| Table 1: | WSS Temperature vs. Sensor Resistance (RWD only) |
| Table 2: | WSS Temperature vs. Sensor Resistance (S4WD only) |
| Table 3: | WSS Temperature vs. Sensor Resistance (C3500HD only) |
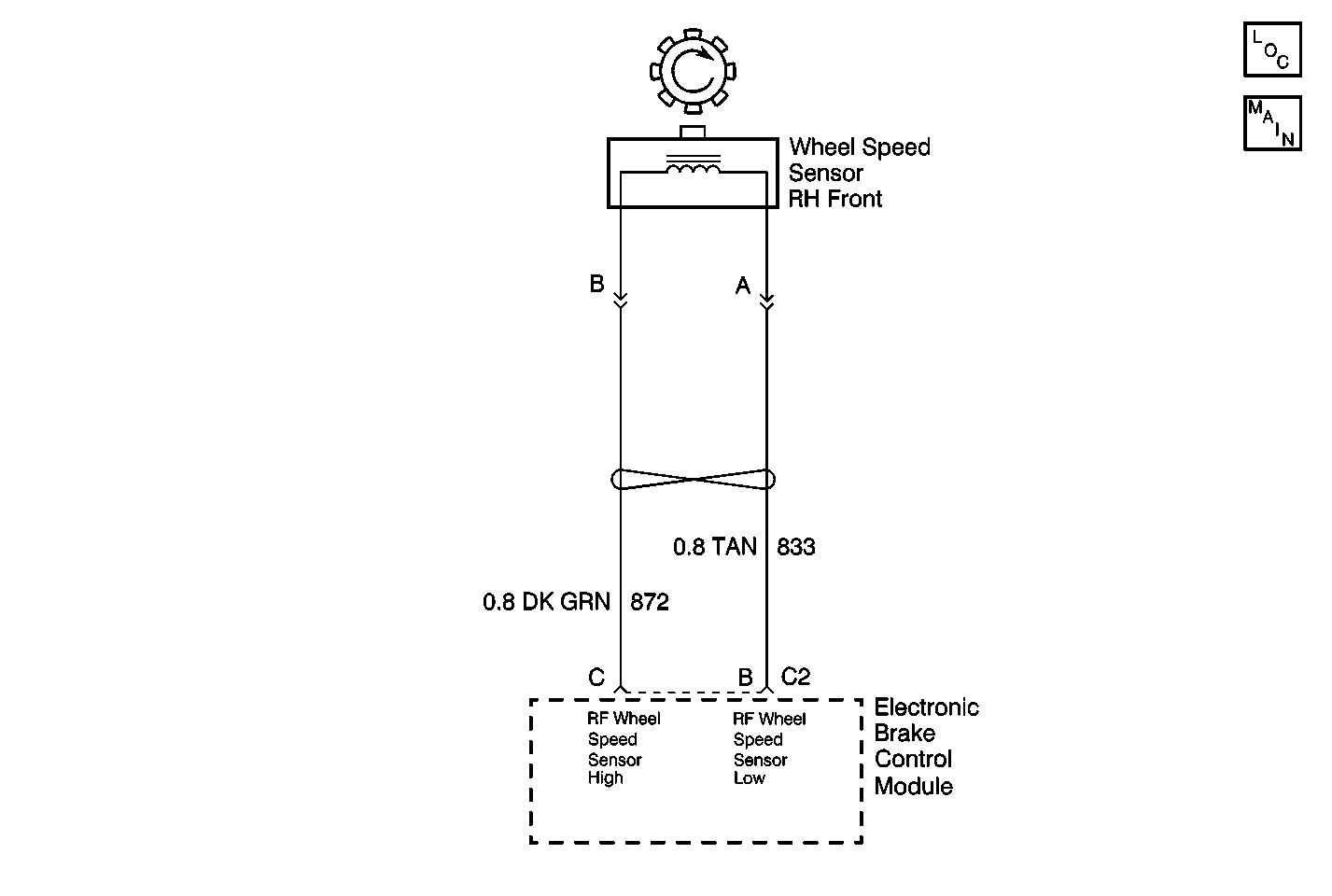
Circuit Description
The wheel speed sensor coil emits an electromagnetic field. A toothed ring on the wheel passes by the wheel speed sensor and disrupts this electromagnetic field. The disruption in the field causes the wheel speed sensor to produce a sinusoidal (AC) voltage signal. The frequency and amplitude of the sinusoidal (AC) voltage signal are proportional to the speed of the wheel. The amplitude of the wheel speed signal is also directly related to the distance between the wheel speed sensor coil and the toothed ring. This distance is referred to as the air gap.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
| • | The average wheel speed for all wheel signals is greater than 40 km/h (25 mph). |
| • | The average right front wheel speed is greater than 40 km/h (25 mph). |
| • | No speed signal input to the EBCM from the right front wheel speed sensor for 15 ms. Anything which suddenly prevents (intermittent) the right front wheel speed signal to drop to zero while the vehicle is moving greater than 40 km/h (25 mph). |
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
| • | The ABS indicator lamp turns on |
| • | The ABS disables |
DTC C0223 is a Condition Latched DTC, which indicates that the above actions remain true only as long as the condition persists.
