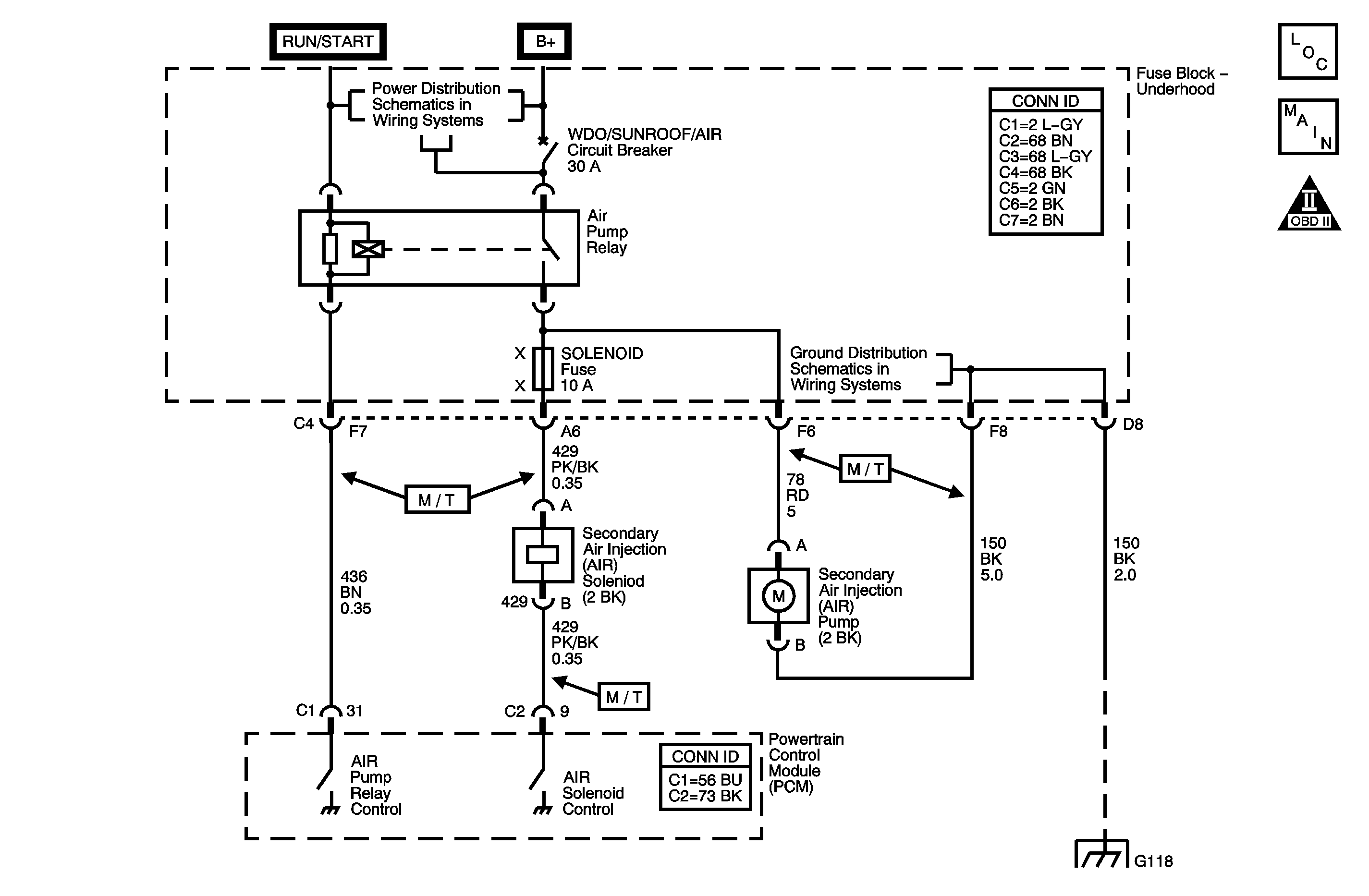
Circuit Description
The Secondary Air Injection (AIR) system reduces exhaust emissions after the engine starts. This occurs when the start-up coolant temperature is between 2°-40°C (36°-104°F) and the intake air temperature (IAT) is more than 1°C (33°F). The powertrain control module (PCM) activates the AIR system by suppling a ground to the AIR pump relay and the AIR solenoid simultaneously. The AIR solenoid applies engine vacuum to the AIR shut-off valve, opening the valve. The AIR pump forces pressurized fresh air into the pipes/hoses and past the exhaust check valve into the exhaust manifold, accelerating catalyst operation. When the AIR system is inactive, the AIR shut-off valve and the exhaust check valve prevent airflow in either direction. The PCM will run up to two diagnostic active tests during the same key cycle, using the HO2S 1 voltage parameter to verify system operation. When the PCM detects an insufficient heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) 1 response, DTC P0410 sets.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | DTCs P0105, P0107, P0108, P0112, P0113, P0116, P0117, P0118, P0122, P0123, P0130, P0131, P0132, P0133, P0134, P0135, P0171, P0172, P0201-P0204, P0300, P0301-P0304, P0336, P0340, P0341, P0506, P0507, P0601, P0604, P0606, P1133, P1134, P1171, P1621 are not set. |
| • | The AIR system is commanded ON for more than 2.6 seconds. |
| • | The IAT is more than 1°C (33°F). |
| • | The engine coolant temperature (ECT) is between 5°-115°C (41°-239°F). |
| • | The battery voltage is more than 11 volts. |
| • | The engine run time is more than 10 minutes. |
| • | The fuel trim is in cells 2,3 or 17. |
| • | The throttle position (TP) sensor changes less than 5 percent. |
| • | The manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor is less than 30 kPa. |
| • | The engine speed is more than 1,000 RPM. |
| • | The engine is in Closed Loop. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The PCM does not detect a decrease in the HO2S 1 voltage parameter to less than 75 mV for 1 second during a 2.6 second active test for two consecutive active tests.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The control module illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) on the second consecutive ignition cycle that the diagnostic runs and fails. |
