| Table 1: | Starter Enable (Crank) Relay |
Refer to Engine Controls Schematics
Transaxle Range Switch Outputs
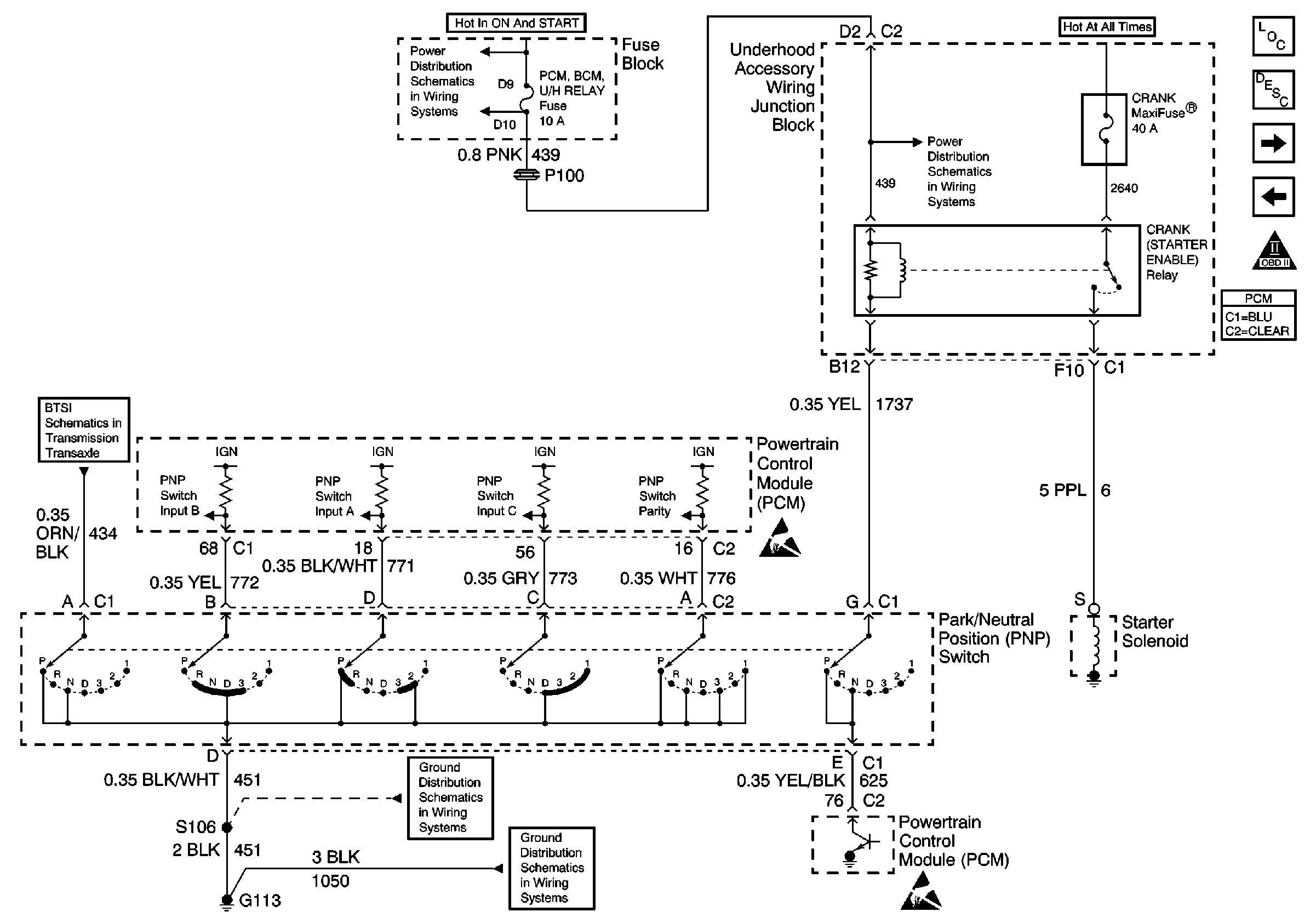
.
Circuit Description
The PCM controlled starter system consists of the following components:
| • | The ignition switch |
| • | The crank request signal circuit |
| • | The powertrain control module (PCM) |
| • | The starter enable (crank) relay |
| • | The transaxle range switch |
| • | The starter solenoid |
When the ignition switch is turned to the Start position, B+ is sent to the PCM via the Crank Request Signal circuit. The PCM has the ability to disallow starter operation if conditions inappropriate for starter operation exist. The PCM will disable the starter under the following conditions:
| • | The engine is running |
| • | A correct vehicle theft deterrent (VTD) password is not received from the body control module (BCM) |
| • | The vehicle operator continues to engage the starter for an extended period of time |
If no inhibiting conditions are present, and the PCM detects voltage on the Crank Request Signal circuit, the PCM grounds the Starter Enable (Crank) relay control circuit. The Transaxle Range switch must be in Park or Neutral for the control circuit to operate the relay. Current from the crank maxifuse flows through the relay to the starter solenoid.
Diagnostic Aids
This diagnostic procedure is intended to identify electrical malfunctions within the PCM controlled portion of the starting system. For additional system diagnosis, refer to Diagnostic System Check - Engine Electrical in Wiring Systems.
Use the J 35616 connector test adapter kit for any test that requires probing the PCM harness connectors, electrical center fuse/relay cavities, component terminals or a component harness connector. Using this kit will prevent damage caused by improper probing of connector terminals.
