Refer to
EVAP Control System Overview
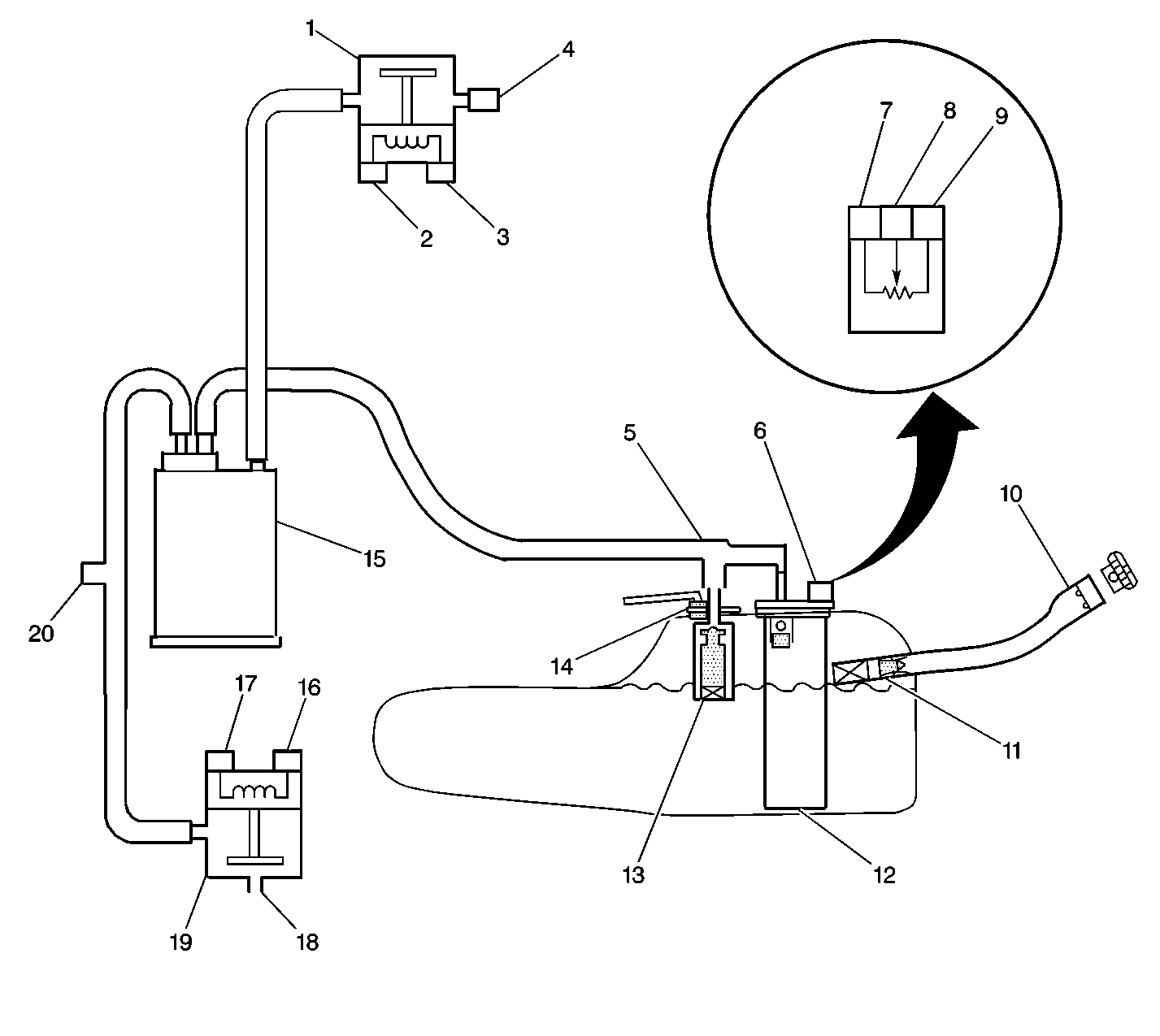
Circuit Description
The evaporative emissions (EVAP) system includes the following components:
| • | The fuel tank. |
| • | The EVAP vent valve/solenoid. |
| • | The fuel tank pressure sensor. |
| • | The fuel pipes and hoses. |
| • | The fuel fill cap. |
| • | The EVAP vapor lines. |
| • | The EVAP purge lines. |
| • | The EVAP canister. |
| • | The EVAP canister purge valve/solenoid. |
The EVAP Small Leak Test is based up on applying vacuum to the EVAP system and monitoring the vacuum decay. The powertrain control module (PCM) monitors the vacuum level via the fuel tank pressure sensor input. At an appropriate time, the EVAP purge solenoid and the EVAP vent solenoid are turned on allowing engine vacuum to draw a small vacuum on the entire EVAP system. After the desired vacuum level is achieved, the EVAP purge solenoid is turned off, sealing the system. A leak is detected by monitoring for a decrease in vacuum level over a given time period, all other variables remaining constant. A small leak in the system causes DTC P0442 to be set.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | None of the following DTCs are set: |
| - | Throttle position (TP) sensor DTCs |
| - | Intake air temperature (IAT) sensor DTCs |
| - | Manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor DTCs |
| - | ODM DTCs |
| • | The DTC P0440 diagnostic test has passed. |
| • | The startup engine coolant temperature (ECT) is between 4° C and 30° C (40° F 86°F). |
| • | The startup ECT is not over 8° C (14° F) more than the IAT. |
| • | The startup IAT is between 2° C and 30° C (40° F and 86° F). |
| • | The startup IAT is not over 2° C (4°F) more than the ECT. |
| • | The fuel tank level is between 15% and 85%. |
| • | BARO is greater than 75 kPa. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
A vacuum decay condition indicating a small leak is detected during the diagnostic test.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
