Evaporative Emission Control System Diagnosis VIN 1
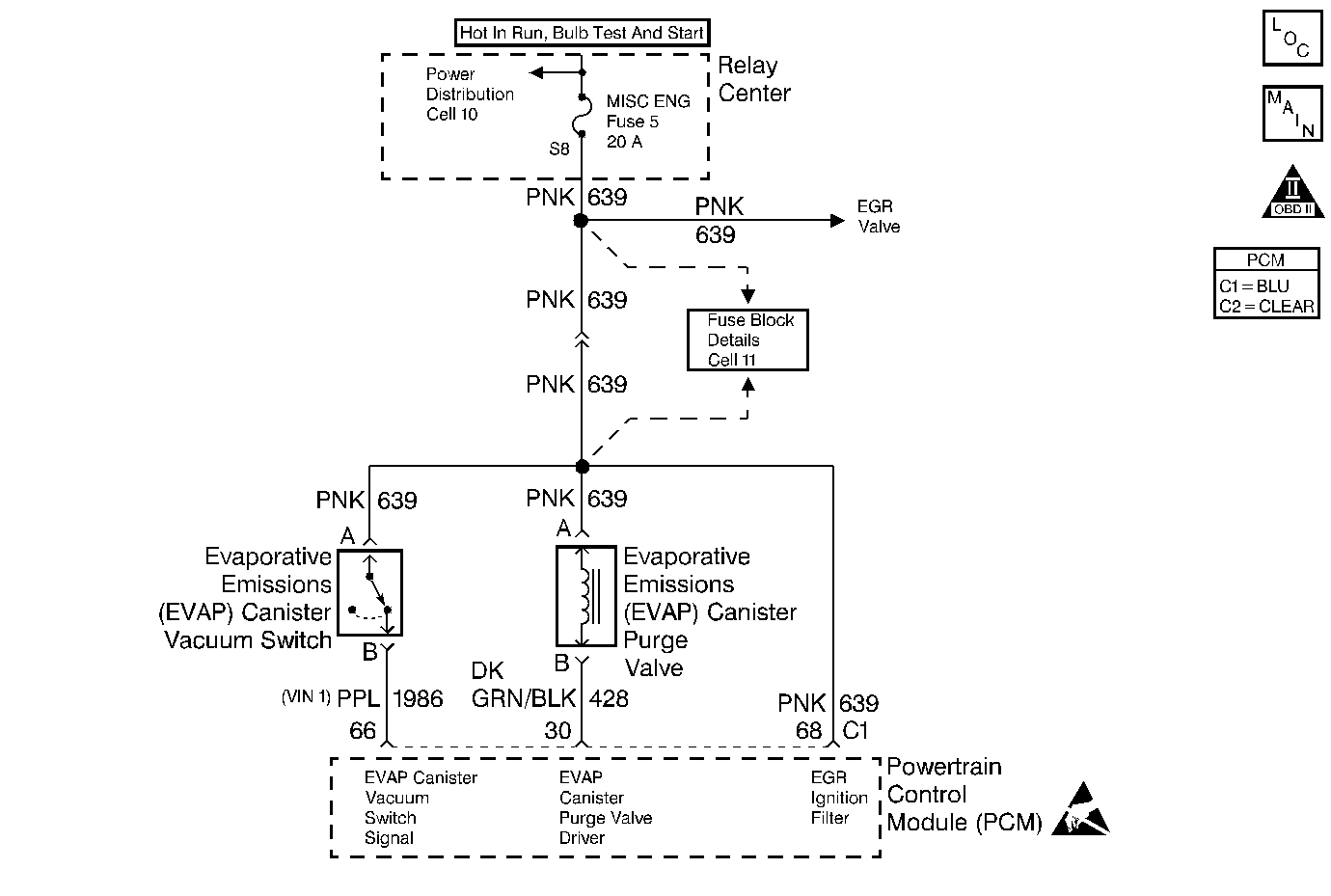
Circuit Description
The EVAP purge valve allows manifold vacuum to purge the canister. The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) supplies a ground to energize the EVAP purge valve (purge ON). The EVAP purge valve control circuit is Pulse Width Modulated (PWM) or turned ON and OFF several times a second. The duty cycle (pulse width) is determined by engine operating conditions including load, throttle position, coolant temperature and ambient temperature. The duty cycle is calculated by the PCM and the output is commanded when the appropriate conditions have been met.
The EVAP purge vacuum switch is a normally closed switch positioned in the purge line between the canister and the EVAP purge valve. The EVAP purge vacuum switch will open when vacuum increases to greater than 5 inches of water in the purge line. The PCM monitors the EVAP purge vacuum switch signal to determine of the evaporative emission control system is working properly. If the switch is closed (no purge flow) when the PCM is commanding the EVAP purge valve ON, DTC P0441 should be set. If the switch is open (purge flow detected) when the PCM is not commanding the EVAP purge valve ON, DTC P1441 should be set.
