Refer to Engine Control Schematics
Front and Rear Ignition Control Modules
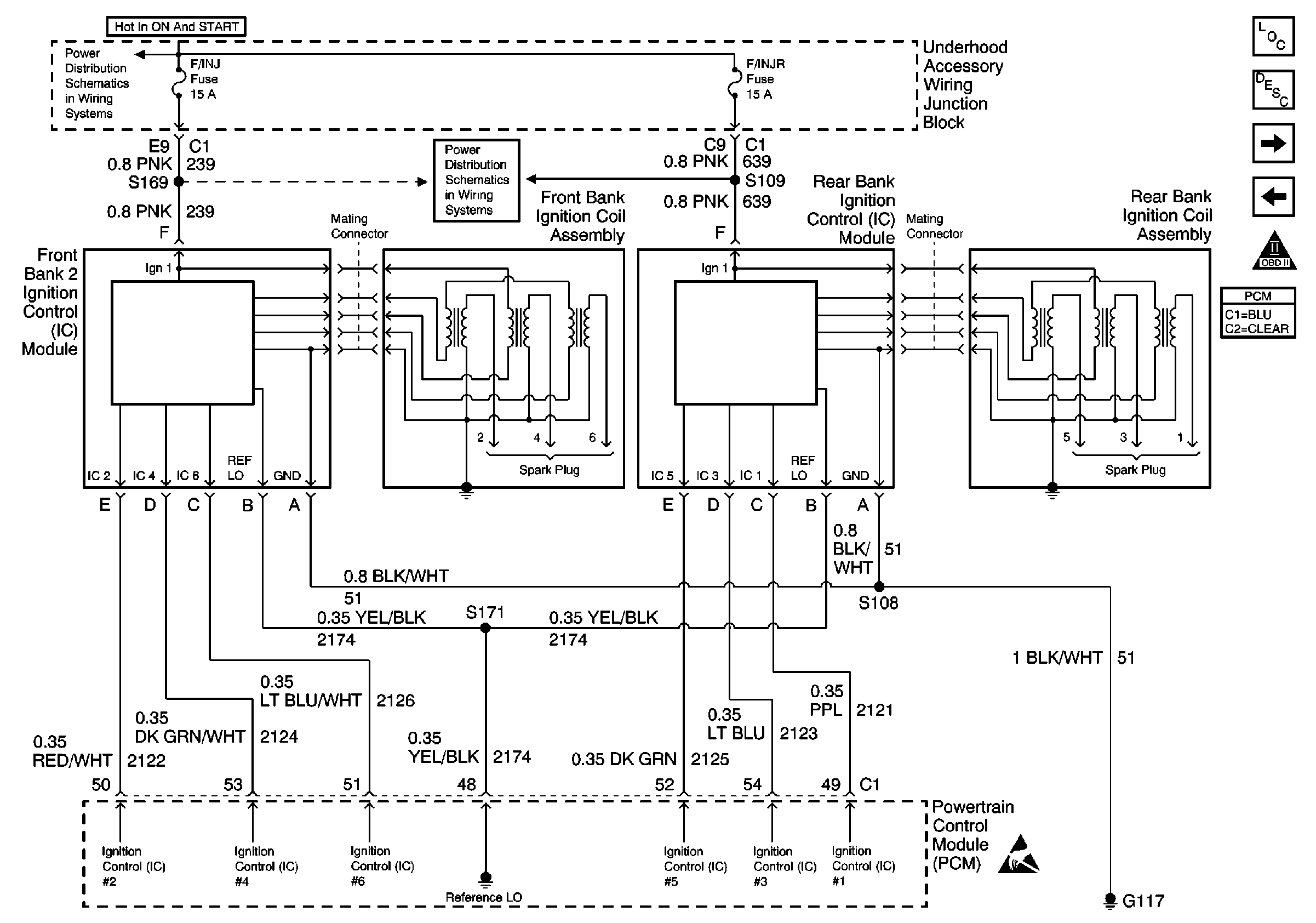
.
