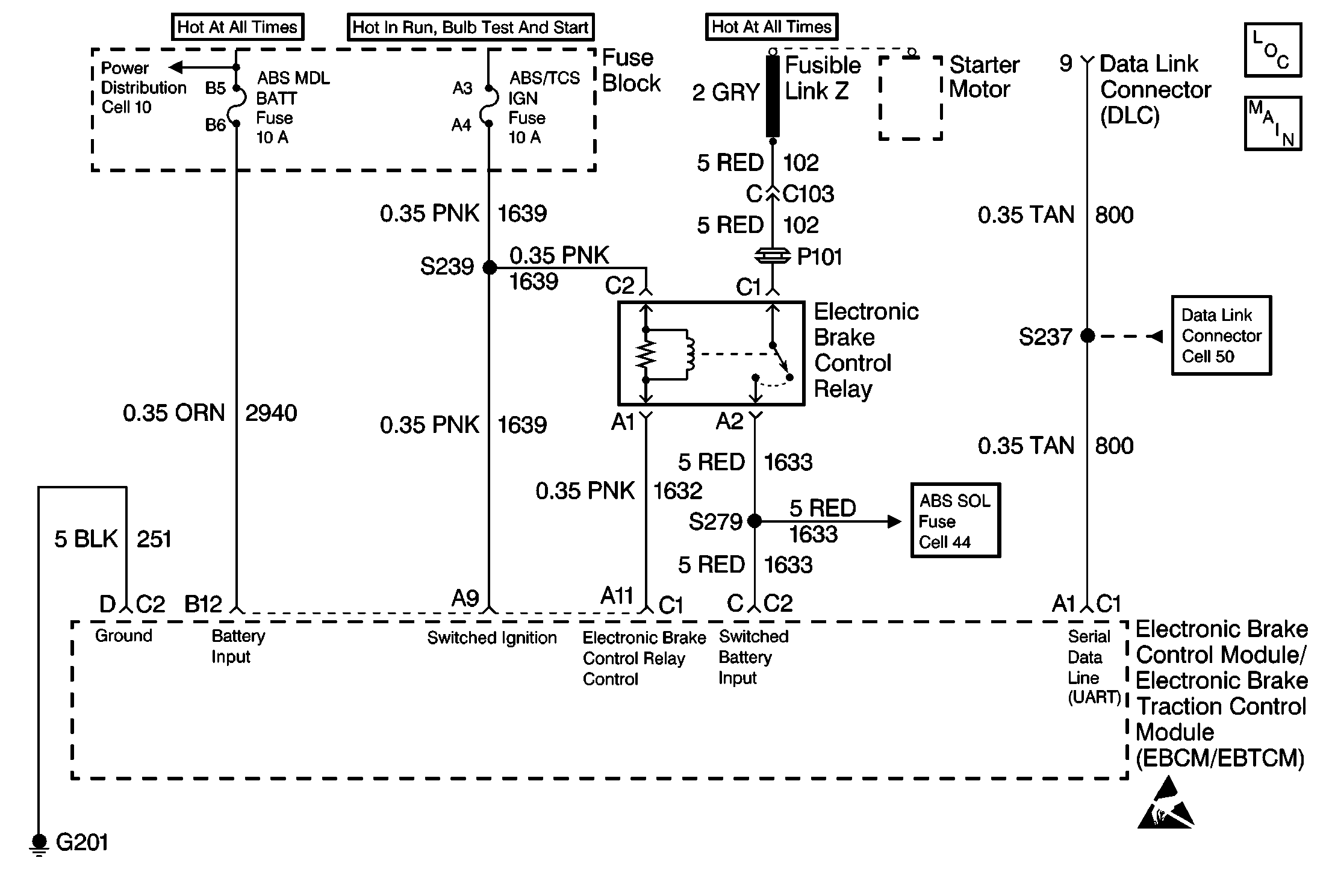
Circuit Description
DTC C1236 monitors the voltage level available to the EBCM/EBTCM controller. If the voltage drops below 11.4 volts, full performance of the ABS system may be inhibited. During ABS operation there are several current requirements that will cause battery voltage at the EBCM/EBTCM to drop. As a result voltage is monitored prior to an ABS event to indicate good charging system condition. Voltage is also monitored during an ABS event when voltage may drop significantly.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DTC C1236 can set only if the vehicle's speed is greater than 5 km/h (3 mph).
A malfunction exists if the switched battery voltage is less than 11.4 volts during a non-ABS event or less than 8.4 volts during an ABS event.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | A malfunction DTC stores. |
| • | The ABS/TCS disables. |
| • | The amber ABS/TCS warning indicators turn on. |
| • | The red BRAKE warning indicator turns on if the rear piston in the ABS brake motor pack is not in the home position. |
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
| • | The condition responsible for setting the DTC no longer exists and the Scan Tool Clear DTC function is used. |
| • | 100 drive cycles pass with no DTC detected. |
Diagnostic Aids
The following conditions may cause an intermittent malfunction:
| • | A poor connection |
| • | Rubbed-through wire insulation |
| • | A broken wire inside the insulation |
Use the enhanced diagnostic function of the Scan Tool in order to measure the frequency of the malfunction. Refer to the Scan Tool manual or Scan Tool Diagnostics located in this section for the procedure. While performing a Voltage Load test, CKT 1639 should be measured for high resistance or an open condition if it is noted that only the ignition voltage drops below acceptable voltage levels. Thoroughly inspect any circuitry that may be causing the intermittent complaint for the following conditions:
| • | Backed out terminals |
| • | Improper mating |
| • | Broken locks |
| • | Improperly formed or damaged terminals |
| • | Poor terminal-to-wiring connections |
| • | Physical damage to the wiring harness |
Important: Zero the J 39200 test leads before making any resistance measurements.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Was the Diagnostic System Check performed? | -- | Go to Step 2 | |||||||||||||||||||
2 |
Does DTC C1236 set as a current DTC? | -- | Go to Step 9 | Go to Step 3 | ||||||||||||||||||
3 |
Are the ignition voltage and the battery voltage equal to or greater than the specified value? | 10V | Go to Step 4 | Go to Charging System Check | ||||||||||||||||||
4 |
Is the resistance within the specified range? | 0-2ohms | Go to Step 5 | Go to Step 9 | ||||||||||||||||||
5 | Use the J 39200 and measure the voltage at the electronic brake control relay connector terminal C1. Is the voltage within the specified range? | 10.0-14.0 V | Go to Step 6 | Go to Step 10 | ||||||||||||||||||
6 | Remove and inspect the ABS/TCS IGN fuse (10A). Is the fuse good? | -- | Go to Step 11 | Go to Step 7 | ||||||||||||||||||
7 |
Are there signs of terminal damage, poor terminal contact, or terminal corrosion? | -- | Go to Step 12 | Go to Step 8 | ||||||||||||||||||
8 |
Does DTC C1236 set as a current DTC? | -- | Go to Step 13 | Go to Step 14 | ||||||||||||||||||
9 | Repair the open or high resistance in CKT 1633. Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||||||||||
10 | Repair the open or high resistance in CKT 102. Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||||||||||
11 | Repair the open or high resistance in CKT 1639. Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||||||||||
12 | Replace all of the terminals or the connectors that exhibit signs of poor terminal contact, corrosion, or damaged terminals. Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||||||||||
13 | Replace the EBCM/EBTCM. Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||||||||||
14 | The malfunction is intermittent or not present at this time. Is a concern still present? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids |
