Refer to
Ignition System
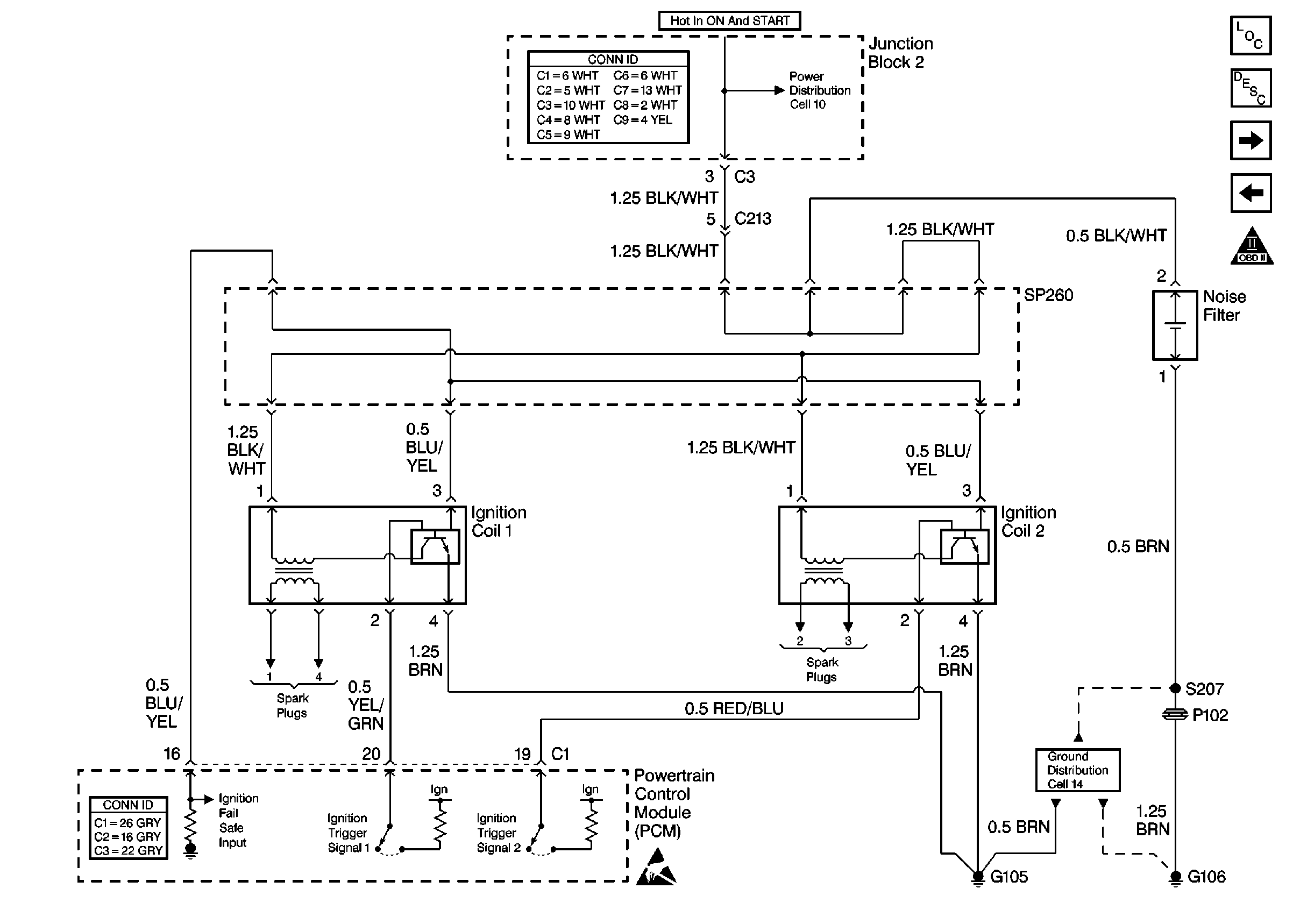
schematics.
