Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
The temperature stick is a pencil-like device that has a wax material containing certain chemicals which melt at a given temperature. Use the temperature sticks to determine a thermostat's operating temperature by rubbing 87°C (188°F) and 97°C (206°F) sticks on the thermostat housing. The marks made by the sticks should melt when coolant temperatures reach 87°C (188°F) and 97°C (206°F), respectively. These temperatures are the normal operating range of the thermostat. If the coolant flows as indicated in the table, the thermostat may be worn. | ||||
1 |
Is there coolant flow before the mark melts? | -- | ||
2 | The problem is caused from something other than the thermostat. Does the engine still overheat? | -- | Go to Engine Overheating . | System OK |
3 |
Does the engine still overheat? | -- | -- | System OK |
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
The temperature stick is a pencil-like device that has a wax material containing certain chemicals which melt at a given temperature. Use the temperature sticks to determine a thermostat's operating temperature by rubbing 87°C (188°F) and 97°C (206°F) sticks on the thermostat housing. The marks made by the sticks should melt when coolant temperatures reach 87°C (188°F) and 97°C (206°F), respectively. These temperatures are the normal operating range of the thermostat. If the coolant flows as indicated on the table, the thermostat may be worn. | ||||
1 |
Is there coolant flow before the mark melts? | -- | ||
2 | The problem is caused from something other than the thermostat. Does the engine warm up properly? | -- | System OK | -- |
3 |
Does the engine still fail to reach normal operating temperature? | -- | -- | System OK |
Thermostat Inspection and Testing
Do an operational test of the thermostat using the following procedure:
- Drain the coolant to a level just below the thermostat. Refer to Cooling System Draining and Filling .
- Remove the coolant outlet. Refer to Engine Coolant Thermostat Replacement .
- Remove the thermostat.
- Unless the thermostat is obviously faulty, test the thermostat before replacing the thermostat using the following procedure:
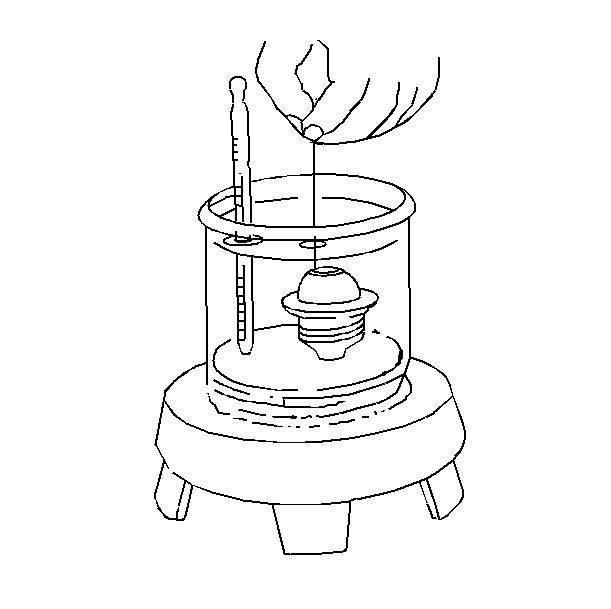
| 4.1. | Place the thermostat and a thermometer in a container with a 50/50 solution of water and ethylene glycol antifreeze. |
| Important: While heating, do not rest the thermostat or the thermometer on the bottom of the container. This causes the thermostat and the thermometer to be at a higher temperature than the solution. |
| 4.2. | Place the container over a heater. |
| 4.3. | Agitate the solution in order to maintain a uniform temperature of the solution, the thermostat, and the thermometer. |
The thermostat valve should start to open at the rated temperature. The thermostat should be fully open after the temperature has increased 15°C (27°F).
A used thermostat can be about 6°C (10°F) above or below these settings without adversely affecting the thermostat and you do not need to replace the thermostat. If the thermostat does not operate at the temperatures specified, replace the thermostat. You cannot adjust the thermostat. Refer to Engine Coolant Thermostat Replacement .