Circuit Description
The Secondary Ignition Diagnosis tests the spark plugs, the coils and the ignition coil modules (ICM). Diagnosis of the ignition control (IC) circuits is covered in DTCs P1351- P1366. This table requires the following special tools:
Diagnostic Aids
When servicing the ignition system components, use the following recommended procedures:
| • | If a boot remains attached to a coil or a spark plug, twist the boot prior to removal. Use the J 43094 Spark Plug Boot Removal Tool. |
| • | Check the boot for a missing or damaged internal spring. |
| • | Do not re-install any component that has visible signs of damage. |
| • | Install the boots onto the coils until bottomed out. Then install the assembly onto the spark plugs. If this is not possible due to space limitations, just-start the boots onto the spark plugs and then install the coil assembly as straight down onto the plugs as possible. |
| • | Ensure the boots are installed right side up. |
| • | Lift the module beauty cover at the end opposite the module to remove the cover. |
| • | Repair a torn perimeter seal with an RTV sealant. |
| • | Adhere to the torque specifications when installing the cassette to the cam cover and the module to the cassette. Refer to Ignition Control Module Replacement and Ignition Coil Replacement . |
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
If any IC circuit DTCs are set, perform the DTC table first. If no IC circuit DTCs are set, check the IC Circuit Status for all cylinders. If an IC Circuit Status indicates anything other than OK, even momentarily, perform the corresponding IC circuit DTC table as if the DTC were set.
-
A misfiring or dead cylinder can sometimes affect the misfire counters for other cylinders. When performing this table, concentrating on the cylinder with the highest level of misfire and correcting the problem may also correct the other cylinders that indicate misfire. If multiple cylinders are suspected, perform each test on all affected cylinders. An ignition coil, the boots, or the spark plugs may fail only when moisture is present. Although difficult to test on this engine, selectively wetting down parts of the system and rechecking for a misfire or any arcing may uncover a problem with one or more components. If moisture is present in the spark plug and ignition coil cavity of the cam cover, check the perimeter seal for damage. Repair tears in the perimeter seal with an RTV sealant. Ensure that the 7 cassette mounting bolts are tightened to the specified torque. Refer to Ignition Coil Replacement .
-
TheJ 26792 spark tester (ST 125) presents a more difficult load on the secondary ignition than a normal spark plug. If a miss, a stumble, or a hesitation is being caused by a spark plug not firing, the spark tester should also not fire.
-
A suspected ignition system miss may actually be a fuel system problem. Perform the Fuel System Diagnosis , if the diagnosis has not yet been performed. An internal engine problem can also cause a driveability concern. Refer to Base Engine Misfire Diagnosis .
If the misfire disappears when running the engine using the J 36012 Spark Plug Jumper wires, and misfire is present when the boots are installed, replace the affected boot.
-
An ignition coil, the boots, or the spark plugs may fail only when moisture is present. Although difficult to test on this engine, selectively wetting down parts of the system and rechecking for a misfire or any arcing may uncover an intermittent problem. If moisture is present in the spark plug/ignition coil cavity of the cam cover, check the perimeter seal for damage. Repair tears in the perimeter seal with an RTV sealant. Ensure that the 7 cassette mounting bolts are tightened to the specified torque. Refer to Ignition Coil Replacement .
-
Ensure good DMM contact when measuring the spark plug resistance. When manufactured, the normal resistance for the spark plug is 3000-8000 ohms. A suspected ignition system miss may actually be a fuel system problem. Perform the Fuel System Diagnosis . An internal engine problem can also cause a driveability concern. Refer to Base Engine Misfire Diagnosis .
-
If the spark plug exhibits unusual signs of damage or deposits, diagnose and correct the root cause of the problem (e.g. excessive detonation, the wrong spark plug or an incorrect heat range for the application, a base engine problem, etc.).
-
Be sure to use the correct adaptor harness when connecting the ignition module tester to the LX5 engine. Using an adaptor harness for a different engine application will result in incorrect tool operation.
The green power LED should come on any time the ignition module tester is connected and the ignition switch is in the run position. This LED simply indicates that the J 43298 is receiving adequate power and ground to perform the test. The Test button is used as an LED check for the 4 red LEDs. To use this function, connect the tool, turn the ignition switch to run, then momentarily press the Test button. All 4 red LEDs should come on brightly. The crank the vehicle. If the 3 red LEDs flash, this confirms correct operation of the primary ignition system. The ignition module tester may get hot during actual testing as the tester is attempting to simulate the load of the ignition coils' primary windings.
Only 3 of the red LEDs are used when testing the LX5 engine. Four LEDs are provided on the tester for 8-cylinder applications.
If 3 LEDs flash, the module output drivers are operating. If one or more LEDs are inoperative, excluding the one unused LED, and no IC circuit DTCs are set, replace the module.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | ||||||||||||||
2 |
Do any cylinders indicate an excessive amount of misfire? | -- | ||||||||||||||
3 | Is an entire bank of cylinders inoperative? | -- | ||||||||||||||
Are any IC circuit DTCs set, or does the IC Circuit Status for any cylinder indicate anything other than OK? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC tables | ||||||||||||||
The remaining steps are to be performed on the cylinder indicating the highest level of misfire.
Was a problem found? | -- | |||||||||||||||
Does a spark jump the tester gap? | -- | |||||||||||||||
7 | Remove the spark plug on the affected cylinder. Does the spark plug show signs of oil or coolant entering the combustion chamber? | -- | Go to Oil Consumption Diagnosis in Engine Mechanical or to Loss of Coolant in Engine Cooling | |||||||||||||
8 | Check the spark plug for the following conditions:
Refer to Spark Plug Visual Diagnosis in Engine Electrical. Was a problem found? | -- | ||||||||||||||
Did the misfire follow the spark plug? | -- | Refer to Test Description | ||||||||||||||
10 |
Important: Remove the fuel pump fuse before proceeding. Running or cranking the engine with an ignition control module disconnected will cause excessive engine fueling if the fuel pump is not disabled. Is the frequency within the specified range? | 2 - 20 Hz | ||||||||||||||
11 | Select the Misfire History counters using the scan tool. Do any cylinders indicate a history of misfiring? | -- | System Ok | |||||||||||||
The remaining steps are to be performed on the cylinder indicating the highest level of misfire.
Was a problem found? | -- | |||||||||||||||
13 | Does the spark plug show signs of oil or coolant entering the combustion chamber? | -- | Go to Oil Consumption Diagnosis in Engine Mechanical or to Loss of Coolant in Engine Cooling | |||||||||||||
14 |
Was a problem found? | -- | ||||||||||||||
Measure the resistance of the affected spark plug. Is the resistance less than the specified value? | 15K ohms | Go to the Test Description | ||||||||||||||
16 |
Does the test lamp illuminate? | -- | ||||||||||||||
17 | Connect a test lamp between the Ignition feed circuit and the ground circuit in the ignition control module harness. Does the test lamp illuminate? | -- | ||||||||||||||
18 | Using the DMM, measure the resistance between the ground circuit and the Reference Low circuit in the harness connector of the ignition control module . Is the resistance less than or equal to the specified value? | 5 ohms | ||||||||||||||
19 |
Important: Remove the fuel pump fuse before proceeding. Running or cranking the engine with an ignition control module disconnected will cause excessive engine fueling if the fuel pump is not disabled. Is the frequency within the specified range for all circuits tested? | 2 - 20 Hz | ||||||||||||||
20 | Perform any repairs as necessary. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||||
21 | Repair the open or high resistance in the ignition feed circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||||
22 | Repair the open or high resistance in the ground circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||||
23 | Repair the open or high resistance in the Reference Low circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||||
Replace the spark plug. Refer to Spark Plug Replacement in Engine Electrical. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | ||||||||||||||
Important: Remove the fuel pump fuse before proceeding. Running or cranking the engine with an ignition control module disconnected will cause excessive engine fueling if the fuel pump is not disabled. Do 3 LEDs flash on and off as the engine is cranked? | -- | |||||||||||||||
26 | Check for poor connections or terminal tension between the IC module and the coil assembly. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections in Wiring Systems . Was a problem found and corrected? | -- | ||||||||||||||
27 | Replace the affected coil assembly. Refer to Ignition Coil Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||||
28 | Check for poor connections or terminal tension at the IC module. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections in Wiring Systems . Was a problem found and corrected? | -- | ||||||||||||||
29 | Replace the ignition control module. Refer to Ignition Control Module Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||||
30 |
Important: The replacement PCM must be programmed. Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement/Programming Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||||
31 |
Do any cylinders indicate an excessive amount of misfire? | -- | System OK | |||||||||||||
32 | Is the misfire indicated on the same cylinders that were just diagnosed? | -- | Go to Fuel System Diagnosis |
