Battery Common Causes of Malfunction Common Causes
With the proper care, the battery will provide many years
of service.
The following factors may reduce the battery performance level:
| • | Vehicle accessories remain ON overnight. |
| • | Insufficient driving time in order to recharge the battery. |
| | Short trips may cause insufficient charging time. |
| • | Insufficient driving speed. |
| | Slow average driving speeds for long periods of time may cause insufficient
charging. |
| • | The vehicle's electrical load is greater than generator output. |
| | The addition of aftermarket equipment often causes the above condition. |
| • | The following charging system conditions: |
| • | The following methods of improper installation of aftermarket
equipment affect the generator: |
| • | Structural failure of aftermarket mounting brackets. |
| • | Failure to keep the battery cable terminals clean and tight. |
| • | Operating the battery with a loose battery hold-down. |
| • | Pinched wires or a cracked battery case resulting from a collision
may cause improper mechanical conditions in the electrical system. |
| | Inspect the outside of the battery periodically for damage, such as
a cracked cover or case. |
Battery Common Causes of Malfunction Electrolyte Freezing
The freezing point of electrolyte depends on the specific
gravity of the electrolyte. Maintaining the battery in a fully charged condition
can protect the electrolyte against freezing. If the green dot appears in
the built-in hydrometer, the battery will not freeze unless the temperature
drops below -32°C (-25°F). A fully charged battery will
not freeze unless the temperature drops below -54°C (-65°F).
Battery Common Causes of Malfunction Carrier and Hold-Down
Ensure that the battery carrier and the battery hold-down(s)
are in the following condition before installing the battery:
Ensure that the carrier is in proper condition because the carrier will
hold the battery securely and keep the battery level. Ensure that no loose
items are in the carrier before installing the battery.
Tighten the hold-down bolts to the specified values in order to prevent
the battery from shaking in its carrier. Refer to
Fastener Tightening Specifications
.
Battery Common Causes of Malfunction Battery Protect During Storage
Caution: Follow all safety precautions on the battery. Failure to do so may result
in personal injury.
Some electronic devices on the vehicle impose small continuous
current drains on the battery. This condition is commonly called parasitic
current drain. If the vehicle is not used for an extended time, these parasitic
loads can discharge and eventually cause permanent damage to the battery.
Discharged batteries can also freeze in cold weather. Refer to
Battery Common Causes of Malfunction
.
Notice: Always turn off the engine control switch when connecting or disconnecting
battery cables, battery chargers, or jumper cables. Failure to do so may damage
the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) or other electronic components.
Perform the following actions if the vehicle is likely to be stored
for over 30 days:
Caution: Unless directed otherwise, the ignition and start switch must be in the OFF or LOCK position, and all electrical loads must be OFF before servicing
any electrical component. Disconnect the negative battery cable to prevent an electrical spark should a tool or equipment come in contact with an exposed electrical terminal. Failure to follow these precautions may result in personal injury and/or damage to
the vehicle or its components.
| • | Verify that
the built-in hydrometer's green dot is visible, then disconnect the negative
battery cable from the battery. This action will protect the battery from
being discharged by parasitic current drain from the vehicle's electrical
system. |
| • | If the battery cable cannot be disconnected, establish a regular
schedule of recharging the battery every 20-45 days in order to maintain
a high state of charge. Any time a battery is found with the green dot not
visible in the hydrometer, promptly recharge the battery. |
| • | Use a battery charger that is capable of providing a charging
voltage of at least 16 volts in order to maintain a low charge time. Charge
rates of 50 amps or more will not damage original equipment maintenance free
batteries if the battery does not exhibit the following conditions: |
| - | Excessive gassing of electrolyte from the vents |
| - | Excessive battery temperature |
| - | Any temperature over 52°C (125°F) is excessive. |
| • | Inspect the battery being charged every 45-60 minutes.
Stop or reduce the charge rate as necessary. Stop charging within one hour
after the green dot appears in the hydrometer in order to avoid overcharging
the battery. |
| | A battery that remains in a discharged state for a long period of time
will be difficult to recharge. The battery may even be permanently damaged
if the battery remains discharged. |
Use the following procedure when reconnecting the battery:
- Use a wire brush in order to lightly clean any oxidation from
the contact face of the battery terminal before reattaching the cable.
Notice: Use the correct fastener in the correct location. Replacement fasteners
must be the correct part number for that application. Fasteners requiring
replacement or fasteners requiring the use of thread locking compound or sealant
are identified in the service procedure. Do not use paints, lubricants, or
corrosion inhibitors on fasteners or fastener joint surfaces unless specified.
These coatings affect fastener torque and joint clamping force and may damage
the fastener. Use the correct tightening sequence and specifications when
installing fasteners in order to avoid damage to parts and systems.
- Tighten the battery
cable.
Tighten
Tighten the top post terminal nut to 17 N·m (13 lb ft).
