | -- | |||||||||||||
Was a repair or replacement made? | -- | |||||||||||||
Does the test lamp illuminate while the engine is cranking? | -- | Go to Lock-Off Relay Diagnosis | ||||||||||||
Is LPL operation heard or felt when energized? | -- | |||||||||||||
Was a repair or replacement made? | -- | |||||||||||||
18 | Replace the low pressure regulator (LPR). Refer to Compressed Natural Gas Low Pressure Regulator and Bracket Replacement . Is the replacement complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||
19 |
Important: If you were sent to this step because the observe fuel pressure was too low ensure that the fuel line between the HPL and the HPR is unobstructed prior to replacing the HPR. Replace the high pressure regulator (HPR). Refer to Compressed Natural Gas High Pressure Regulator Replacement . Is the replacement complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||
20 | Replace the high pressure lock-off (HPL) solenoid. Refer to High Pressure Lock-Off Solenoid Replacement . Is the replacement complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||
21 | Replace the low pressure lock-off (LPL) solenoid. Refer to Low Pressure Lock-Off Solenoid Replacement . Is the replacement complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||
Does the vehicle operate on CNG with normal driveability and no MIL illumination? | -- | System OK | Go to Alternative Fuels (AF) Powertrain On Board (OBD) System Check |
