Powertrain Control Module Controlled Warning Lamps Diagnosis Generator Lamp Control Circuit
Refer to
IAC Valve, Generator, TR, Oil, and Coolant Switches
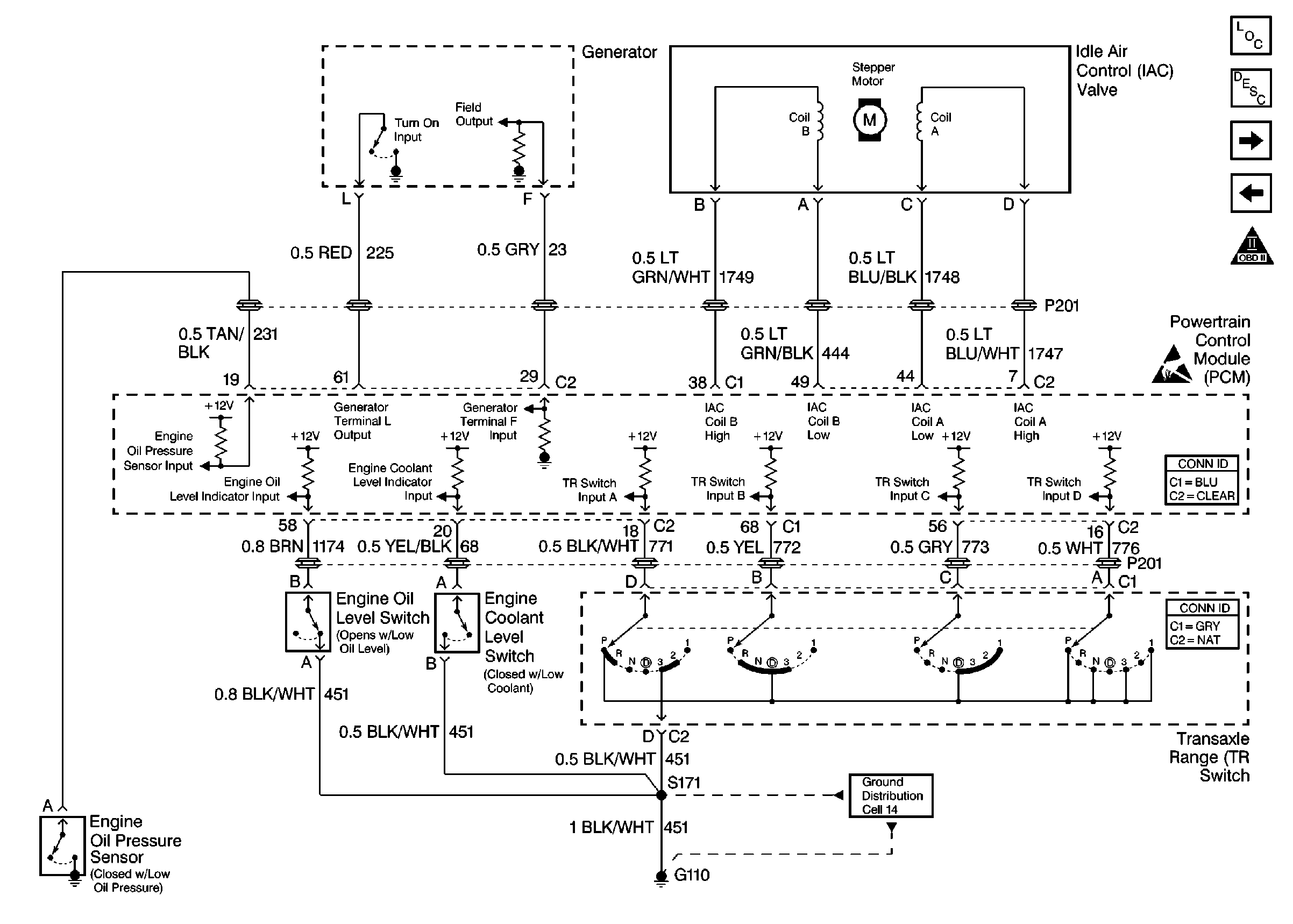
schematic.
Diagnosis
Use the following diagnostic table to diagnose the generator F and L circuit.
Use the following scan tool parameters when diagnosing the PCM controlled generator.
Generator PWM - Range 0-100% : The generator F terminal is a Pulse Width Modulated (PWM) duty cycle or load input to the PCM from the generator. As the generator load increases, the PCM can sense the change and adjust the idle speed accordingly.Generator L Terminal - Range Inactive/Active : The generator L terminal indicates whether the PCM is allowing the generator to operate. The PCM can disable the generator under certain conditions in order to ease starting. Active indicates that the PCM is allowing generator operation, while inactive indicates that the PCM is not allowing generator operation.
Circuit Description
The generator communicates to the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) over two lines, the L or Lamp circuit and the F or Field circuit. The PCM uses the L circuit to monitor faults in the charging system. The F circuit is used by the PCM to monitor the duty cycle or load of the generator. The PCM will adjust the idle speed according to the generator load.
Diagnostic Aids
| • | If the generator terminal F input circuit is shorted to voltage, the volts telltale lamp will operate normally. However, the scan tool Generator PWM will display a generator duty cycle near 10%. Check the generator terminal F input circuit for a short to voltage. If OK, the generator may be faulty, refer to Charging System Check . |
| • | An Intermittent problem may be caused by a poor connection, rubbed through wire insulation, or a wire that is broken inside the insulation. |
| • | Any circuitry, that is suspected as causing the intermittent complaint, should be thoroughly checked for the following items: |
| - | Improper mating |
| - | Broken locks |
| - | Poor terminal to wiring connections |
| - | Physical damage to the wiring harness |
Test Description
The number(s) below refer(s) to the step number(s) on the Diagnostic Table:
-
The Powertrain On Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check prompts you to complete some of the basic checks and to store the freeze frame and failure records data on the scan tool if applicable. This creates an electronic copy of the data captured when the fault occurred. The scan tool stores this data for later reference.
-
If the volts telltale lamp is not operating, the IPC is malfunctioning.
-
If no malfunctions are present at this point, refer to Diagnostic Aids for additional checks and information.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | |||
2 | Was DTC P0560 set? | -- | Go to applicable DTC table | |
Turn ON the ignition leaving the engine OFF. Is the volts telltale lamp on the IPC illuminated? | -- | |||
4 | Start the engine. Did the volts telltale lamp on the IPC turn OFF? | -- | ||
5 | Check if any IPC DTCs are set. Are any IPC DTCs set? | -- | Go to IPC DTC table | Go to Instrument Cluster System Check in Instrument Panel, Gauges and Console |
Operate the vehicle within the conditions under which the original symptom was observed. Does the system now operate properly? | -- | System OK Go to Diagnostic Aids |