- Reset the clock, push-button radio tuning, etc., before the vehicle
returns to service.
Battery Common Causes of Malfunction Built-In Hydrometer
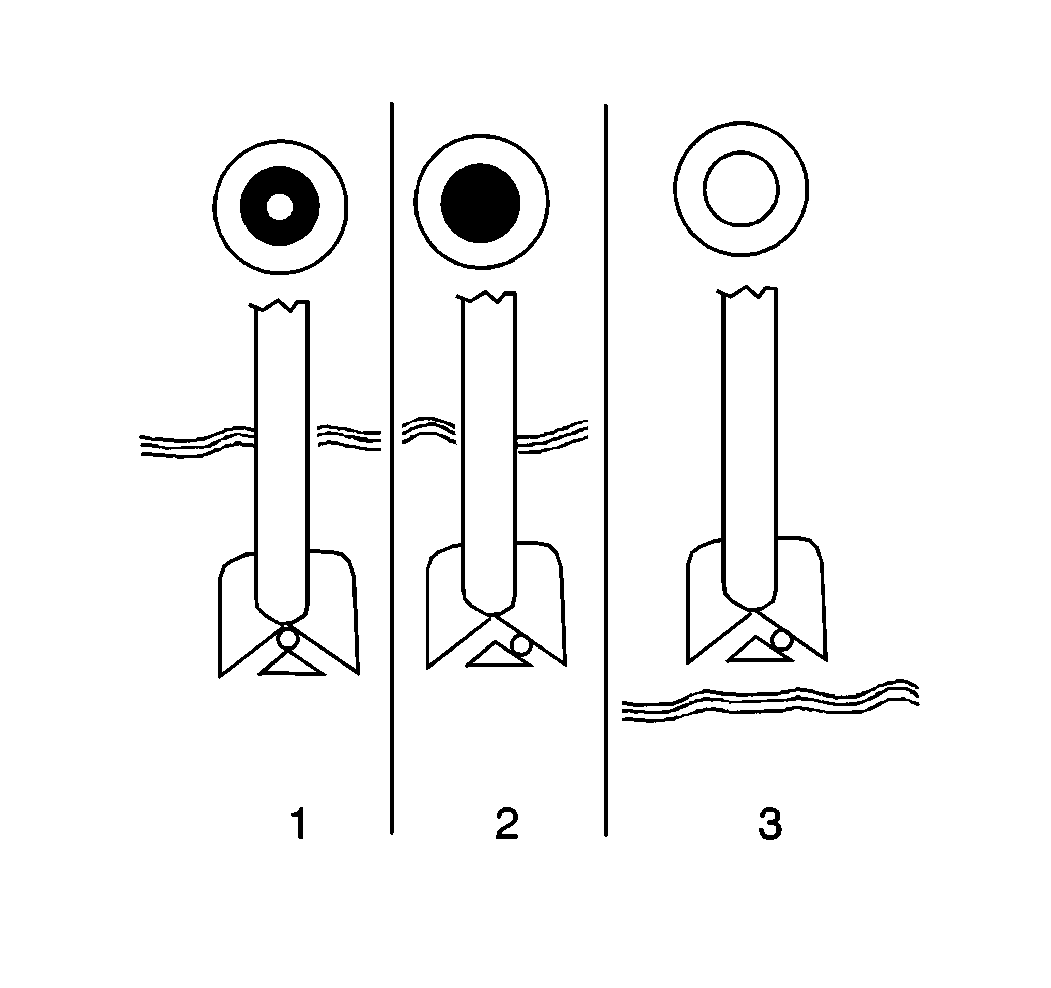
A built-in temperature
compensated hydrometer is molded into the top of the maintenance-free battery.
The hydrometer is an indicator of the battery's state of charge. Use this
hydrometer with the following diagnostic procedure.
When observing the hydrometer, ensure that the battery has a clean top.
A light may be required in some poorly-lit areas.
Under normal operation one of the following three indications can be
observed:
Green Dot Visibility
Any green appearance in the hydrometer is interpreted as a green dot
(1). The presence of a green dot indicates that the battery's state of charge
is 65 percent or more. The battery is ready for testing.
Dark Dot or Lack of Green Dot Visibility
Lack of green dot visibility (dark dot) (2) indicates that the battery's
state of charge is below 65 percent. Test the charging system output and the
electrical system for excessive draws.
Yellow Dot or Clear Dot Visibility
A yellow or clear dot (3) indicates that the electrolyte level is low.
This electrolyte level is also too low for diagnosis. The following conditions
may have caused the reduced electrolyte levels:
| • | Excessive or prolonged charging |
| • | Excessive tipping of the battery |
| | Batteries having the above conditions may indicate excessive charging
voltages, caused by a faulty charging system. Inspect the charging and the
electrical systems. Replace the battery. |