| • | The control module records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The first time the diagnostic fails, the control module stores this information in the Failure Records. If the diagnostic reports a failure on the second consecutive ignition cycle, the control module records the operating conditions at the time of the failure. The control module writes the operating conditions to the Freeze Frame and updates the Failure Records. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The control module turns OFF the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) after 3 consecutive ignition cycles that the diagnostic runs and does not fail. |
| • | A current DTC, Last Test Failed, clears when the diagnostic runs and passes. |
| • | A history DTC clears after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles, if no failures are reported by this or any other emission related diagnostic. |
| • | Clear the MIL and the DTC with a scan tool. |
Diagnostic Aids
| • | An AIR solenoid or AIR shut-off valve that is sticking open may cause an audible exhaust noise to be heard though the AIR pump inlet hose. This condition may not set DTC P0410. This condition may also cause a fuel trim code to set. Fuel trim values may indicate a higher than normal percentage at an idle. |
| • | Verify proper vacuum hose routing at the AIR solenoid. Reversed connections may cause the AIR shut-off valve to remain open for an extended amount of time after normal activation. |
| • | Low system airflow may cause this DTC to set. |
| • | Excessive exhaust system back pressure may cause this DTC to set. |
| • | An intermittent may be caused by any of the following conditions: |
| - | Pinched, restricted, split, heat damaged or deteriorated pipes/hoses or vacuum lines |
| - | Restrictions in the AIR pump inlet hose |
| - | Pitted or burnt contacts, internal to the AIR pump relay--Tap on the AIR pump relay to attempt duplicating an intermittent condition. |
| • | Heat damage to the AIR crossover hose may indicate an exhaust check valve failure. |
| • | If the vacuum check valve does not hold vacuum, DTC P0410 may set. This condition may be intermittent due to a low vacuum condition or operating the vehicle at high altitudes. |
| • | Water or debris ingested into the AIR pump may cause this DTC to set. If water is found in the AIR pump, the exhaust check valve may be leaking. Inspect for an exhaust odor in the water sample. If no exhaust odor is present, ensure that the AIR inlet hose is securely fastened to the air cleaner assemble. |
| • | Observe the Freeze Frame/Failure Records to see what conditions set DTC P0410. |
Thoroughly inspect any circuits, hoses/pipes and vacuum lines that may be causing the intermittent condition. Refer to Intermittent Conditions .
