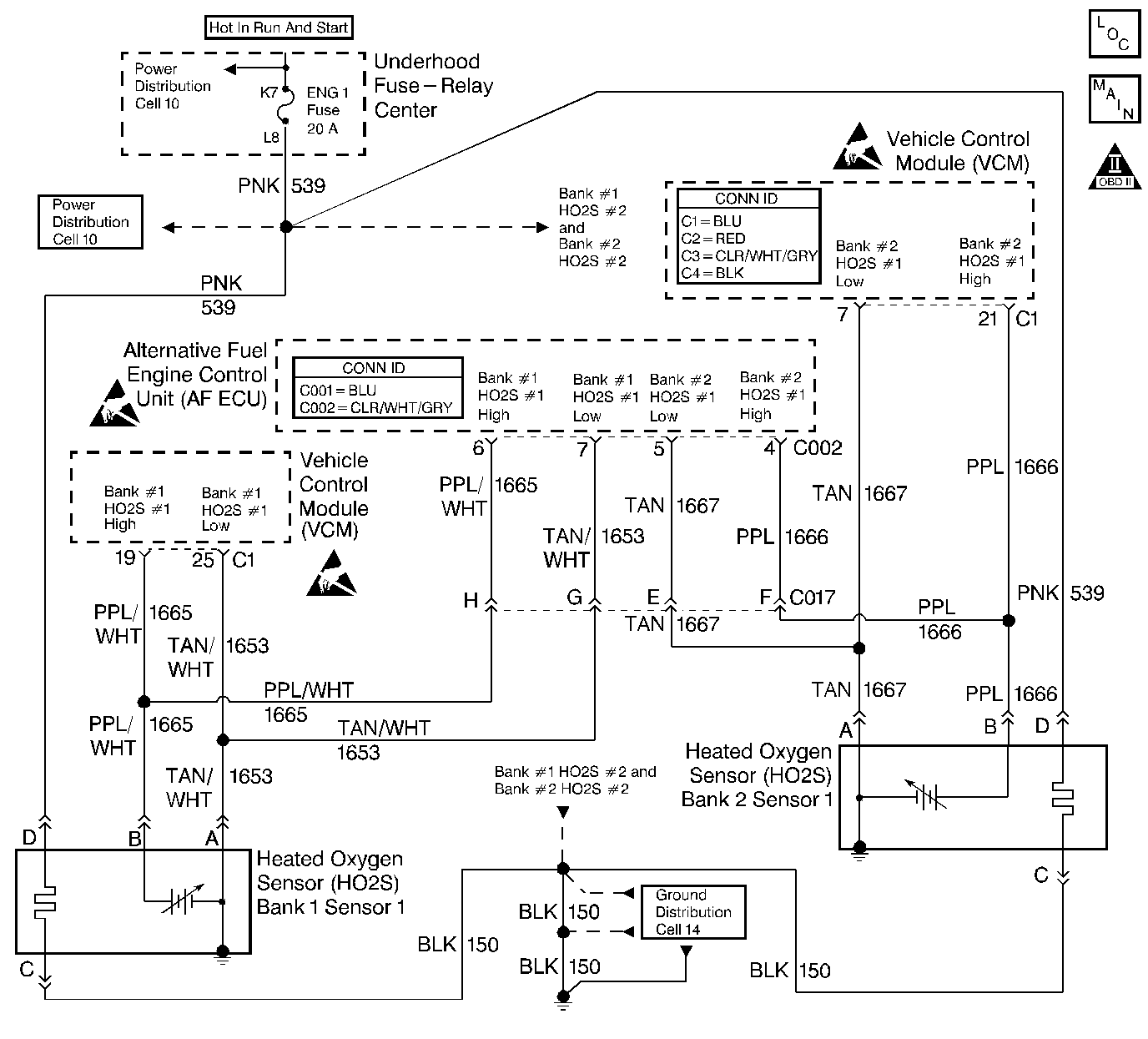
Circuit Description
The Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S) is used in order to determine the oxygen content of the engine's exhaust. The oxygen content of the exhaust indicates when the engine is operating lean or rich. When the engine is operating lean the exhaust will have more oxygen content. Once at operating temperature, the HO2S will produce a voltage in relation to the oxygen content of the exhaust. The HO2S requires an operating temperature of 360°C (600°F) to produce voltage. The HO2S will produce more voltage when the exhaust is rich and less voltage when the exhaust is lean. The HO2S operating voltage range is around 0.10 volts (100 mV) to 1 volt (1000 mV).
The gasoline control module (VCM / PCM or ECM) supplies a bias (or reference) voltage to the HO2S. This bias voltage is around 450 millivolts. The AF ECU monitors the bias voltage as well as the voltage produced by the HO2S.
During normal Closed Loop fuel control operation the AF ECU will add fuel (enriches the mixture) when the HO2S indicates a lean exhaust content. When the HO2S indicates a rich exhaust content the AF ECU will subtract fuel (leans-out the mixture). This oscillation above and below the bias voltage (sometimes referred to as activity or switching) can be monitored with the HO2S signal voltage.
The oxygen sensor contains a heater. The heater is necessary in order to quickly warm the sensor to operating temperature. The heater will also maintain operating sensor temperature during extended idle conditions.
This DTC is used to indicate an HO2S with in-active signal voltage.