Important: Although these diagnostics are considered type A, they act like type B diagnostics under certain conditions. Whenever the EVAP diagnostics report that a system has passed, or if the battery is disconnected, the diagnostic must fail during 2 consecutive cold start trips before setting a DTC. The initial failure is not reported to the diagnostic executive or displayed on a scan tool. A passing system always reports to the diagnostic executive immediately.
| • | The PCM illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) during the first trip in which the diagnostic test has run and failed. |
| • | The PCM stores the conditions which were present when the DTC set as Freeze Frame and Fail Records data. |
Important: Although these diagnostics are considered type A, they act like type B diagnostics under certain conditions. Whenever the EVAP diagnostics report that the system has passed, or if the battery is disconnected, the diagnostic must fail during two consecutive cold start trips before setting a DTC. The initial failure is not reported to the diagnostic executive or displayed on a scan tool. A passing system always reports to the diagnostic executive immediately.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The PCM turns the MIL off during the third consecutive trip in which the diagnostic run and passed. |
| • | The history DTC clears after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles have occurred without a malfunction. |
| • | The DTC may be cleared by using the scan tool Clear Info function or by disconnecting the PCM battery feed. |
Diagnostic Aids
Inspect for the following conditions:
| • | A cracked or punctured EVAP canister. |
| • | A damaged source vacuum line, EVAP purge line, EVAP vent hose, or fuel tank vapor line. |
| • | A faulty connection at the PCM. Inspect the harness connectors for backed out terminals, improper mating, broken locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and faulty terminal to wire connections. |
| • | A damaged harness. Inspect the wiring harness to the EVAP vent solenoid EVAP purge solenoid and the fuel tank pressure sensor for an intermittent open or a short circuit. |
Reviewing the Fail Records vehicle mileage since the diagnostic test last failed may help determine how often the condition that caused the DTC to be set occurs. This may assist in diagnosing the condition.