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
-
This step determines if excessive resistance in the AIR supply voltage circuit is the cause for an inoperative AIR pump. Two ohms of resistance on this circuit can prevent the AIR pump from running.
-
This step determines if excessive resistance in the AIR ground circuit or connection is the cause for an inoperative AIR pump. Two ohms of resistance on this circuit can prevent the AIR pump from running.
-
This step determines if the AIR system is operating properly.
-
This step determines if the AIR solenoid is stuck open.
Step | Action | Values | Yes | No | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Schematic Reference: Engine Controls Schematics | ||||||||||||||
1 | Did you perform the Diagnostic System Check-Engine Controls? | -- | Go to Step 2 | |||||||||||
2 | Turn ON the ignition, with the engine OFF. Does the secondary air injection (AIR) pump run continuously? | -- | Go to Step 3 | Go to Step 4 | ||||||||||
3 | Remove the AIR pump relay. Refer to Relay Replacement in Wiring Systems. Does the AIR pump run continuously? | -- | Go to Step 53 | Go to Step 6 | ||||||||||
4 | Command the AIR pump relay ON and OFF with a scan tool. Does the AIR pump turn ON and OFF when commanded with a scan tool? | -- | Go to Step 19 | Go to Step 5 | ||||||||||
5 | Does the WDO/SUNROOF/AIR circuit breaker cycle when the AIR pump relay is commanded ON with a scan tool? | -- | Go to Step 38 | Go to Step 7 | ||||||||||
6 |
Does the test lamp illuminate? | -- | Go to Step 41 | Go to Step 62 | ||||||||||
7 |
Does the test lamp illuminate? | -- | Go to Step 8 | Go to Step 34 | ||||||||||
8 |
Does the test lamp illuminate? | -- | Go to Step 9 | Go to Step 15 | ||||||||||
9 |
Does the test lamp turn ON and OFF when commanded with a scan tool? | -- | Go to Step 10 | Go to Step 37 | ||||||||||
10 | Measure the resistance of the AIR pump relay control circuit with a DMM. Refer to Circuit Testing in Wiring Systems. Is the resistance less than the specified amount? | 10 ohms | Go to Step 11 | Go to Step 55 | ||||||||||
11 |
Does the AIR pump turn ON? | -- | Go to Step 65 | Go to Step 12 | ||||||||||
12 | Probe the AIR solenoid control circuit with a test lamp connected to a good ground. Refer to Probing Electrical Connectors in Wiring Systems. Does the test lamp illuminate? | -- | Go to Step 56 | Go to Step 13 | ||||||||||
13 |
Does the AIR pump turn ON? | -- | Go to Step 44 | Go to Step 14 | ||||||||||
14 |
Does the test lamp illuminate? | -- | Go to Step 16 | Go to Step 52 | ||||||||||
15 | Inspect the ignition EIS fuse in the underhood fuse block. Is the ignition EIS fuse open? | -- | Go to Step 40 | Go to Step 43 | ||||||||||
16 | Probe the AIR pump ground circuit at the air pump connector with a test lamp connected to battery voltage. Refer to Troubleshooting with a Test Lamp in Wiring Systems. Does the test lamp illuminate? | -- | Go to Step 17 | Go to Step 51 | ||||||||||
Is the voltage drop more than the specified value? | 0.9 V | Go to Step 52 | Go to Step 18 | |||||||||||
Measure the voltage from the AIR pump ground circuit of the AIR pump connector to a good ground with a DMM. Refer to Measuring Voltage Drop in Wiring Systems. Is the voltage more than the specified value? | 0.9 V | Go to Step 51 | Go to Step 46 | |||||||||||
Does the HO2S 1 voltage parameter drop below the specified value within 10 seconds? | 75 mV | Go to Diagnostic Aids | Go to Step 20 | |||||||||||
20 |