Conditions for Running the DTC
| • | The engine is operating on alternative fuel. |
| • | Engine speed is greater than 400 RPM. |
| • | The engine has been operating for at least 1 minute. |
| • | The AF ECU determines the HO2S has been at operating temperature for at least 30 seconds. The engine coolant temperature must be greater than 40°C (104°F) AND desired gas flow must be above 0.3 grams per second for 30 seconds in order for the AF ECU to determine the HO2S is at operating temperature. |
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The AF ECU monitors an O2S signal voltage stuck between 0.300 V and 0.600 V (in-active) for 8 seconds continuously.
OR
The AF ECU monitors an O2S signal voltage between 0.00 V and 1.0 V that has not performed a Rich/Lean switch for 15 seconds continuously.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The AF ECU will control fuel trim based upon the Bank 1 Sensor 1 signal. If a Bank 1 Sensor 1 DTC sets the AF ECU will operate in Open Loop fuel control.
| • | A first failure of this DTC will NOT illuminate the MIL and will store as Last Test Failed but not as History. |
| • | The AF ECU will illuminate the MIL and store the DTC as History after TWO consecutive drive trips that the diagnostic runs and fails. |
| • | The AF ECU will record operating conditions at the time the DTC sets. This information will be stored as Freeze Frame data. |
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
| • | The Last Test Failed status will clear when the DTC runs and passes. |
| • | The AF ECU will turn OFF the MIL after 3 consecutive drive trips that the DTC runs and passes. |
| • | The History status will clear after 40 consecutive WARM-UP cycles with NO failures of ANY DTC. |
| • | All DTC Information can be cleared using a scan tool. |
| • | Interruption of Control Module (AF ECU / VCM / PCM or ECM) power or ground MAY clear DTC Information. Clearing DTC Information with this method is inconsistent and should not be performed. |
Diagnostic Aids
Fault Not Present
Fault Not Present indicates the condition that caused the DTC to set is intermittent and not currently present. Refer to Intermittent Conditions Symptom diagnosis for additional information. If any additional DTCs were stored proceed to the applicable DTC table in the order stated in the OBD System Check.
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the diagnostic table.
-
This step determines if proper sensor activity is present. When in Closed Loop fuel control the HO2S voltage should rapidly swing above and below the bias voltage.
-
This step determines if the gasoline control module and the High and Low circuits between the control module and the HO2S connector are operating properly.
-
This step determines if the HO2S heater circuit operate correctly up to the HO2S connector.
-
This step determines if the proper circuit resistance exists between the HO2S Low circuit and control module ground.
-
This step determines if the proper circuit resistance exists between the HO2S Low circuit and control module ground with a COLD sensor. A loose HO2S or poor thread to exhaust electrical contact will cause higher resistance when the HO2S is cold. Although 500 ohms is allowed, typical resistance should be less than 50 ohms.
Step | Action | Value(s) | Yes | No | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | Did you perform the AF Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check? | -- | Go to Alternative Fuels (AF) Powertrain On Board (OBD) System Check | |||||||||||||||||||
Is the HO2S voltage fixed within the voltage range specified? | 0.10-1.0 V | |||||||||||||||||||||
3 | The condition that set this DTC is not present. This DTC may have been set by one of the following conditions:
Repair any of the above conditions as necessary. Was a condition found and repaired? | -- | ||||||||||||||||||||
4 | The fault is not present. Refer to Diagnostic Aids. Are any DTC's stored that have not been diagnosed? | -- | Go to the Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) List | Go to Intermittent Conditions | ||||||||||||||||||
5 |
Is the HO2S voltage fixed within the voltage range specified? | 0.10 to 1.0 V | ||||||||||||||||||||
Is the HO2S voltage less than the value specified? | 20 mV | |||||||||||||||||||||
7 |
Is the individual resistance of both circuits less than the value specified? | 5 ohms | ||||||||||||||||||||
8 |
Was a terminal repair made? | -- | ||||||||||||||||||||
Turn the ignition ON while leaving the engine OFF. Is the test lamp illuminated? | -- | |||||||||||||||||||||
Is the resistance measured less than the value specified? | 500 ohms | |||||||||||||||||||||
11 | Repair the circuit that measured high resistance. Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||||||||||
12 | Repair the HO2S Heater ignition or ground circuit. Probable causes include the following:
Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||||||||||
13 | Repair the high resistance between the HO2S Low circuit and the control module ground circuit. Probable causes include the following:
Is the action complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||||||||||
14 |
The leak may be very small and will typically be within 12 inches of the suspect HO2S. Was an exhaust system repair made? | -- | ||||||||||||||||||||
Is the resistance less than the value specified? | 500 ohms | |||||||||||||||||||||
16 |
Is the resistance less than the value specified? | 500 ohms | ||||||||||||||||||||
17 |
Ensure the oxygen sensor, gasoline control module and the AF ECU connectors are disconnected before testing circuits. Was a wire repair made? | -- | ||||||||||||||||||||
18 | Replace the AF ECU. Refer to Engine Control Unit Replacement . Is the replacement complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||||||||||
19 | Perform the AF Fuel System diagnosis and return to this step. Refer to Fuel System Diagnosis . Was a CNG fuel system problem found and repaired? | -- | ||||||||||||||||||||
20 | Replace the HO2S sensor. Refer to Heated Oxygen Sensor Replacement in the Engine Controls section of the gasoline service manual. Is the replacement complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||||||||||
21 |
Important: The following control module replacement procedures must all be completed before attempting to operate the vehicle.
Important: In order to perform the variation learn procedure a switch-over to gasoline operation is necessary. Remove the CNG 20 amp fuse in order to perform the switch-over. All of the above procedures are located in the gasoline service manual. Is the replacement complete? | -- | -- | |||||||||||||||||||
22 |
Does the scan tool indicate the DTC passed? | -- | System OK |
