DTC P0753 1-2 Shift Solenoid Circuit Electrical Gas
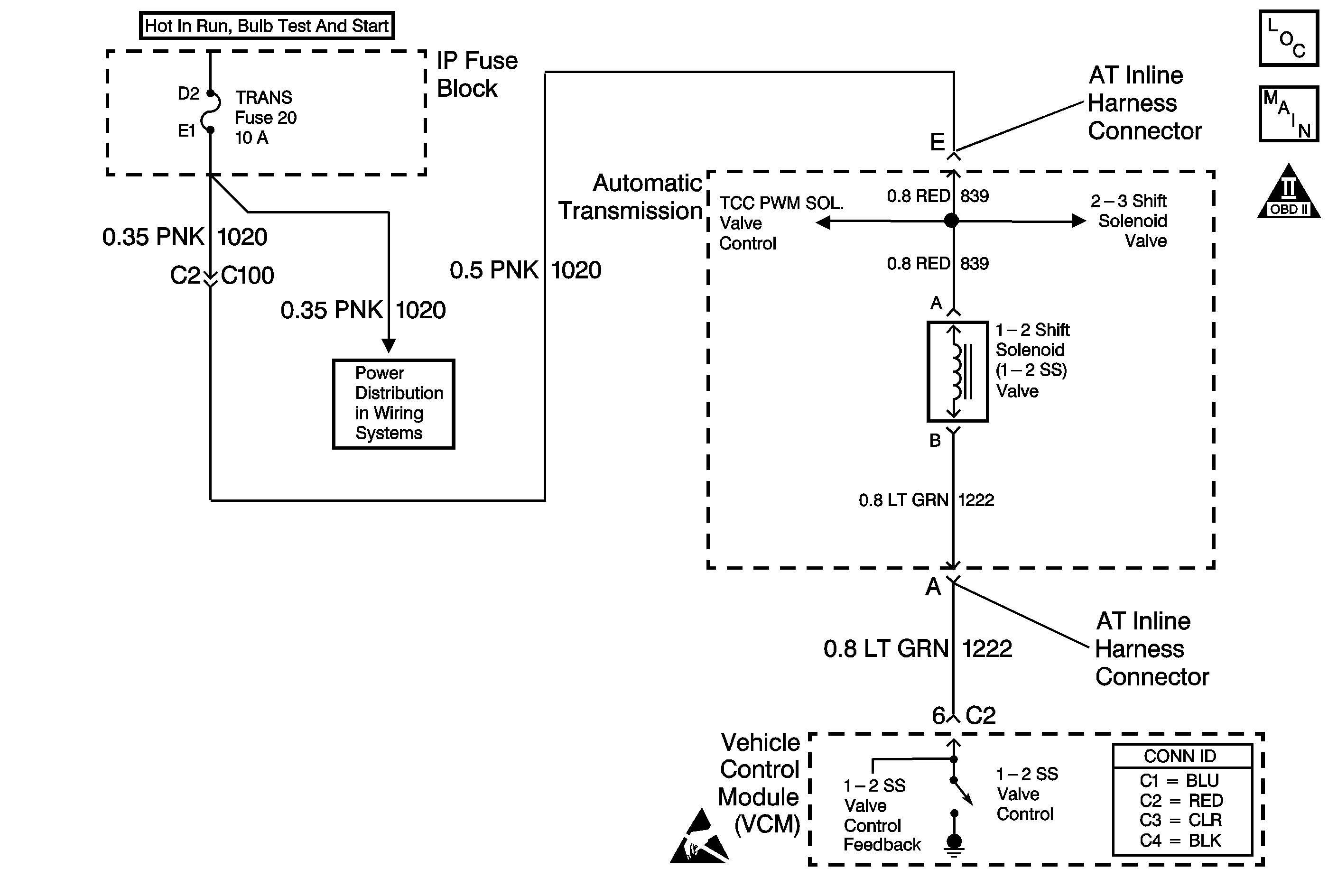
Circuit Description
The 1-2 shift solenoid (SS) valve controls the fluid flow action on the 1-2 and the 3-4 shift valves. The 1-2 SS valve is a normally-open exhaust valve that is used with the 2-3 SS valve to allow for four different shifting combinations. The 1-2 SS valve attaches to the control valve body within the transmission. The ignition voltage goes directly to the 1-2 SS valve. The VCM controls the 1-2 SS Valve by providing the ground path through circuit 1222.