Refer to the DTC charts for further diagnostic procedures regarding the EVAP system.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
| • | Poor connection at PCM, the EVAP canister vent valve, the EVAP purge valve, or the fuel tank pressure sensor. |
| Inspect harness connectors for backed out terminals, improper mating, broken locks, improperly f:ormed or damaged terminals, and poor terminal to wire connection. |
| • | Damaged harness. |
| Inspect the wiring harness for damage. |
| • | If the harness appears to be OK, observe the Fuel Tank Pressure display on the scan tool while moving connectors and wiring harnesses related to the sensor. A change in the display will indicate the location of the malfunction. |
| • | Incorrect EVAP purge or vacuum source line routing. |
| Verify that the source vacuum and purge lines to the EVAP purge valve are not switched. |
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Was the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check performed? | -- | ||||||
2 |
Was a problem found? | -- | System OK | |||||
3 | Engine idling, observe EVAP Vacuum Switch while commanding the EVAP purge valve OFF with the scan tool. Does EVAP Vacuum Switch display No Purge with the EVAP purge valve commanded OFF? | -- | Go to DTC P1441 Evaporative Emission (EVAP) System Flow During Non-Purge | |||||
4 | Engine idling, observe EVAP Vacuum Switch while commanding the EVAP purge valve ON with the scan tool. Does EVAP Vacuum Switch display Purge with the EVAP purge valve commanded ON? | -- | System OK | Go to DTC P0441 Evaporative Emission (EVAP) System No Flow During Purge |
Evaporative Emission Control System Diagnosis VIN K
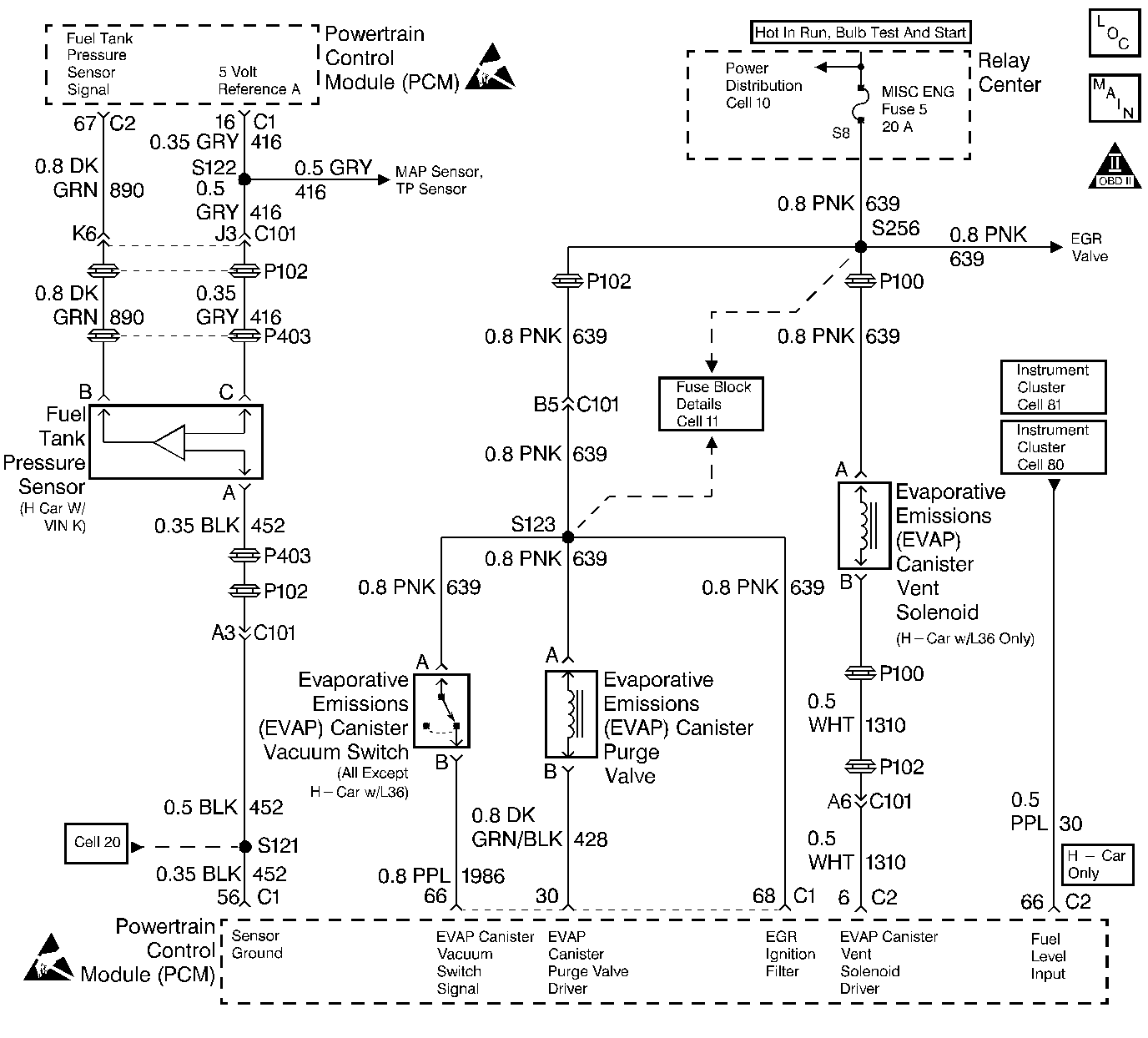
Circuit Description
The evaporative system includes the following components:
| • | The fuel tank. |
| • | The EVAP vent solenoid. |
| • | The fuel tank pressure sensor. |
| • | The fuel pipes and hoses. |
| • | The vapor lines. |
| • | The fuel cap. |
| • | The evaporative emission canister. |
| • | The purge lines. |
| • | The EVAP purge solenoid. |
The EVAP purge solenoid valve allows manifold vacuum to purge the canister. The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) supplies a ground to energize the solenoid valve (purge ON ). The EVAP purge solenoid control is Pulse Width Modulated (PWM) or turned ON and OFF several times a second. The duty cycle (pulse width) is determined by engine operating conditions including load, throttle position, coolant temperature and ambient temperature. The duty cycle is calculated by the PCM and the output is commanded when the appropriate conditions have been met.