Does the AIR shut-off valve hold vacuum for the specified amount of time? | 30 seconds | Go to Step 21 | Go to Step 63 | ||||||||||
Is the vacuum displayed on gage more than specified value? | 0 mm/0 in Hg | Go to Step 65 | Go to Step 22 | |||||||||||
22 | Command the AIR pump relay ON and OFF with the scan tool. Does the vacuum displayed on the gage increase to the specified value when the scan tool is commanded ON, then decrease to zero mm/Hg when commanded OFF? | 254 mm/10 in Hg | Go to Step 31 | Go to Step 23 | ||||||||||
23 |
Does the vacuum on the gage increase to the specified value? | 254 mm/10 in Hg | Go to Step 61 | Go to Step 24 | ||||||||||
24 |
Does the vacuum on the gage increase to the specified value? | 254 mm/10 in Hg | Go to Step 25 | Go to Step 42 | ||||||||||
25 |
Does the test lamp turn ON and OFF with each command of the scan tool? | -- | Go to Step 26 | Go to Step 29 | ||||||||||
26 | Measure the resistance of the AIR solenoid control circuit with a DMM. Refer to Circuit Testing in Wiring Systems. Is the resistance less than the specified value? | 10 ohms | Go to Step 27 | Go to Step 54 | ||||||||||
27 |
Does the test lamp turn ON and OFF with each command of the scan tool? | -- | Go to Step 28 | Go to Step 30 | ||||||||||
28 | Measure the resistance of the AIR solenoid supply voltage circuit with a DMM. Refer to Circuit Testing in Wiring Systems. Is the resistance less than the specified value? | 10 ohms | Go to Step 45 | Go to Step 54 | ||||||||||
29 | Does the test lamp remain illuminated? | -- | Go to Step 35 | Go to Step 36 | ||||||||||
30 | Inspect the AIR solenoid fuse. Is the fuse open? | -- | Go to Step 39 | Go to Step 54 | ||||||||||
31 |
Is a forceful airflow present at the AIR crossover hose? | -- | Go to Step 57 | Go to Step 32 | ||||||||||
32 |
Is a forceful airflow present at the AIR pump outlet? | -- | Go to Step 60 | Go to Step 33 | ||||||||||
33 | Inspect for a restriction at the AIR pump inlet hose. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 68 | Go to Step 64 | ||||||||||
34 |
Is the circuit breaker good? | -- | Go to Step 58 | Go to Step 59 | ||||||||||
35 | Test the AIR solenoid control circuit for a short to ground. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 68 | Go to Step 47 | ||||||||||
36 | Test the AIR solenoid control circuit for an open or short to voltage. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 68 | Go to Step 47 | ||||||||||
37 |
Important: A short to voltage on this circuit will cause the AIR pump to run constantly with the key in the OFF position. Retest the AIR pump operation after repairs. Test the AIR pump relay control circuit for an open or short to voltage. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 67 | Go to Step 47 | ||||||||||
38 |
Does the WDO/SUNROOF/AIR circuit breaker continue to cycle? | -- | Go to Step 49 | Go to Step 64 | ||||||||||
39 |
Replace the AIR solenoid fuse as necessary. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 68 | Go to Step 48 | ||||||||||
40 |
Important: The ignition 1 voltage circuit is spliced to other components of the vehicle.
Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 68 | Go to Step 58 | ||||||||||
41 | Test the AIR pump relay control circuit for a short to ground. Refer to Wiring Repairs and Circuit Testing in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 67 | Go to Step 47 | ||||||||||
42 |
Important: Inspect the vacuum check valve for proper installation. The tapered side of the check valve goes towards the vacuum source.