When the vehicle control module (VCM) detects a continuous open or short in the 1-2 SS valve circuit or the 1-2 SS valve, then DTC P0753 sets. DTC P0753 is a type C DTC. For California emissions vehicles, DTC P0753 is a type A DTC.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | The system voltage is 10-16 volts. |
| • | The ignition is ON. |
| • | The engine runs more than 475 RPM for greater than 7 seconds. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
All conditions for running the DTC are met, and either of the following conditions occur for 4.3 out of 5 seconds.
| • | The VCM commands the solenoid on, and the voltage input remains high (B+). |
| • | The VCM commands the solenoid off and the voltage input remains low. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The VCM illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) for California emissions vehicles. |
| • | The VCM commands maximum line pressure. |
| • | The VCM freezes shift adapts. |
| • | The VCM inhibits 3-2 downshifts above 25 MPH. |
| • | The VCM records the operating conditions when the Conditions for Setting the DTC are met. The VCM stores this information as Freeze Frame and Failure Records. |
| • | The VCM stores DTC P0753 in VCM history. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | For California emissions, the VCM turns OFF the MIL during the third consecutive trip in which the diagnostic test runs and passes. |
| • | A scan tool can clear the MIL/DTC. |
| • | For California emissions, the VCM clears the DTC from VCM history if the vehicle completes 40 consecutive warm-up cycles without an emission related diagnostic fault occurring. |
| • | For Federal emissions, the VCM clears the DTC from VCM history if the vehicle completes 40 consecutive warm-up cycles without a non-emission related diagnostic fault occurring. |
| • | The VCM cancels the DTC default actions when the fault no longer exists and/or the ignition switch is OFF long enough in order to power down the VCM. |
Diagnostic Aids
| • | First diagnose and clear any engine DTCs or TP sensor codes that are present. Then inspect for any transmission DTCs that may have reset. |
| • | An open ignition feed on circuit 1020 can cause multiple DTCs to set. |
| • | Refer to Shift Solenoid Valve State and Gear Ratio table. |
| • | Inspect the connectors at the VCM, the AT wiring harness and all other circuit connecting points for an intermittent condition. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections in Wiring Systems. |
| • | Inspect the circuit wiring for an intermittent condition. Refer to Testing for Electrical Intermittents in Wiring Systems. |
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
This step tests the function of the 1-2 SS valve and the internal wiring harness.
-
This step tests the power to the 1-2 SS valve from the ignition through the fuse.
-
This step tests the ability of the VCM and the wiring to control the ground circuit.
-
This step measures the resistance of the automatic transmission wiring harness assembly and the 1-2 SS valve.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain Diagnostic System Check? | -- | Go to Powertrain On Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check (4.3L) or Powertrain On Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check (5.0/5.7L) or Powertrain On Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check (7.4L) | |||||||
2 |
Important: Before clearing the DTC, use the scan tool in order to record the Freeze Frame and Failure Records for reference. The Clear Info function will erase the data. Are any of the following DTCs set?
| -- | ||||||||
3 | Inspect the transmission fuse for an open. Is the fuse open? | -- | ||||||||
Use the scan tool in order to command the 1-2 SS valve ON and OFF three times while listening to the bottom of the transmission pan (a stethoscope may be necessary). Does the solenoid click when commanded? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | ||||||||
Refer to Automatic Transmission Inline Harness Connector End View . Does the test lamp illuminate? | -- | |||||||||
6 |
Refer to Automatic Transmission Inline Harness Connector End View . Does the test lamp turn ON and OFF with each command? | -- | ||||||||
Is the test lamp always ON? | -- | |||||||||
8 |
Refer to Automatic Transmission Inline Harness Connector End View . Does the resistance measure within the specified range? | 19-31 ohms | ||||||||
9 | Measure the resistance from terminal A to ground and terminal E to ground. Do both readings measure greater than the specified value? | 250K ohms | Go to Diagnostic Aids | |||||||
Does the resistance measure within the specified range? | 19-31 ohms | |||||||||
11 |
Do both readings measure greater than the specified value? | 250K ohms | ||||||||
12 |
Important: The condition that affects this circuit may exist in other connecting branches of the circuit. Refer to Power Distribution Schematics in Wiring Systems for complete circuit distribution. Test the power feed circuit (CKT 1020) of the 1-2 SS valve for a short to ground between the IP fuse block and the AT inline 20-way connector. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||
13 |
Important: The condition that affects this circuit may exist in other connecting branches of the circuit. Refer to Power Distribution Schematics in Wiring Systems for complete circuit distribution. Test the power feed circuit (CKT 839) of the 1-2 SS valve for a short to ground between the AT inline 20-way connector and the 1-2 SS valve. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find a short to ground condition? | -- | ||||||||
14 |
Did you complete the replacement? | -- | -- | |||||||
15 |
Important: The condition that affects this circuit may exist in other connecting branches of the circuit. Refer to Power Distribution Schematics in Wiring Systems for complete circuit distribution. Test the power feed circuit (CKT 1020) of the 1-2 SS valve for an open. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | -- | |||||||
16 | Test the control circuit (CKT 1222) of the 1-2 SS valve for a short to ground between the VCM connector C2-6 and the AT inline 20-way connector. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||
17 | Test the control circuit (CKT 1222) of the 1-2 SS valve for an open or short to power between the VCM connector C2-6 and the AT inline 20-way connector. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||
18 | Replace the AT wiring harness assembly from the 1-2 SS valve. Refer to Wiring Harness Replacement. Did you complete the replacement? | -- | -- | |||||||
19 | Replace the 1-2 SS valve. Refer to Control and Shift Solenoids Replacement. Did you complete the replacement? | -- | -- | |||||||
20 | Replace the VCM. Refer to VCM Replacement/Programming (4.3L) or VCM Replacement/Programming (5.0/5.7L) or VCM Replacement/Programming (7.4L) in Engine Controls. Did you complete the replacement? | -- | -- | |||||||
