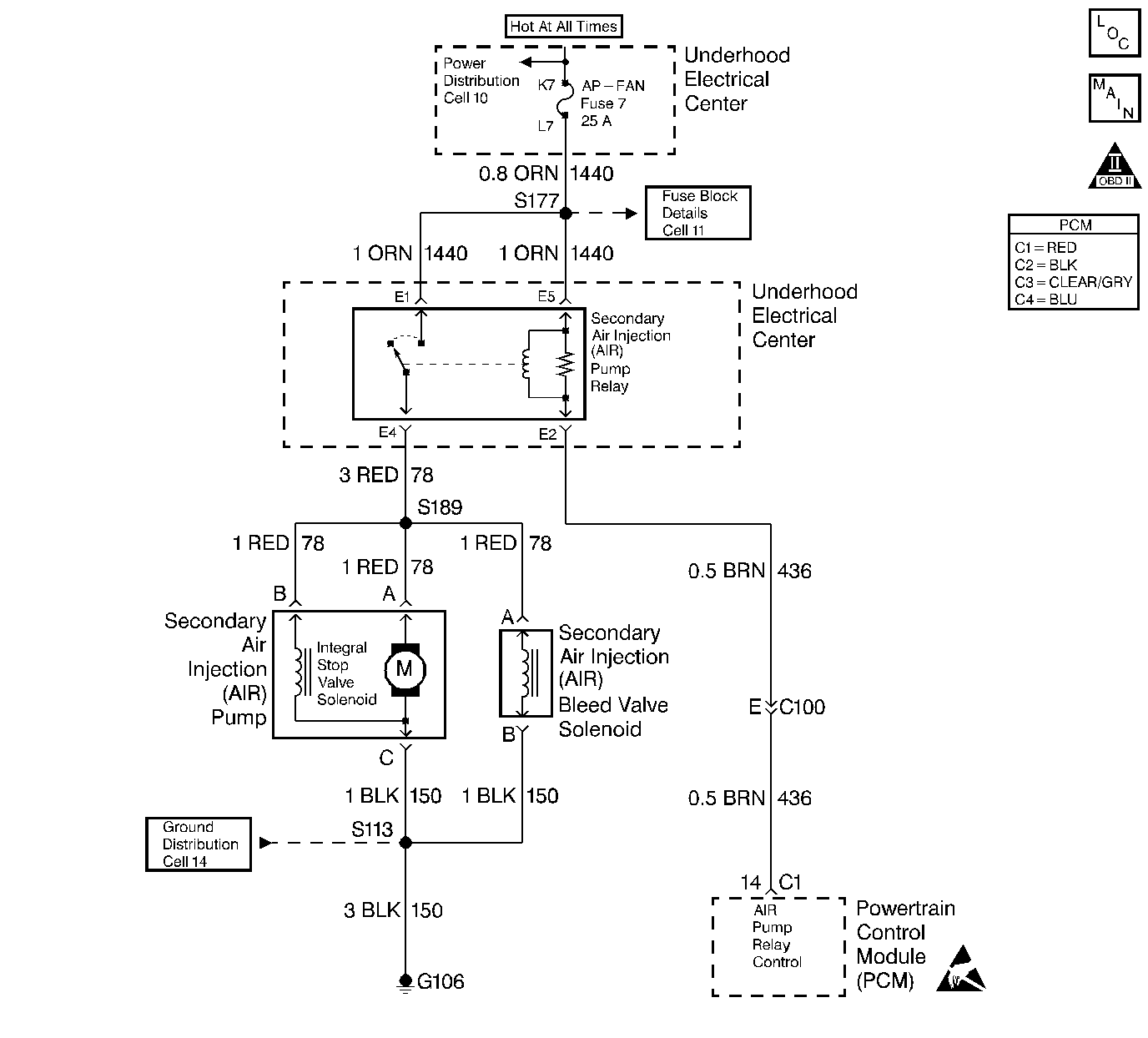
Circuit Description
An AIR pump is used on this vehicle to lower tail pipe emissions on start-up. The PCM supplies a ground to the AIR pump relay, which energizes the AIR pump.