Circuit Description
When the ignition switch is turned to the ON or START positions, voltage is applied to the ignition coil and ignition control circuitry. When the ignition coil receives the trigger signal from the powertrain control module (PCM), it turns the primary coil windings of the ignition coil OFF. By toggling these windings ON and OFF, a high voltage is produced in the secondary coil windings. The high voltage induced by the secondary coil windings is forced to find a ground path through the coil's high voltage terminals, both spark plug wires and across the spark plug electrodes. The PCM can detect a malfunction in the process just described and set a DTC P1300 or P1310. Both the ignition system and the fuel delivery system depend upon input from the crankshaft position sensor in order to operate. Many other information sensors are critical to proper operation of the PCM and can cause a no start.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for any of the following conditions:
| • | Insufficient fuel can cause a no start condition. Thoroughly inspect the fuel delivery system for sufficient fuel volume to the fuel injectors. Inspect the fuel supply components for partial blockage or restrictions. |
| • | Fuel injectors with partially blocked and restricted nozzles, or a malfunctioning solenoid, can cause a no start condition. Refer to Fuel Injector Balance Test and Fuel Injector Solenoid Coil Test - Engine Coolant Temperature Between 10-35 Degrees C (50-95 Degrees F) . |
| • | There may be fuel spray at the fuel injectors and the indicated fuel pressure may be correct, yet there may not be enough fuel to start the engine. If the fuel injectors and the injector circuit are OK, and fuel spray is detected, the fuel injector ON time may be inadequate. If the PCM receives incorrect inputs from the various information sensors, the fuel delivered by the fuel injectors may be inadequate to start the engine. Check all the engine data parameters with a scan tool and compare the values indicated with the expected values or the values from a known good vehicle. |
| • | Check engine electrical grounds at G106 and G105 (both located at the rear of the cylinder head) if the engine has no spark and no fuel injector pulse with no DTCs. |
| • | Check the engine electrical ground G106 (four wires) at the rear of the cylinder head, if there is spark but no fuel injector pulse. |
| • | Check the CKP sensor and CMP sensor ground circuit for an open to PCM terminal C1-17 if the engine almost starts and then stalls. |
| • | Water or foreign material in the fuel can cause a no start or engine won't stay running condition. During freezing weather water can freeze inside the fuel system. The engine may start after 30 minutes in a heated shop. The malfunction may not recur until parked overnight in freezing temperatures. Extreme weather conditions can cause contaminated fuel to prevent the vehicle from starting. |
| • | A vehicle that starts and runs after being brought to the shop for an Engine Cranks But Will Not Run complaint, may have an ignition system that is susceptible to moisture. Spray water on the ignition system components and wiring in order to check for an engine starting or won't stay running concern. |
An intermittent malfunction may be caused by fault in any of the critical information or component electrical circuits. Inspect the wiring harness and components for any of the following conditions:
| • | Backed out terminals. |
| • | Improper mating of terminals. |
| • | Broken electrical connectors locks. |
| • | Improperly formed or damaged terminals |
| • | Faulty terminal to wire connections. |
| • | Physical damage to the wiring harness. |
| • | A broken wire inside the insulation. |
| • | Corrosion of electrical connections, splices, or terminals. |
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers in the Diagnostic Table.
-
The OBD System Check prompts the technician to complete some basic checks and store the freeze frame data on the scan tool if applicable. This creates an electronic copy of the data taken when the fault occurred. The information is then stored in the scan tool for later reference.
-
If a fuse is found to be the cause of the no start, locate and repair any shorts that may have caused the fuse to blow before replacing the fuse.
-
The fuel mixture may be too rich or too lean to start the engine if the ECT sensor signal is incorrect.
-
The fuel mixture may be too rich or too lean to start the engine if the TP sensor signal is incorrect.
-
The fuel mixture may be too rich or too lean to start the engine if the MAP sensor signal is incorrect.
-
This step checks to see if the engine will start and run. The repair that may have led to this step may only have been a secondary cause of the no start condition, such as fouled spark plugs, that may have been caused by incorrect fuel pressure. The diagnostics in this table may need to be performed a second time in order to discover the root cause of the no start condition.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Did you perform the Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | |||||||||||||||||||||
Was a repair necessary? | -- | |||||||||||||||||||||
3 | Check for any DTCs with a scan tool. Is a DTC P0335 or P0340 set? | -- | Go to DTC P0335 Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor Circuit or DTC P0340 Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor Circuit | |||||||||||||||||||
4 | Is a DTC P1300 or P1310 set? | -- | Go to DTC P1300 Ignition Coil 1 Primary Feedback Circuit or DTC P1310 Ignition Coil 3 Primary Feedback Circuit | |||||||||||||||||||
Is the coolant temperature displayed on the scan tool near the actual coolant temperature? | -- | Go to DTC P0115 Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor Circuit | ||||||||||||||||||||
Observe the TP sensor parameter on a scan tool with the throttle closed. Is the throttle position opening displayed on the scan tool within the specified value? | 0-23% | |||||||||||||||||||||
Was the kPa reading of both vehicles within 2kPa of each other? | -- | Go to DTC P0106 Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) System Performance | ||||||||||||||||||||
8 |
Did the fuel injector test lamp flash for each injector while cranking the engine? | -- | ||||||||||||||||||||
9 |
Is spark present at each ignition wire? | -- | ||||||||||||||||||||
10 |
Did any of the ignition wires fail any of the above inspections? | 25k ohms | ||||||||||||||||||||
11 |
Did any of the spark plugs need replacement? | -- | ||||||||||||||||||||
12 |
Was any pressure indicated on the fuel pressure gauge while cranking the engine? | -- | ||||||||||||||||||||
13 |
Is the fuel pressure indicated within the specified value? | 301-347 kPa (44-50 psi) | Go to Fuel System Diagnosis | |||||||||||||||||||
14 |
Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||||||||||||||||||||
15 |
Was a repair necessary? | -- | ||||||||||||||||||||
16 |
Was a basic engine mechanical problem found and repaired? | -- | Go to Diagnostic Aids | |||||||||||||||||||
17 | Replace the ignition coil of the cylinders that had no spark. Refer to Ignition Coil Replacement . Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||||||||||
18 | Replace any ignition wires that were found to be faulty. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||||||||||
Does the engine start and continue to run? | -- | |||||||||||||||||||||
20 |
Are any DTCs displayed? | -- | Go to the Applicable DTC Table | System OK |