DTC C0223 is a DRP non-critical malfunction. If another front WSS DTC sets before this DTC is investigated and cleared, this will become a DRP critical malfunction and the BRAKE indicator lamp will also turn on.
For a detailed explanation of malfunction responses, refer to Self-Diagnostics .
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
| • | Repair the conditions responsible for setting the DTC |
| • | Use the Scan Tool Clear DTCs function |
| • | A Condition Latched DTC may exist momentarily, or constantly. In either case, the DTC will be stored in the EBCM memory until it is repaired, and/or the DTC is cleared. After the DTC is repaired and/or cleared and the ignition is turned to ON, the ABS lamp will remain lit until the EBCM completes a power-up self test. This test concludes when the vehicle has reached a speed of greater than 13 km/h (8 mph) and the wheel speed inputs have been checked by the EBCM. |
Diagnostic Aids
Any of the following conditions may cause an intermittent malfunction:
| • | A poor connection |
| • | Wire insulation that is rubbed through |
| • | A wire breaks inside the insulation |
Thoroughly check any circuitry that is suspected of causing the intermittent complaint for the following conditions:
| • | Backed out terminals |
| • | Improper mating |
| • | Broken locks |
| • | Improperly formed or damaged terminals |
| • | Poor terminal to wiring connections |
| • | Physical damage to the wiring harness |
If the customer says that the ABS indicator lamp is on only during humid conditions such as rain, snow, or vehicle wash, then thoroughly inspect all wheel speed sensor circuits for signs of water intrusion. Use the following procedure:
- Spray the suspected area with a 5% salt water solution (two teaspoons of salt to 12 oz. of water)
- Drive the vehicle above 24 km/h (15 mph) for at least 30 seconds
If the DTC returns, replace the suspected harness.
When inspecting a wheel speed sensor, inspect the sensor terminals and the harness connector for corrosion. If evidence of corrosion exists, then replace the wheel speed sensor. Refer to Wheel Speed Sensor Replacement .
Resistance of the wheel speed sensor will increase with an increase in sensor temperature. Refer to the following tables for temperature/resistance values.
°C | °F | Ohms |
|---|---|---|
Temperature vs Resistance Values (Approximate) | ||
-40 to 4 | -40 to 40 | 1575 to 2420 |
5 to 43 | 41 to 110 | 1980 to 2800 |
44 to 93 | 111 to 200 | 2250 to 3280 |
94 to 150 | 201 to 302 | 2750 to 3850 |
°C | °F | Ohms |
|---|---|---|
Temperature vs Resistance Values (Approximate) | ||
-40 to 4 | -40 to 40 | 702 to 1060 |
5 to 43 | 41 to 110 | 855 to 1230 |
44 to 93 | 111 to 200 | 1000 to 1440 |
94 to 150 | 201 to 302 | 1170 to 1661 |
°C | °F | Ohms |
|---|---|---|
Temperature vs Resistance Values (Approximate) | ||
-40 to 4 | -40 to 40 | 1362 to 2675 |
5 to 43 | 41 to 110 | 1655 to 3133 |
44 to 93 | 111 to 200 | 1925 to 3671 |
94 to 150 | 201 to 302 | 2300 to 4309 |
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the steps in the diagnostic table:
-
This step checks the EBCM 4-way connector for looseness, corrosion, etc.
-
This step uses the wheel speed sensor resistance check to help isolate an intermittent connection.
-
This step checks the right front wheel speed sensor for the proper resistance.
-
This step checks for proper mounting and orientation of the right front wheel speed sensor.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Was the Diagnostic System Check performed? | -- | Go to Step 2 | |
Are all connections clean and tight? | -- | Go to Step 3 | Go to Step 6 | |
Using a J 39200 , measure the resistance between terminals C and E of the 4-way EBCM harness connector. Wiggle the WSS harness in various locations between the sensor and the EBCM while performing this measurement. (Refer to the WSS Temperature vs. Resistance tables for applicable sensor resistance values. The values in these tables are for the temperature of the sensor, not the air temperature.) Is the resistance measurement within the specified range without fluctuation when the harness is wiggled? | -- | Go to Step 5 | Go to Step 4 | |
Is the resistance measurement within the specified range? | -- | Go to Step 7 | Go to Step 8 | |
Is the wheel speed sensor in good condition? | -- | Go to Step 9 | Go to Step 10 | |
6 | Make necessary repairs to the 4-way EBCM harness connector. Refer to Connector Repairs . Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |
7 | Repair the open, high resistance or short in CKTs 833 or 872. Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |
8 | Replace the right front wheel speed sensor. Refer to Wheel Speed Sensor Replacement . Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |
9 | Malfunction is intermittent. Inspect all connectors for damage which may result in high resistance when all components are connected. Refer to Diagnostic aids for more information. Repair all damage found. Is the repair complete? | -- | -- | |
10 | Make necessary repairs. Is the repair complete? | -- | -- |