The PCM will run two tests using the HO2S voltages to diagnose the AIR system. Both tests have two parts.
Test one consists of the following:
Part 1
When the AIR pump is enabled, the PCM monitors the HO2S voltage. If the HO2S voltages go below a threshold, the PCM interprets this as an indication that the AIR system is operational.
Part 2
When the AIR pump is disabled, the PCM monitors the HO2S voltages. The HO2S voltages should increase above a threshold and switch normally.
If the PCM did not sense more then a predetermined amount of HO2S rich switches, a malfunction will be reported. If both of these test indicate a pass, no further action is taken. If one of the above tests failed or is inconclusive, the diagnostic will proceed to test two.
Test two consist of the following:
Part 1
During this test the PCM will activate the AIR pump during closed loop operation. When the AIR is activated, the PCM will monitor the HO2S voltages and short term fuel trim values for both banks of the engine. If the AIR system is operating properly, the HO2S voltages should go low and the short term fuel trim should go high.
Part 2
The PCM checks that the HO2S voltages return to above a rich threshold when the air pump is disabled.
If the PCM determines that the HO2S voltages for both banks did not respond as expected during the tests, DTC P0410 will set. If only one sensor responded, the PCM will set either a DTC P1415 or P1416 to indicate on which bank the AIR system is inoperative.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | DTCs P0107, P0108, P0116, P0117, P0118, P0133, P0135, P0153, P0155, P0171, P0172, P0174, P0175, not set. |
| • | Engine operating about 2 seconds. |
Test 1
| • | TP angle not moving more than 1%. |
| • | Engine load less than 6.6%. |
| • | Engine air flow less than 26 grams per second. |
| • | Air fuel ratio greater than 13:1. |
| • | ECT less than 115°C (239°F). |
| • | HO2S bias voltage between 365 mV and 513 mV. |
| • | HO2S voltage does not go below 400 mV for 19 seconds (Engine coolant temperature less than 75°C (167°F) when the engine is started.) or HO2S voltage does not go below 417 mV for 7 seconds (Engine coolant temperature greater than 75°C (167°F) when the engine is started.) |
| • | HO2S voltage does not go above 722 mV for 19 seconds (Engine coolant temperature less than 75°C (167°F) when the engine is started.) or HO2S voltage does not go above 700 mV for 7 seconds (Engine coolant temperature greater than 75°C (167°F) when the engine is started.) |
Test 2
| • | Engine operating longer than 200 seconds. |
| • | Engine speed greater than 600 RPM. |
| • | Maximum air flow 17 gm/s. |
| • | Engine coolant temperature between 60°C (140°F) and 115°C (239°F.) |
| • | IAT greater than 10°C (50°C). |
| • | Ignition voltage greater than 11.0 volts. |
| • | Engine load less than 5.5%. |
| • | HO2S voltage does not go below 222 mV within 1.5 seconds. |
| • | Short term fuel trim does not go above a predetermined amount. |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The PCM will illuminate the Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) on the second consecutive drive trip that the diagnostic runs and fails. |
| • | The PCM will record operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The first time the diagnostic fails, this information will be stored in Failure Records. If the diagnostic reports a failure on the second consecutive drive trip, the operating conditions at the time of failure will be written to Freeze Frame and the Failure record will be updated. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The PCM will turn the MIL OFF after three consecutive drive trips that the diagnostic runs and does not fail. |
| • | A last test failed (Current DTC) will clear when the diagnostic runs and does not fail. |
| • | A History DTC will clear after forty consecutive warm-up cycles, if no failures are reported by this or any other emission related diagnostic. |
| • | PCM battery voltage is interrupted. |
| • | Using a Scan tool. |
Diagnostic Aids
| • | If the #7 underhood fuse is open, inspect AIR system for water intrusion. Inspect the AIR pump for water. Check the AIR check valves for proper operation. Refer to Secondary Air Injection Check Valve and Pipe Replacement for procedure. |
| • | The AIR vacuum bleed system contains a one way check valve. If the system checks out OK, make sure this valve is not stuck closed, restricted or blocked. The check valve is in-line in the hose that goes to the vacuum bleed valve. |
| • | Using Freeze Frame and/or Failure Records data may aid in locating an intermittent condition. If the DTC cannot be duplicated, the information included in the Freeze Frame and/or Failure Records data can be useful in determining how many miles since the DTC set. The Fail Counter and Pass Counter can also be used to determine how many ignition cycles the diagnostic reported a pass and/or a fail. Operate vehicle within the same freeze frame conditions (RPM, load, vehicle speed, temperature etc.) that were noted. This will isolate when the DTC failed. |
| • | For intermittents, refer to Symptoms . |
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
For any test that requires probing the PCM or a component harness connector, must use the Connector Test Adapter Kit J 35616-A. Using this kit will prevent damage to the harness connector terminals.