The EVAP Vent solenoid is used to seal the EVAP system during the EVAP leak diagnostic tests. The fuel tank pressure sensor is used to monitor vacuum in the system during the diagnostic tests.
A stuck closed EVAP purge solenoid, stuck open EVAP vent solenoid, disconnected or damaged EVAP purge line or vent hose, leaking fuel cap, or fill neck should set a DTC P0440. A small leak in the EVAP system should set a DTC P0442. An EVAP vent solenoid stuck closed, a restricted vent hose, or a blocked EVAP canister should set a DTC P0446. A continuous purge condition with no purge commanded by the PCM (EVAP purge solenoid stuck open or leaking) should set a DTC P1441. Refer to the DTC tables for further diagnostic procedures regarding the EVAP system.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
| • | Poor connection at PCM. |
| Inspect harness connectors for backed out terminals, improper mating, broken locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and poor terminal to wire connection. |
| • | Damaged harness. |
| Inspect the wiring harness for damage. If the harness appears to be OK, observe the Fuel Tank Pressure display on the scan tool while moving connectors and wiring harnesses related to the sensor. A change in the display will indicate the location of the malfunction. |
| • | Incorrect EVAP purge or vacuum source line routing. |
| Verify that the source vacuum and purge lines to the EVAP purge valve are not switched. |
Important: Although these diagnostics are considered type A, they act like type B diagnostics under certain conditions. Whenever the EVAP diagnostics report that the system has passed, or if the battery has been disconnected, the diagnostic must fail during two consecutive cold start trips before setting a DTC. The initial failure is not reported to the diagnostic executive or displayed on a scan tool. A passing system always reports to the diagnostic executive immediately.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the Diagnostic Table.
-
The PCM will command the EVAP purge and EVAP canister vent valves closed with the scan tool Seal System EVAP output control function activated. Fuel tank pressure should not decrease under this condition.
