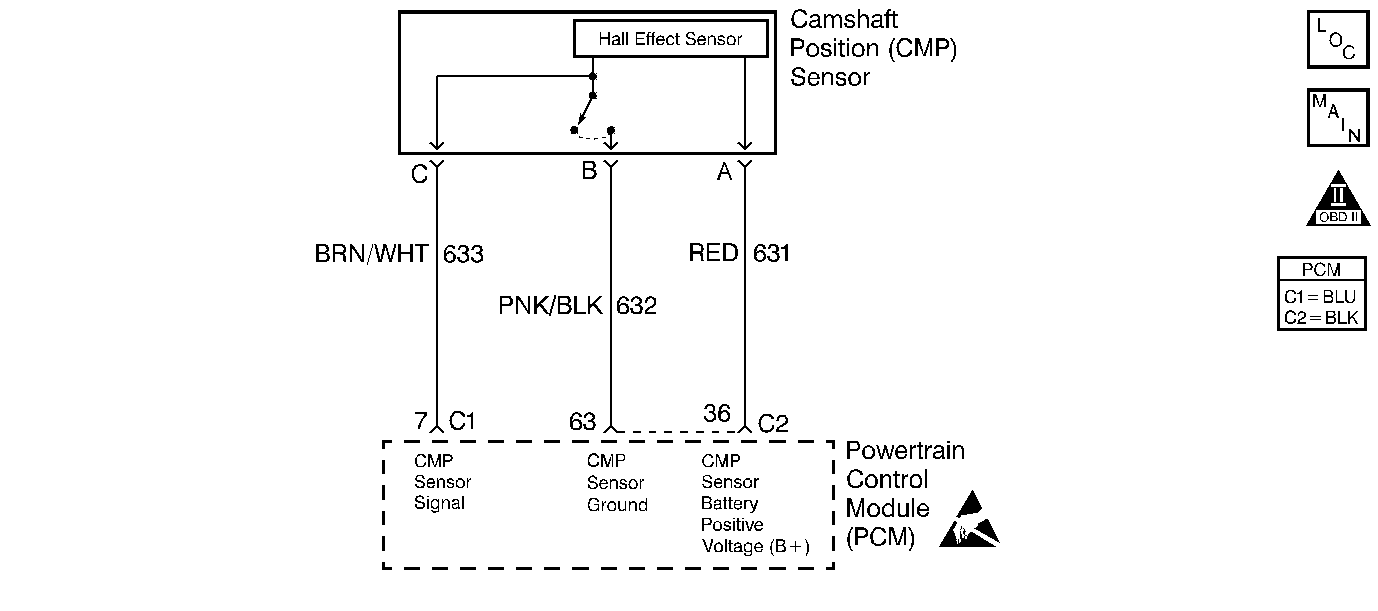
Circuit Description
The camshaft position (CMP) sensor indicates the camshaft position so the powertrain control module (PCM) can determine which cylinder is misfiring when a misfire is present. Whenever the PCM receives an intermittent signal from the CMP, then the CMP actrivity counter will increment. In order to set a DTC, the PCM must see a minimum number of resyncs within a maximum time.
Conditions for Running the DTC
The engine is running.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The CMP active counter is not incrementing.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) will illuminate after two consecutive ignition cycles in which the diagnostic runs with the malfunction present. |
| • | The PCM will record the operating conditions at the time that the diagnostic fails. The Freeze Frame and Failure Records buffers will store this information. |
| • | A history DTC stores. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) will turn OFF after 3 consecutive ignition cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault. |
| • | A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm up cycles without a fault. |
| • | Use a scan tool to clear the DTCs. |
Diagnostic Aids
| • | A poor connection, rubbed through wire insulation, or a wire that is broken inside the insulation may cause an intermittent problem. |
| • | Thoroughly check any circuitry, that is suspected as causing the intermittent complaint, proper mating, broken locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, or physical damage to the wiring harness. |
| • | Whenever the PCM sees less than 15 resyncs in 256 seconds, the counter resets to 0. Anytime a poor connection is present, the cam sensor reference activity counter stops incrementing and the cam sensor resync counter starts to increment. |
Test Description
The number(s) below refer(s) to the step number(s) on the Diagnostic Table.
-
The Powertrain OBD System Check prompts you to complete some of the basic checks and to store the freeze frame and failure records data on the scan tool if applicable. This creates an electronic copy of the data captured when the malfunction occurred. The scan tool stores this data for later reference.
-
This step determines if the DTC P0342 is the result of a hard malfunction or an intermittent condition.
-
This step determines if the voltage is available to the CMP sensor through the PCM.
-
This step determines if the voltage is available to the CMP sensor through the PCM.
-
This step checks for a signal from the CMP sensor. It is necessary to supply B+ to the CMP sensor ignition positive voltage terminal in order for the CMP sensor to have B+ supplied to the CMP sensor. While cranking the engine, the CMP sensor will send a varying voltage signal that can be read by the DMM as a frequency check.
-
Reprogram the replacement PCM and perform the crankshaft position system variation learning procedure. Refer to the latest Isuzu Technical Communication Systems (ITCS) procedures for PCM reprogramming and the Crankshaft Position System Variation Learn for the crankshaft position system variation learn procedure.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | |||||||
Is the CMP Active counter incrementing? | -- | |||||||
3 |
Is the CMP Active Counter incrementing? | -- | ||||||
Did the test light illuminate? | -- | |||||||
Did the test light illuminate? | -- | |||||||
6 |
Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||||||
Does the DMM display a frequency reading that is varying between the specified values? | 0.5-2.6 Hz | |||||||
8 |
Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||||||
9 |
Does the test light illuminate? | -- | ||||||
10 |
Does the test light illuminate? | -- | ||||||
11 |
Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||||||
12 |
Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||
13 |
Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||
14 |
Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||
Is the action complete? | -- | -- | ||||||
16 |
Does the scan tool indicate that this diagnostic has ran and passed? | -- | ||||||
17 | Check to see if any additional DTCs are set. Does the scan tool display any DTCs that you have not diagnosed? | -- | Go to applicable DTC table | System OK |