If the problem is intermittent, refer to Intermittent Conditions for diagnosis.
Relay Terminal Identification
Use the following relay cavity table in order to locate the correct cavities to probe during diagnosis. The table layout corresponds to the cavity layout in the underhood accessory junction block. Four blade relays can be inserted 2 ways. Use the table and NOT the numbering on the relay to avoid probing incorrectly.
Top of Junction Block | |
|---|---|
Switch Power (crank MaxiFuse) | Coil Ground (PCM) |
Coil Power (fuse) | Switch Load (starter) |
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table:
-
Ensure that there are no problems with the battery or the battery connections before attempting the starter diagnosis. If the battery required a charge, but was otherwise OK, check for a charging system problem or for a parasitic drain. Refer to Diagnostic System Check - Engine Electrical or to Battery Electrical Drain/Parasitic Load in Engine Electrical.
-
The starter should disengage when the key is released.
-
If the test lamp illuminates, the PCM controlled portion of the circuit is functioning.
-
If the status of the Starter Enable (Crank) relay indicates anything other than OK with the key in either position, there is a problem with the Starter Enable (Crank) relay control circuit.
-
Check for poor connections or terminal tension at the fuse. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections in Wiring Systems .
Step | Action | Values | Yes | No | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | Go to Step 2 | |||||
|
Important: Check the battery connections. Fully charge and load test the battery before proceeding with the starter diagnosis. Refer to Battery Inspection/Test in Engine Electrical.Turn the key to Off. Is the starter operating with the key Off? | -- | Go to Step 3 | Go to Step 4 | |||||
3 | Disconnect the Starter Enable (Crank) relay. Is the starter operating? | -- | Go to Step 31 | |||||
4 | Turn the key to On. Is the starter operating? | -- | Go to Step 5 | |||||
5 | Turn the key to Start. Is the starter operating? | -- | Go to Step 6 | Go to Step 7 | ||||
Does the starter continue to operate after the key is released to the On position? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids. | ||||||
Does the test lamp illuminate with the key in Start? | -- | Go to Diagnostic System Check - Engine Electrical in Engine Electrical | Go to Step 8 | |||||
8 | Using the scan tool, check for the following DTCs:
Are any VTD related DTCs set? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | Go to Step 9 | ||||
9 | Monitor the Crank Request with the scan tool. Does scan tool indicate No with the key in the On position, and Yes with the key in Start? | -- | Go to Step 10 | |||||
Does the status continuously indicate OK in both key positions? | -- | Go to Step 11 | ||||||
Check the Crank Maxifuse. Is the fuse OK? | -- | Go to Step 16 | Go to Step 12 | |||||
12 |
Is the resistance more than the specified value? | 2 ohms | Go to Step 13 | Go to Step 23 | ||||
13 |
Is the resistance more than the specified value? | 2 ohms | Go to Step 14 | Go to Step 27 | ||||
14 |
Is the fuse OK? | -- | Go to Step 15 | Go to Step 31 | ||||
15 |
Is the fuse OK? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | Go to Step 33 | ||||
16 |
Does the test lamp illuminate? | -- | Go to Step 17 | Go to Step 25 | ||||
17 | Jumper the B+ feed circuit to the Starter Solenoid circuit in the relay connector. Does the starter operate? | -- | Go to Step 30 | Go to Step 18 | ||||
18 |
Does the test lamp illuminate? | -- | Go to Step 19 | Go to Step 26 | ||||
19 |
Does the starter operate? | -- | Go to Step 26 | Go to Step 20 | ||||
20 |
Does the test lamp illuminate? | -- | Go to Step 32 | Go to Step 21 | ||||
21 |
Does the test lamp illuminate? | -- | Go to Step 29 | Go to Step 26 | ||||
22 |
Does the starter operate with the key On? | -- | Go to Step 23 | Go to Step 28 | ||||
23 | Repair the short to ground in the B+ feed circuit to the relay. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | Go to Step 34 | -- | ||||
24 | Repair the short to ground in the Starter Solenoid Control circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | Go to Step 34 | -- | ||||
25 | Repair the open or the high resistance in the B+ feed circuit to the relay. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | Go to Step 34 | -- | ||||
26 | Repair the open or the high resistance in the Starter Solenoid Control circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | Go to Step 34 | -- | ||||
27 | Repair the Starter Solenoid Control circuit shorted to ground. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | Go to Step 34 | -- | ||||
28 |
Important: The replacement PCM must be programmed. Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement/Programming . Is the action complete? | -- | Go to Step 34 | -- | ||||
29 | Check for a loose solenoid or starter motor, or any mounting surface corrosion causing a loss of ground continuity. Repair as necessary. Is the action complete? | -- | Go to Step 34 | -- | ||||
30 | Check for poor connections or terminal tension at the relay connector. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections in Wiring Systems . Was a problem found and corrected? | -- | Go to Step 34 | Go to Step 31 | ||||
31 | Replace the Starter Enable (Crank) relay. Is the action complete? | -- | Go to Step 34 | -- | ||||
32 | Check for poor connections or terminal tension at the starter solenoid. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections . Was a problem found and corrected? | -- | Go to Step 34 | Go to Step 33 | ||||
33 | Replace the starter solenoid. Is the action complete? | -- | Go to Step 34 | -- | ||||
34 | Turn the key to Start. Does the starter operate? | -- | System OK | Go to Step 2 |