21 | Perform the following procedure in order to verify the repair:
Has the test run and passed? | -- | System OK |
DTC P0753 1-2 Shift Solenoid Circuit Electrical Diesel
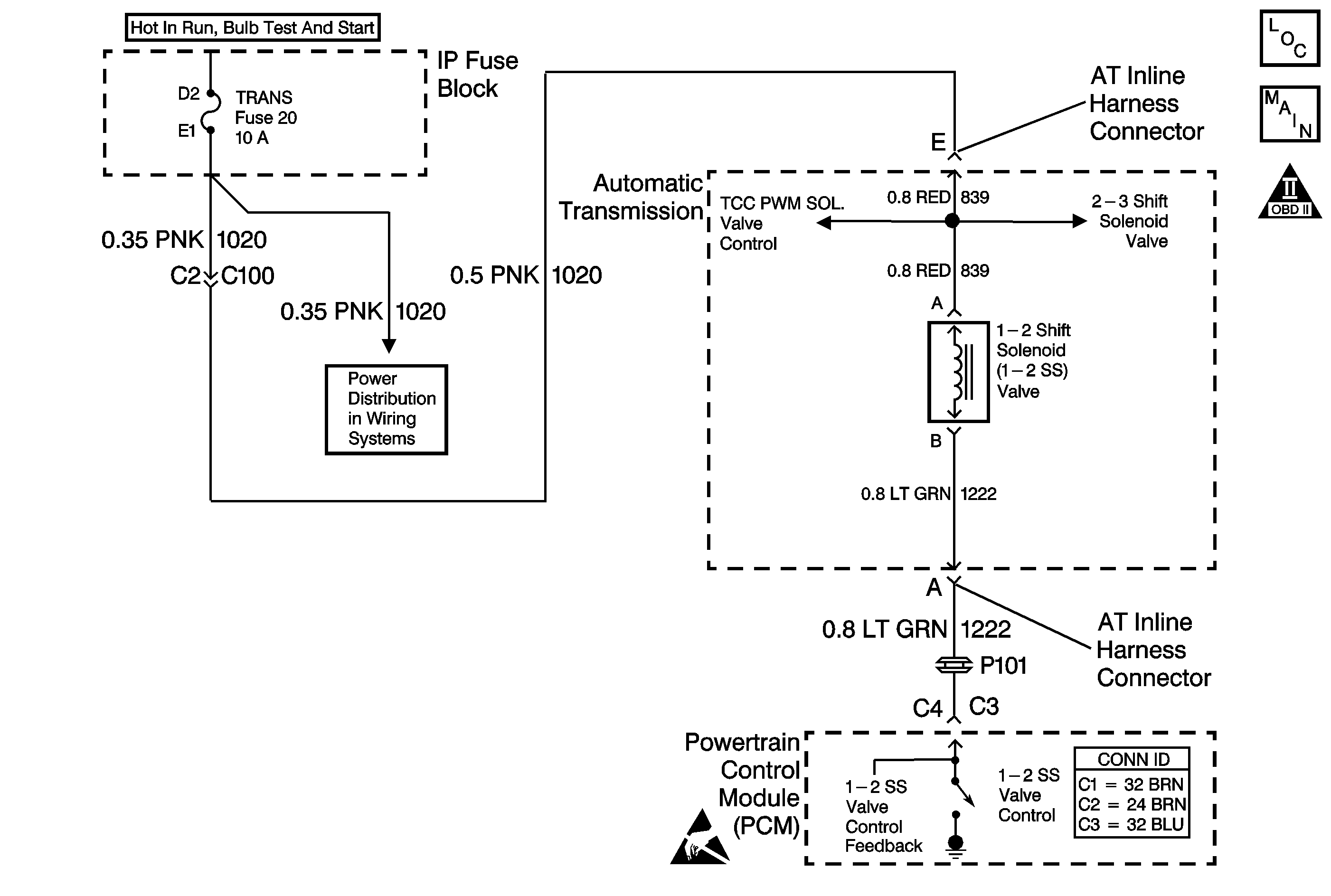
Circuit Description
The 1-2 shift solenoid (1-2 SS) valve controls the fluid flow acting on the 1-2 and the 3-4 shift valves. The 1-2 SS valve is a normally-open exhaust valve that is used with the 2-3 shift solenoid (2-3 SS) valve in order to allow four different shifting combinations. The 1-2 SS valve attaches to the control valve body within the transmission. The ignition voltage goes directly to the 1-2 SS valve. The powertrain control module (PCM) controls the 1-2 SS valve by providing the ground path through circuit 1222.
If the PCM detects a continuous open or short to ground in the 1-2 SS valve circuit or the 1-2 SS valve, then DTC P0753 sets. DTC P0753 is a type A DTC.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | The engine runs more than 475 RPM for greater than 7 seconds. |
| • | System voltage is 8.0-18.0 volts. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The above conditions are met and either of the following conditions occur for 4.3 out of 5 seconds:
| • | The PCM commands the Solenoid ON and the voltage input remains high (B+). |
| • | The PCM commands the Solenoid OFF and the voltage input remains low (0 volts). |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL). |
| • | The PCM commands maximum line pressure. |
| • | The PCM freezes shift adapts. |
| • | The PCM records the operating conditions when the Conditions for Setting the DTC are met. The PCM stores this information as Freeze Frame and Failure Records. |
| • | The PCM stores DTC P0753 in PCM history. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | For Federal and California emissions, the PCM turns OFF the MIL during the third consecutive trip in which the diagnostic test runs and passes. |
| • | A scan tool can clear the MIL/DTC. |
| • | For Federal and California emissions, the PCM clears the DTC from PCM history if the vehicle completes 40 consecutive warm-up cycles without an emission related diagnostic fault occurring. |
| • | For vehicles equal to or greater than 15,000 lbs GVW, the PCM clears the DTC from PCM history if the vehicle completes 40 consecutive warm-up cycles without a non-emission related diagnostic fault occurring. |
| • | The PCM cancels the DTC default actions when the fault no longer exists and the ignition switch is OFF long enough in order to power down the PCM. |
Diagnostic Aids
| • | First diagnose and clear any engine DTCs that are present. Then inspect for any transmission DTCs that may have reset. |
| • | An open ignition feed circuit can cause multiple DTCs to set. |
| • | Refer to Shift Solenoid Valve State and Gear Ratio table. |
| • | Inspect the connectors at the PCM, the AT wiring harness and all other circuit connecting points for an intermittent condition. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections in Wiring Systems. |
| • | Inspect the circuit wiring for an intermittent condition. Refer to Testing for Electrical Intermittents in Wiring Systems. |
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
This step tests the function of the 1-2 SS valve and the automatic transmission wiring harness assembly.