-
This checks whether B+ supply is available at the integral stop valve at the AIR pump.
-
This step begins a test of the vacuum bleed portion of the system. Normal engine operation can cause vacuum to build up within the AIR pipes and hoses. If there is vacuum present in the system when the PCM commands the AIR pump ON, the integral stop valve within the AIR pump may not be able to overcome this vacuum and no air will enter the system. The AIR vacuum bleed solenoid valve is designed to open whenever the AIR pump is commanded ON, to eliminate this problem.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Was the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check performed? | -- | ||
2 |
Does the AIR pump turn ON? | -- | ||
Does the test light illuminate? | -- | |||
4 |
Does the test light illuminate? | -- | ||
5 |
Does the test light illuminate? | -- | ||
Does the test light illuminate? | -- | |||
7 |
Is air present at the AIR pump outlet? | -- | ||
8 | Check for a restriction or blockage in AIR hoses/pipes between the AIR pump and the point where the system branches to both sides of the engine. Was a problem found and corrected? | -- | ||
Does the vacuum hold? | -- | |||
10 | Using a scan tool, enable the AIR pump. Does the vacuum bleed off? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | |
11 |
Does the test light illuminate? | -- | ||
12 |
Does the test light illuminate? | -- | ||
13 | Check the vacuum hose to the valve for cracks, splits or other damage. Was a problem found and corrected? | -- | ||
14 | Repair the B+ supply circuit to relay. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
15 | Check the fuse for the battery feed circuit to the relay. Is the fuse OK? | -- | ||
16 | Using a test light to ground, check for power at the fuse. Is there power to the fuse? | -- | ||
17 | Using a test light to B+, probe the relay battery feed circuit in the relay connector. Is the test light OFF? | -- | ||
18 |
Is the test light OFF? | -- | ||
19 |
Does the test light illuminate? | -- | ||
20 |
Did the fuse open? | -- | ||
21 |
Did the fuse open? | -- | Refer to Symptoms | |
22 | Repair the open circuit between the AIR pump and the AIR pump relay. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
23 | Repair the faulty ground connection or open AIR pump ground circuit. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
24 | Repair the open circuit from terminal B of AIR pump to splice. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
25 | Repair the open vacuum bleed solenoid valve power circuit between the solenoid electrical connector and the splice. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
26 | Repair the open vacuum bleed solenoid valve ground circuit. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
27 | Repair the open circuit between the fuse and the relay. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
28 | Repair the power feed circuit to the fuse. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
29 | Repair the short to ground between the fuse and the relay. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
30 | Repair the short to ground between the relay and the AIR pump/vacuum bleed solenoid valve. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
31 | Check the AIR pump electrical connections. Was a problem found and corrected? | -- | ||
32 | Replace the AIR pump relay. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
33 | Replace the vacuum bleed solenoid valve. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |
34 | Replace the AIR pump. Is the action complete? | |||
35 |
Does the scan tool indicate that this test ran and passed? | -- | ||
36 | Using the scan tool, select Capture Info, Review Info. Are any DTCs displayed that have not been diagnosed? | -- | Go to the applicable DTC table | System OK |