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the Diagnostic Table:
-
The powertrain OBD System Check promps you to complete some of the basic checks and store the freeze frame and failure records data on the Scan Tool if applicable.
-
If a vent valve or EVAP purge valve electrical malfunction is present, the purge system will not operate correctly. Repairing the electrical malfunction that caused the additional DTC to set will very likely correct the condition that set this DTC.
-
Checks for a fuel tank pressure sensor stuck high condition. The fuel tank pressure must be relieved by removing the canister line from the fuel tank or EVAP canister. The fuel fill cap will not relieve the tank due to a check valve in the filler neck. the check valve seals when pressure is applied to prevent vapors from escaping through the filler neck. The Scan Tool should read within +/- 1.0 in. H2O of the specified value.
-
Verifies that the fuel tank pressure sensor accurately reacts to EVAP system pressure changes. The EVAP station is pressurizing a sensor that normally reads vacuum. The tech II reads high pressure at 0 volts and high vacuum at 5 volts. The Tech II can only read a max pressure of 6.0 inches of H2O (0 Volts). However the EVAP Service station can pressurize the system to much higher pressures. The Scan Tool value should be within +/- 0.5 of the specified value.
-
Checks for a small leak in the EVAP system.
-
Checks for a leak in the Canister, vent line, or a leaking EVAP Vent Valve.
-
Checks for a leaking or stuck open EVAP canister purge valve/solenoid. The scan tool should read within +/- 1.0 in. HG of the specified value.
-
The EVAP station is pressurizing a sensor that normally reads vacuum. The Tech II reads high pressure at 0 volts and high vacuum at 5 volts. The Tech II can only read a max pressure of 6.0 inches of H2O (0 Volts). However the EVAP Service station can pressurize the system to much higher pressures. The Scan Tool value should be within +/- 0.5 of the specified value.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Was the Powertrain OBD System Check performed? | -- | |||||||
|
Important: : Visually/physically inspect for the following conditions:
Is DTC P1665 Evaporative Emission (EVAP) Vent Solenoid Control Circuit or DTC P1676 Evaporative Emission (EVAP) Purge Solenoid Control Circuit also set? | -- | Go to the other DTC first | ||||||
Is the Fuel Tank Pressure near the specified value? | 0 in. H2O | |||||||
|
Important: : Before continuing with diagnosis, zero the EVAP Pressure and Vacuum (inches of H2O) gauges on the J 41413 EVAP Pressure/Purge Diagnostic Station. Important:: Do not exceed the pressure in the specified value .
Is the Fuel Tank Pressure near the specified value? | 5 in. H2O | |||||||
|
Important: Do not exceed the pressure in the specified (higher) value
Does the EVAP Pressure decrease to less than the second specified (lower) value within 2 minutes with the rotary switch in the "Off/Hold position? | 15 in. H2O 10 in. H2O | Go to Diagnostic Aids | ||||||
Can vacuum be maintained at the specified value? | 5 in. Hg | |||||||
7 |
Was a problem found? | -- | Go to DTC P0452 Fuel Tank Pressure Sensor Circuit Low Voltage | |||||
8 |
Was a problem found? | -- | ||||||
9 |
Was a problem found? | -- | ||||||
Is vacuum level near the specified value? | 0 in. Hg | |||||||
11 |
Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||
12 |
Important: Do not exceed the 15 in. H2O pressure in the specified value.
Is the action complete? | 15 in. H2O | -- | |||||
13 |
Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||
14 |
Is action complete? | 0 in. H2O | -- | |||||
15 |
Is the Fuel Tank Pressure near the specified value? | 0 in. H2O | Go to DTC P0453 Fuel Tank Pressure Sensor Circuit High Voltage | |||||
|
Important:: Do not exceed the pressure in the specified value .
Does the EVAP pressure decrease to less than the second specified (lower) value within 2 minutes with the rotary switch in the 'Off/Hold' position? | 15 in. H2O 10 in. H2O | System OK |