-
This step tests the power to the 1-2 SS valve from the ignition through the fuse.
-
This step measures the resistance of the 1-2 SS valve.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain Diagnostic System Check? | -- | ||||||||
2 |
Important: Before clearing the DTC, use the scan tool in order to record the Freeze Frame and Failure Records for reference. The Clear Info function will erase the data. Are any of the following DTCs set?
| -- | ||||||||
3 | Inspect the transmission fuse for an open. Is the fuse open? | -- | ||||||||
Use the scan tool in order to command the 1-2 SS valve ON and OFF three times while listening to the bottom of the transmission pan. (A stethoscope may be necessary.) Does the solenoid click when commanded? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | ||||||||
Refer to Automatic Transmission Inline Harness Connector End View . Does the test lamp illuminate? | -- | |||||||||
6 |
Refer to Automatic Transmission Inline Harness Connector End View . Does the test lamp turn ON and OFF with each command? | -- | ||||||||
7 | Is the test lamp always ON? | -- | ||||||||
8 |
Refer to Automatic Transmission Inline Harness Connector End View . Does the resistance measure within the specified range? | 19-31 ohms | ||||||||
9 | Measure the resistance from terminal A to ground and terminal E to ground. Do both readings measure greater than the specified value? | 250K ohms | Go to Diagnostic Aids | |||||||
Does the resistance measure within the specified range? | 19-31 ohms | |||||||||
11 |
Do both readings measure greater than the specified value? | 250K ohms | ||||||||
12 |
Important: The condition that affects this circuit may exist in other connecting branches of the circuit. Refer to Power Distribution Schematics in Wiring Systems for complete circuit distribution. Test the power feed circuit (CKT 1020) of the 1-2 SS valve for a short to ground between the IP fuse block and the AT inline 20-way connector. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||
13 |
Important: The condition that affects this circuit may exist in other connecting branches of the circuit. Refer to Power Distribution Schematics in Wiring Systems for complete circuit distribution. Test the power feed circuit (CKT 839) of the 1-2 SS valve for a short to ground between the AT inline 20-way connector and the 1-2 SS valve. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find a short to ground condition? | -- | ||||||||
14 |
Did you complete the replacement? | -- | -- | |||||||
15 |
Important: The condition that affects this circuit may exist in other connecting branches of the circuit. Refer to Power Distribution Schematics in Wiring Systems for complete circuit distribution. Test the power feed circuit (CKT 1020) of the 1-2 SS valve for an open. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | -- | |||||||
16 | Test the control circuit (CKT 1222) of the 1-2 SS valve for a short to ground between the PCM connector C3-C4 and the AT inline 20-way connector. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||
17 | Test the control circuit (CKT 1222) of the 1-2 SS valve for an open or short to power between the PCM connector C3-C4 and the AT inline 20-way connector. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | ||||||||
18 | Replace the AT wiring harness assembly from the 1-2 SS valve. Refer to Wiring Harness Replacement. Did you complete the replacement? | -- | -- | |||||||
19 | Replace the 1-2 SS valve. Refer to Control and Shift Solenoids Replacement. Did you complete the replacement? | -- | -- | |||||||
20 | Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement/Programming in Engine Controls. Did you complete the replacement? | -- | -- | |||||||
21 | Perform the following procedure in order to verify the repair:
Has the test run and passed? | -- | System OK |