Does the vacuum increase to greater than the specified amount? | 254 mm/10 Hg | Go to Step 61 | Go to Step 50 | ||||||||||
43 |
Important: The ignition 1 voltage circuit is spliced to other components. Test the ignition 1 voltage circuit for an open or high resistance. Refer to Circuit Testing and Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 68 | Go to Step 58 | ||||||||||
44 | Test for shorted terminals and for poor connections at the AIR pump relay. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections and Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 68 | Go to Step 62 | ||||||||||
45 | Test for shorted terminals and for poor connections at the AIR solenoid. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections and Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 68 | Go to Step 65 | ||||||||||
46 | Test for shorted terminals and for poor connections at the AIR pump. Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections and Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 68 | Go to Step 64 | ||||||||||
47 | Test for shorted terminals and for poor connections at the powertrain control module (PCM). Refer to Testing for Intermittent Conditions and Poor Connections and Connector Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 68 | Go to Step 66 | ||||||||||
48 | Test the AIR solenoid supply voltage circuit for a short to ground. Refer to Wiring Repairs and Circuit Testing in Wiring Systems. Replace the AIR solenoid fuse as necessary. Did you find and correct the condition? | -- | Go to Step 68 | Go to Intermittent Conditions | ||||||||||
49 | Repair the short to ground in the AIR pump supply voltage circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs and Circuit Testing in Wiring Systems. Did you complete the repair? | -- | Go to Step 68 | -- | ||||||||||
50 | Repair the restriction in the intake port. Did you complete the repair? | -- | Go to Step 68 | -- | ||||||||||
51 | Repair the open or high resistance in the AIR pump ground circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you complete the repair? | -- | Go to Step 68 | -- | ||||||||||
52 | Repair the open or high resistance in the AIR pump supply voltage circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs and Circuit Testing in Wiring Systems. Did you complete the repair? | -- | Go to Step 68 | -- | ||||||||||
53 | Repair the short to voltage in the AIR pump supply voltage circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs and Circuit Testing in Wiring Systems. Did you complete the repair? | -- | Go to Step 67 | -- | ||||||||||
54 | Repair the open or high resistance in the AIR solenoid circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs and Circuit Testing in Wiring Systems. Did you complete the repair? | -- | Go to Step 68 | -- | ||||||||||
55 | Repair the high resistance in the AIR pump relay control circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs and Circuit Testing in Wiring Systems. Did you complete the repair? | -- | Go to Step 68 | -- | ||||||||||
56 | Repair the short to voltage in the AIR solenoid control circuit. Refer to Wiring Repairs and Circuit Testing in Wiring Systems. Did you complete the repair? | -- | Go to Step 67 | -- | ||||||||||
57 |
Caution: Allow the check valve to cool off before proceeding with the next check in order to avoid being burned. Tap on the check valve in order to remove any debris that may be inside the valve. Repair the restriction or leak in one of the following components:
Did you complete the repair? | -- | Go to Step 68 | -- | ||||||||||
58 |
Important: Test all spliced circuits to the battery and the ignition 1 voltage circuits for a short to ground before replacing the underhood fuse block. Replace the underhood fuse block. Refer to Wiring Repairs in Wiring Systems. Did you complete the replacement? | -- | Go to Step 67 | -- | ||||||||||
59 | Replace the WDO/SUNROOF/AIR circuit breaker. Did you complete the replacement? | -- | Go to Step 67 | -- | ||||||||||
60 | Replace the AIR crossover hose. Did you complete the replacement? | -- | Go to Step 68 | -- | ||||||||||
61 | Replace the vacuum check valve or vacuum harness assembly. Refer to Air Vacuum Harness Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | Go to Step 68 | -- | ||||||||||
62 | Replace the AIR pump relay. Refer to Relay Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | Go to Step 67 | -- | ||||||||||
63 | Replace the AIR shut-off valve. Refer to Secondary Air Injection Shut Off Valve Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | Go to Step 68 | -- | ||||||||||
64 | Replace the AIR pump. Refer to Secondary Air Injection Pump Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | Go to Step 67 | -- | ||||||||||
65 | Replace the AIR solenoid. Refer to Secondary Air Injection Vacuum Control Solenoid Valve Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | Go to Step 68 | -- | ||||||||||
66 | Replace the PCM. Refer to Powertrain Control Module Replacement . Did you complete the replacement? | -- | Go to Step 67 | -- | ||||||||||
67 |
Does the AIR pump turn ON and OFF when commanded with a scan tool? | -- | Go to Step 68 | Go to Step 2 | ||||||||||
68 |
Did the DTC fail this ignition? | -- | Go to Step 2 | Go to Step 69 | ||||||||||
69 | Observe the Capture Info with a scan tool. Are there any DTCs that have not been diagnosed? | -- | System OK | |||||||||||