-
The PCM commands the EVAP purge valve OFF (open) and the EVAP canister vent valve ON (closed) with the scan tool System Perf. EVAP output control function activated. Engine vacuum should cause fuel tank pressure to decrease when System Perf. is activated.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Was the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check performed? | -- | ||||||
2 |
Important: Visually/physically inspect for the following conditions:
Is Fuel Tank Pressure at the specified value? | 0 in. H2O | ||||||
3 |
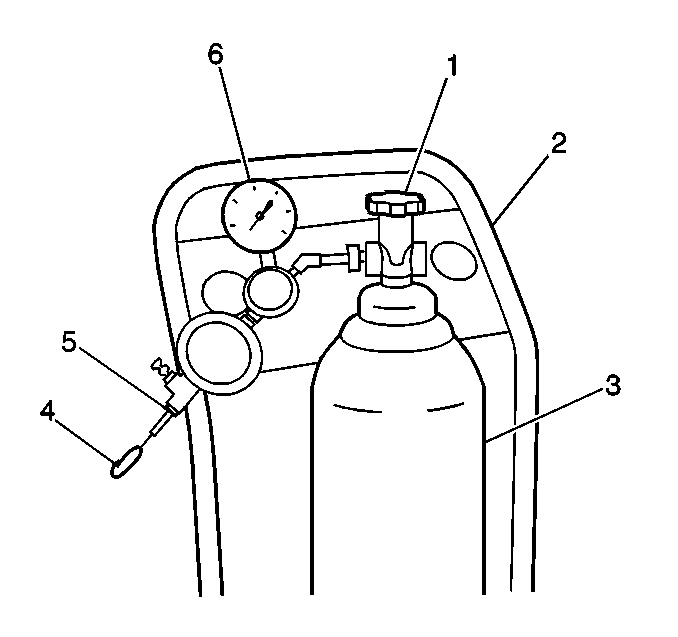
Important:: Before continuing with diagnosis, zero the EVAP Pressure and Vacuum
(inches of H2O) gauges on the
Is Fuel Tank Pressure at the specified value? | 5 in. H2O | ||||||
4 | Monitor the EVAP Pressure gauge on the EVAP pressure/purge diagnostic station while commanding the EVAP canister vent valve OFF (Open). Does EVAP Pressure decrease to the specified value within 5 seconds? | 0 in. H2O | Go to DTC P0446 Evaporative Emission (EVAP) Vent System Performance | |||||
Is vacuum increasing to a value greater than the specified value? | 0 in. H2O | Go to DTC P1441 Evaporative Emission (EVAP) System Flow During Non-Purge | ||||||
Did vacuum increase to a value greater than the specified value? | -5 in H2O | System OK |
Evaporative Emission Control System Diagnosis Fuel Tank Press Sensor Check

Circuit Description
The Fuel Tank Pressure sensor responds to changes in fuel tank pressure or vacuum. The fuel tank pressure sensor signal voltage to the PCM varies from a minimum of about 0.2 volts with pressure in the fuel tank to above 4 volts with a high vacuum situation in the fuel tank (EVAP canister vent valve stuck closed). The fuel tank pressure sensor is used to detect vacuum decay and excess vacuum during the enhanced EVAP diagnostic routine.
The Fuel Tank Pressure Sensor Diagnosis table is intended to isolate and diagnose electrical problems with the sensor wiring or the sensor.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
| • | Inspect the PCM and fuel tank pressure sensor harness connectors for backed out terminals, improper mating, broken locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and poor terminal to wire connection. |
| • | Inspect the wiring harness for damage. If the harness appears to be OK, observe the Fuel Tank Pressure display on the scan tool while moving connectors and wiring harnesses related to the sensor. A change in the display will indicate the location of the malfunction. |
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the Diagnostic Table.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Was the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic(OBD) System Check performed? | -- | ||
2 |
Is voltage near the specified value? | 5V | ||
3 | Check the 5 volt reference A circuit for a poor terminal connection at the PCM. Was a problem found? | -- | ||
4 | Check for an open in the 5 volt reference A circuit to the fuel tank pressure sensor harness connector. Was a problem found? | -- | ||
5 |
Is voltage between the specified values? | 1.3V - 1.7V | ||
6 | Check the fuel tank pressure sensor signal circuit for a poor terminal connection at the PCM. Was a problem found? | -- | ||
7 | Check the fuel tank pressure signal circuit between the fuel tank pressure sensor connector and the PCM for an open, short to ground, or short to voltage. Was a problem found? | -- | ||
8 | Check the sensor ground circuit for a poor terminal connection at the PCM. Was a problem found? | -- | ||
9 | Check for an open in the sensor ground circuit. Was a problem found? | -- | ||
10 | Check for a poor circuit terminal connection at the fuel tank pressure sensor connector. Was a problem found? | -- | ||
11 | Replace the malfunctioning harness connector terminals as necessary. Refer to Repair Procedures in Electrical Diagnosis. Is action complete? | -- | -- | |
12 | Locate and repair open/short circuit in wiring harness as necessary. Refer to Repair Procedures in Electrical Diagnosis. Is action complete? | -- | -- | |
13 | Replace the fuel tank pressure sensor. Refer to Fuel Tank Pressure Sensor Replacement . Is action complete? | -- | -- | |
Replace the PCM. Important:: The replacement PCM must be programmed. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement/Programming . Is action complete? | -- | -- | ||
15 |
Is Fuel Tank Pressure at the specified value? | 0 in. H2O | ||
16 |
Is Fuel Tank Pressure at the specified value? | 5 in. H2O | System OK |